Chapter 5 - DNA and Chromosomes
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cell biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Chromosome vs Chromatin
Chromatin is loosely packed DNA found in the nucleus during normal cell activity, allowing gene expression. Chromosomes are tightly coiled DNA structures that form during cell division to ensure accurate DNA distribution.
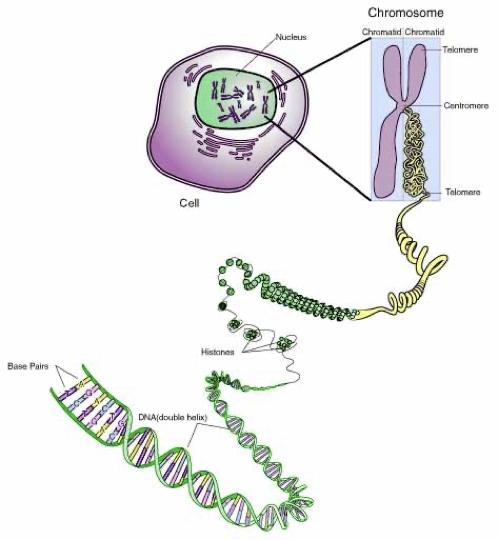

Chromosome
A structurally organized single piece of coiled DNA containing many different genes. Each gene will code for ONE single PROTEIN.
What is the structure of DNA and who helped discover it?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is a nucleic acid made of subunits called nucleotides. Using research by Rosalind Franklin and Linus Pauling, James Watson and Francis Crick built the first model of DNA in 1953.
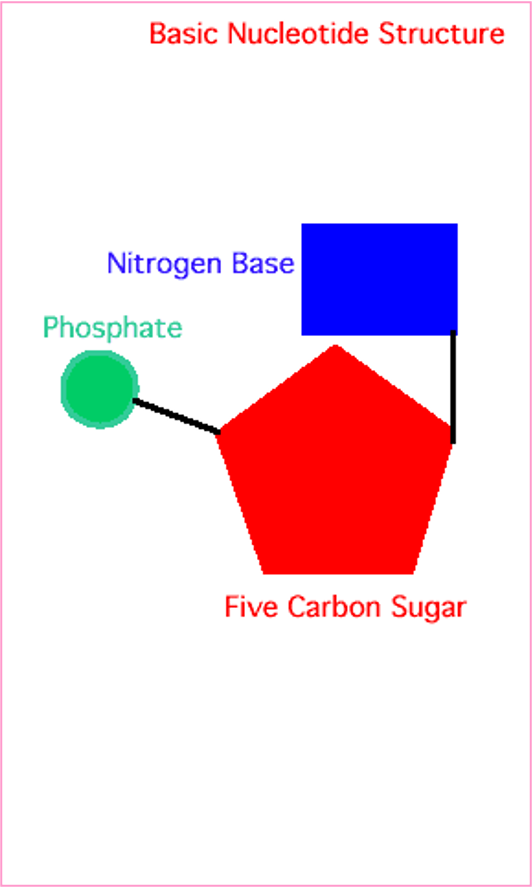
Basic Nucleotide Structure
A 5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose in DNA)
A phosphate group
A nitrogenous base (Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, or Guanine)
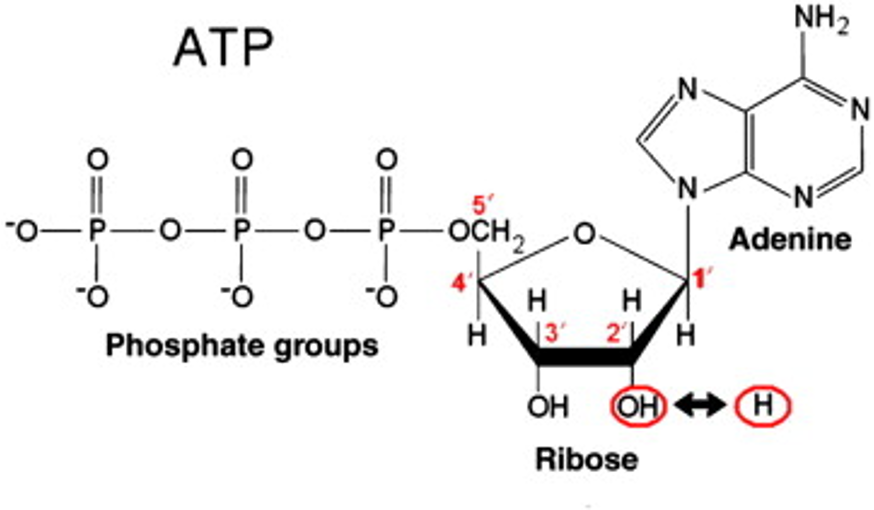
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA has a double alpha-helix shape with antiparallel chains. It has a phosphate backbone on the outside and nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C) facing inward.
How do DNA bases pair and what do they encode?
Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine via hydrogen bonds. The sequence of these bases encodes genetic information that forms genes.
What are the three components of a DNA nucleotide?
Deoxyribose (a 5-carbon sugar)
Phosphate group
Nitrogen base (A, T, C, or G)
How are the nitrogen bases in DNA classified?
Purines: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines: Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C)
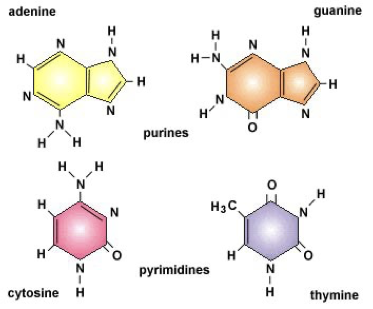
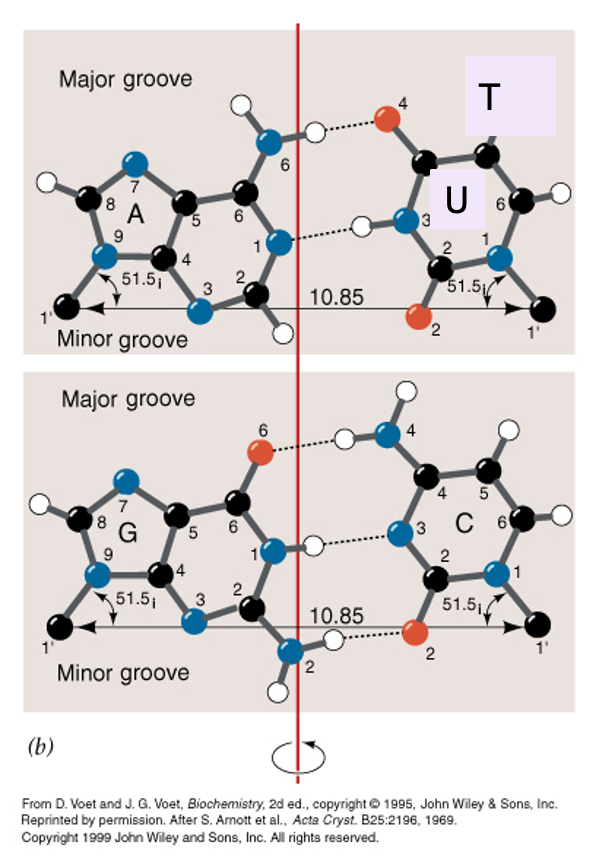
How do nitrogen bases pair and what is the role of hydrogen bonds?
Bases form specific base pairs through hydrogen bonds:
A-T in DNA
A-U in RNA
G-C in both
These bonds help form stable, folded structures and enable accurate transmission of genetic information
What is the "ladder" in DNA and what shape does it form?
It is two long chains of nucleotides joined together like a ladder, twisted into a double helix or spiral.
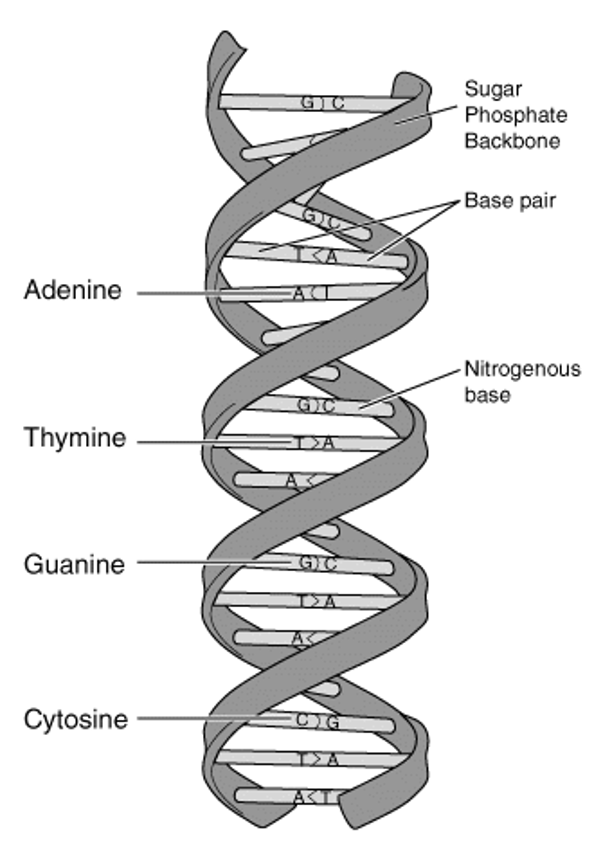
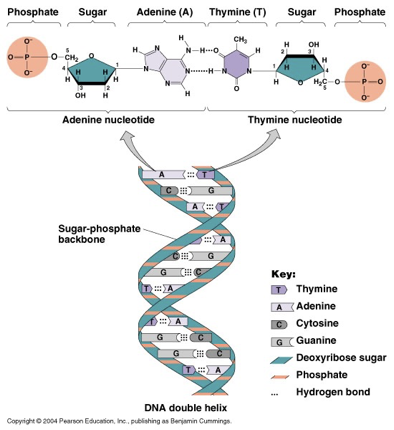
What makes up the sides and rungs of the DNA ladder?
