STS - HISTORICAL ANTECEDENTS
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
SCIENCE
systematic body of knowledge
basis for technology
TECHNOLOGY
application of scientific knowledge
ANCIENT TIMES
concerned with:
a. transportation and navigation
b. communication and record-keeping
c. mass production
d. security and protection
e. health
f. aesthetics and architecture
Sumerian
Babylon
Egyptian
Greek
Roman
Chinese
SUMERIAN CIVILIZATION
4500 - 4000 BC
first Mesopotamian civilization
Fertile Crescent Land (situated between Tigris and Euphrates River
known for their high degree of cooperation with one another and their desire for great things
Not contented with basic things - pushed them to develop many things connected to S&T.
first to divide the passages of time
cuneiform script
Uruk City
Great Ziggurat of Ur
hydraulic engineering
sailboat
wheel
plow
roads
fabrication of copper
time
sexagesimal
lunar calendar
CUNEIFORM SCRIPT
oldest writing form in the world (3400 BC)
used word pictures and triangular symbols
used clay tablets
used to record things with great historical value or their everyday life
URUK CITY
first true city in the world
walled with sunbaked bricks (clay from river mixed with reed, then dried after)
GREAT ZIGGURAT OF UR
mountain of God
sacred place of their chief god
only priests are allowed to enter
non-priests that will enter will not be able to come back
IRRIGATION AND DIKE
hydraulic engineering
irrigation and agriculture were developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers
for flood control
uses floods in dry lands
SAILBOAT
5000 years ago
for trading of productions and migrations
make it easy to move in the waters
lightweights sailboats made from wood and papyrus
square-shaped and made up of cloth.
WHEEL
bronze age
first made up of woods
for easier movement of heavy objects
used for chariots for battle
for agriculture (animal transactions and irrigation), craft industries
originally for milling
PLOWS
turn and break up soil, bury crop residues, and control weeds
ROADS
better transportation
for trading
FABRICATION OF COPPER
Sumerians were the first users of copper
COPPER: earliest non-precious metals
helped in significant growth of various Mesopotamia cities like URUK, SUMER, UR and al’UBAID
used in arrowheads, razors, and harpoons
TIME
3000 BC
passages of time were first divided by Sumerians
introduced the passage of weeks, months, and years
BEFORE: knowledge of Sumerians about astronomy was used to figure out approximate time
sexagesimal system
SEXAGESIMAL SYSTEM
divided a day into 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness
further divided into 60 minute-hours and 60 second-minute
SEXAGESIMAL
numeral system
record of numerous subjects instead of naming all
LUNAR CALENDAR
based entirely on the recurrence of lunar phases
counting of 12 months
two seasons observed: summer & winter
To make up the difference between this year, and the year of seasons, they added an extra month to every year after four years
BABYLONIAN CIVILIZATION
1844 - 1595 BC
great builders, engineers, and architects
hanging gardens of Babylon
trigonometry
astronomy
jewelry making
HANGING GARDENS OF BABYLON
gift of King Nebuchadnezzar II to Amytis
layers of garden of different kinds of plants, ferns, and flowering plants
no physical existence
ASTRONOMY
zodiac
eclipses of the sun and moon could be foretold
stars had been numbered and named at an early date
Possessed tables of lunar longitudes and observations of the phases of Venus
JEWELRY MAKING
originated from the Babylonians
Led way for our modern designs as they were the first to incorporate precious gems and metals to make beautiful pieces of jewelry.
EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
3100 - 332 BCE
their legacy is the engineering feats of the Egyptians, especially the infrastructure established by their Pharaohs
The Civilization of Ancient Egypt began in the Nile River, Valley of Northeastern Africa
death mask
papyrus
Pyramid of Giza
hieroglyphics
calendar system
cosmetics
wigs
ink
clepsydra
PAPER OR PAPYRUS
paper
4th millenium BCE
plant that grows abundantly along the Nile river
stem of the papyrus plant was used to make sails, cloth, mats, cords, and paper
chief writing material in Ancient Egypt
INK
invented by combining soot with different chemicals to produce inks of different colors.
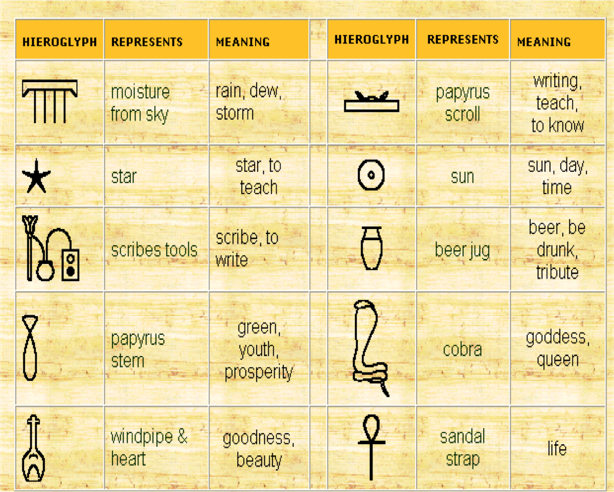
HIEROGLYPHICS
complex system of writing using symbols (logographic and alphabetic elements)
language that tells the world of the history and culture of Egyptians
record historical events, religious texts, and admin record
written in papyrus and walls of pyramids and other Egyptian structures
COSMETICS
used for aesthetics and health purposes
beauty is a sign of holiness
they wore kohl around their eyes
KOHL
created by mixing soot and malachite with mineral galena
believed to cure and prevent eye diseases
WIG
for health wellness rather than aesthetic
used to protect shaved heads of healthy Egyptians from the harmful rays of the sun
CLEPSYDRA
water clock
timekeeping device during ancient times
utilizes gravity that affects the flow of water from one vessel to another
they also made sundial (shadow clock)
PYRAMID OF GIZA
royal tombs for pharaohs
DEATH MASK
believed to lead the dead’s spirit to the body
CALENDAR SYSTEM
devises the earliest known calendar
included 12 months of 30 days each, with five additional days at the end of the year
serves as the basis for the later calendar system
GREEK CIVILIZATION
birthplace of Western Philosophy
major achievements in the field of mathematics and philosophy
built coliseums and pioneered the olympics
parthenon
alarm clocks and odometer
the alarm clock of plato
watermill
rhetoric
democracy
theater
ALARM CLOCKS
still in use
created by Ctesibius (Hellenistic engineer and inventor)
CTESIBIUS’ WATER CLOCK
world’s first alarm clock
ALARM CLOCK OF PLATO
invented in 427 to 348 BC
first human awakening device in history
you need water in it to make it work
may whistle
ODOMETER
measures the distance traveled by a vehicle
Helped Greeks to create roads and bridges for travelling, set milestones at specific distances, and helped developed their empire, boosting their economic standing
WATER MILL
used to grind flour
RHETORIC
art that aims to improve the capability of writers or speakers to inform, persuade, or motivate particular audiences
DEMOCRACY
first form of self-rule
ROMAN CIVILIZATION
the strongest political and social entity in the west
cradle of politics and governance
founded when Augustus Caesar proclaimed himself the first emperor in Rome (31BC)
Came to an end with the fall of Constantinople (1453 CE)
newspaper
bound books / codex
roman architecture
aqueduct
roman numerals
roman alphabet
concretes
roads
medical advancements
public baths
military innovations
caesar cipher
roman library
NEWSPAPER
gazettes
contained announcements of the Roman Empire to the people and is engraved in metal or stone tablets and then publicly displayed before the invention of paper
ACTA SENATUS: minutes of official business
acta diurna
ACTA: things that have been done
ACTA DIURNA
gazette of political and social events
only available to the senators
CODEX
bound books
JULIUS CAESAR: started the tradition of stacking up papyrus to form pages of a book
earlier covers were made of WAX, then later on replaced by animal skin
first books
ROMAN ARCHITECTURE
continuation of the greek architecture
large churches (cathedrals and basilicas), aqueducts, coliseums, amphitheaters, and residential houses
The Maison Carrée
Roman Forum (Forum Romanum)
The Pantheon
AQUEDUCT
used to supply water to the town of Nimes (about 30 miles away from the Mediterranean Sea)
ended up on homes and baths in Nimes
was about 31 miles in length
ROMAN NUMERALS
symbols used in a system of numerical notation based on the ancient Roman system
ROMAN ALPHABET
writing system originally used to write the Latin language
CHINESE CIVILIZATION
oldest civilization in Asia (if not in the world)
ancient writing systems
cultural continuity and heritage
territorial boundaries
philosophical duration
dynastic successions
silk
silk road
great wall of china
gun powder
tea production
SILK
resulted for a creation of a product for trade
the trade opened China to the outside world
paved way for cultural, economic, and scientific exchanges
bridged the gap between the western world and the middle kingdom
silkworm farming: restricted to women
silk-making: many women were employed
from silkworms
SILK ROAD
boosted trade
paved way to Hindi religion, spices, art and science innovations
TEA PRODUCTION
first tea was believed to be drunk by a Chinese empreror
China became known for tea exports aside from silk
GUN POWDER
made originally to prolong life
GREAT WALL OF CHINA
only man-made object visible from space
MEDIEVAL PERIOD
middle ages
5th - 15th century
early middle ages, high middle ages, late middle ages
age of expxloration
heavy plow
horse collar
medieval surgical instrument
herbal medicine
compound microscope
lancets and trepanation tools
windmills
shipbuilding
road construction
magnetic compass
telescope
crossbow
chainmail and plate armor
EARLY MIDDLE AGES
5th - 10th century
fall of western roman empire in the 5th century
catholic church hindered scientific advancement due to the fear that it would be a threat to its authority
FEUDALISM: system in which rulers granted land to lower nobility in return for military service (became the prominent political system in central Europe
HIGH MIDDLE AGES
11th - 13th century
revival of learning and culture
Renaissance of the 12th century
emergence of universities and scholars
decline of feudalism
LATE MIDDLE AGES
14th - 15th century
black death: bubonic plague
hundred years war
saw development of early forms of renaissance art and humanism
HEAVY PLOW
Allowed for more efficient tilling of heavy, clay-rich soils, improving agricultural productivity
HORSE COLLAR
Made it possible for horses to pull heavy loads, increasing in agricultural efficiency
MEDIEVAL SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS
ex. lancets and trepanation tools
developed for medical procedures
HERBAL REMEDIES
botanical knowledge
treating ailments
COMPOUND MICROSCOPE
1950
Zacharias Janssen
features two convex lenses in a tube for higher magnification and improved microscopy
WINDMILLS
grinding grain
pumping water
reduces labor required
MAGNETIC COMPASS
used for transportation, especially on navigation
CROSSBOW
advancement in ranged weaponry
offered greater accuracy and power
CHAINMAIL AND PLATE ARMOR
provided improved protection for soldiers who went to countless wars
MODERN AGES
16th century - 19th century (?)
19th century: world population hit 1 billion
people needed more means of goods and services, transportation to trade, machines to upgrade, faster and easier communication, medicine and vaccine, food safety and preservation
resulted in the making of the industry
steam locomotive
telegraph
sewing machine
rubber vulcanization
internal combustion engine
light bulb
typewriter
process for making steel
cash register
elevator
electric motor
petroleum refinery
calculator
telephone
pasteurization
stethoscope
development of modern vaccine
STEAM LOCOMOTIVE
1814
George Stephenson
revolutionized transportation
played a key in the development of the modern railways system
Type of railway vehicle that moves itself using the expansion of steam
TELEGRAPH
1837
Samuel Morse
transmit messages electronically over long distances
SEWING MACHINE
1846
Elias Howe
made it possible to quickly and accurately sew clothing and other textile
contributed to the clothing industry
RUBBER VULCANIZATION PROCESS
1839
Charles Goodyear
made it possible to produce durable and long-lasting rubber products
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE
1876
Nicholaus Otto and Eugene Longen
powered the first automobiles
still used in many transportations today
LIGHT BULB
1879
Thomas Edison
provided reliable source of electric light
revolutionized the way we live and work
TYPEWRITER
1867
Christopher Latham Sholes
made it possible to quickly and accurately type documents
revolutionized the way we communicate and do business
PROCESS OF MAKING STEEL
1856
Henry Bessemer
made it possible to produce large quantities of high-quality steel
developed the modern steel industry
ELEVATOR
1853
Elisha Otis
made it possible to transport people and goods between levels of a building
CASH REGISTER
1879
James Ritty and Charles Kettering
recorded and stored information about sales transactions
made it easier for business to keep track of their finances
ELECTRIC MOTOR
1821
Michael Faraday
used electricity to generate mechanical motion
led the development of many modern appliances and machines
TELEPHONE
1876
Alexander Graham Bell
PETROLEUM REFINERY
kerosene
for transpo and household
PASTEURIZATION
Louis Pasteur (also focused on vaccination development of animals to avoid diseases)
created to combat wine’s diseases and later on applied to other spoilable substances like milk
STETHOSCOPE
1816
Dr. Rene Laennec
medical instrument used in listening to sound produced within the body (heart and lungs)
DEVELOPMENT OF MODERN VACCINES
later 18th century
Edward Jenner
Started with his discovery of smallpox immunization
This pivotal step led to substantial progress in prevention of infectious diseases
PHILIPPINE INVENTIONS
pre-colonial period
spanish-colonial period
american-colonial period
post-colonial period
PRE-COLONIAL PERIOD
marked by indigenous knowledge and invention
suited with their needs
balangay
baybayin script
agricultural techniques
pottery and earthenware
metalworking
BALANGAY
wooden boat for transporting
BAYBAYIN SCRIPT
ancient script used by various ethnic groups
for writing in inscription to various artifacts
AGRICULTURAL TECHNIQUES
ex. Banaue Rice Terraces
POTTERY AND EARTHENWARE
for cooking, storage, and other domestic purposes
METALWORKING
casting of gold, copper, and other metals into ornament, jewelry, and tools
SPANISH-COLONIAL PERIOD
inventions were introduced and adapted in local context
printing press
irrigation system
agricultural techniques (introduced crops)
cultural and linguistic studies
medical practices
architectural innovation
PRINTING PRESS
Friar Juan de Placensia
IRRIGATION SYSTEM
spanish authorities improves and expanded it for agriculture
CULTURAL AND LINGUISTIC STUDIES
preserving indigenous cultural knowledge
MEDICAL PRACTICES
introduced hospitalization
european and philippine remedy
ARCHITECTURAL INNOVATION
techniques were earthquake resistant
use of coral stone
AMERICAN-COLONIAL PERIOD
electricity and street lightning (late 19th century)
telegraph and telephone system (early 20th century; enhance communication)
railroads (1902-1906; Manila-Dagupan Railroad)
higher education institution (UP)
cinematography (Manila [1897] - first documented film)
POST-COLONIAL PERIOD
biosafety net
molave super
Philippine genome center
coconut oil as bio-diesel fuel
magbanua rice
BIOSAFETY NET
1950S
Gregorio Zara
automatically shuts power when detect abnormalities