Sides = alternating deoxyribose (sugar) and phosphate; Rungs = pairs of nitrogen bases (A-T or C-G).
What happens to DNA during cell division?
DNA is copied through replication so each new cell gets an exact copy of genetic information.
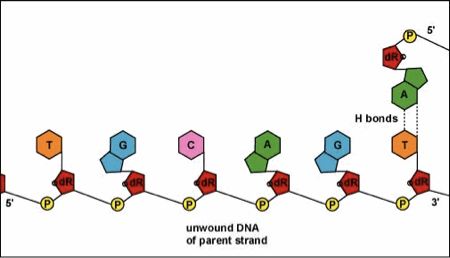
How does DNA replication occur?
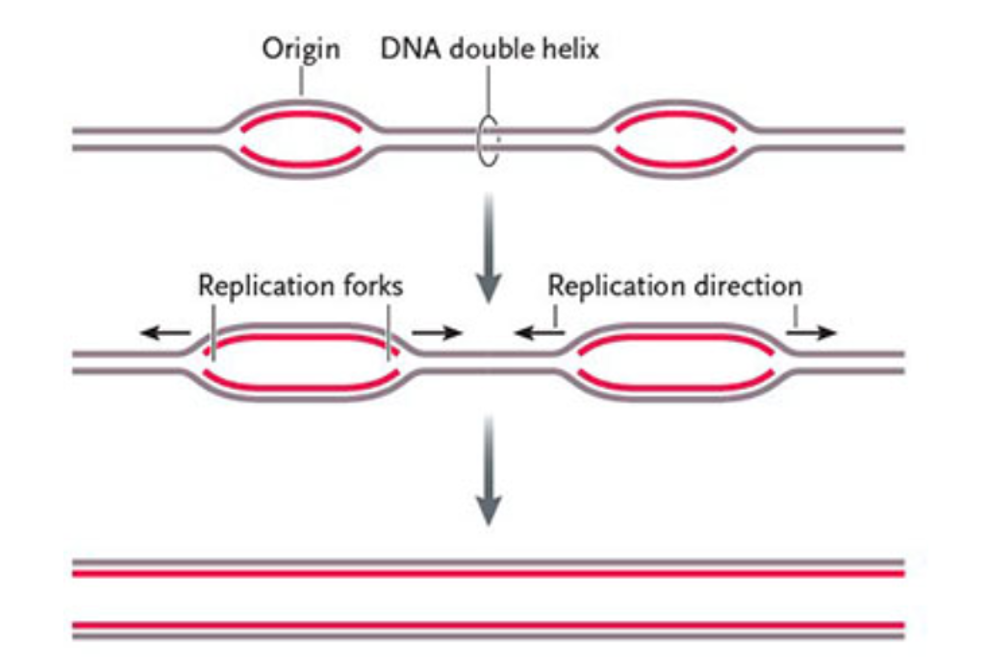
The two strands unzip using DNA helicase; each strand serves as a template to build a new complementary strand by base pairing with free nucleotides, resulting in two DNA molecules each with one original and one new strand.
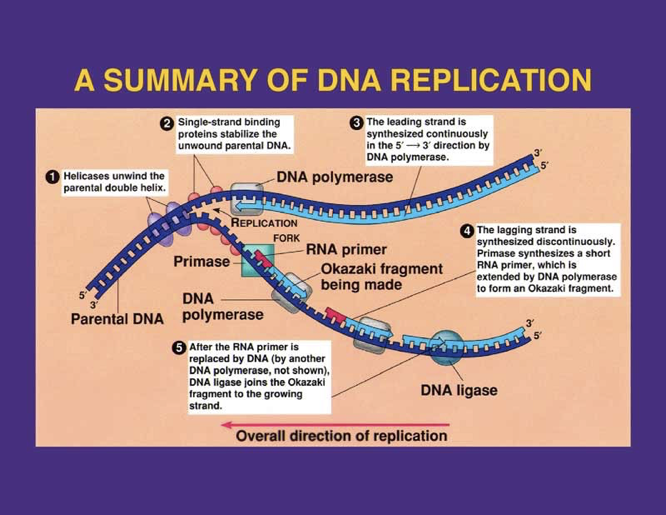
summary of dna replication
What are the key features of DNA replication regarding strand synthesis?
DNA polymerase starts at origin; replication occurs 5’ to 3’. Leading strand is synthesized continuously forward; lagging strand is synthesized backward in Okazaki fragments, which are joined later. Primase makes RNA primers that are later removed.
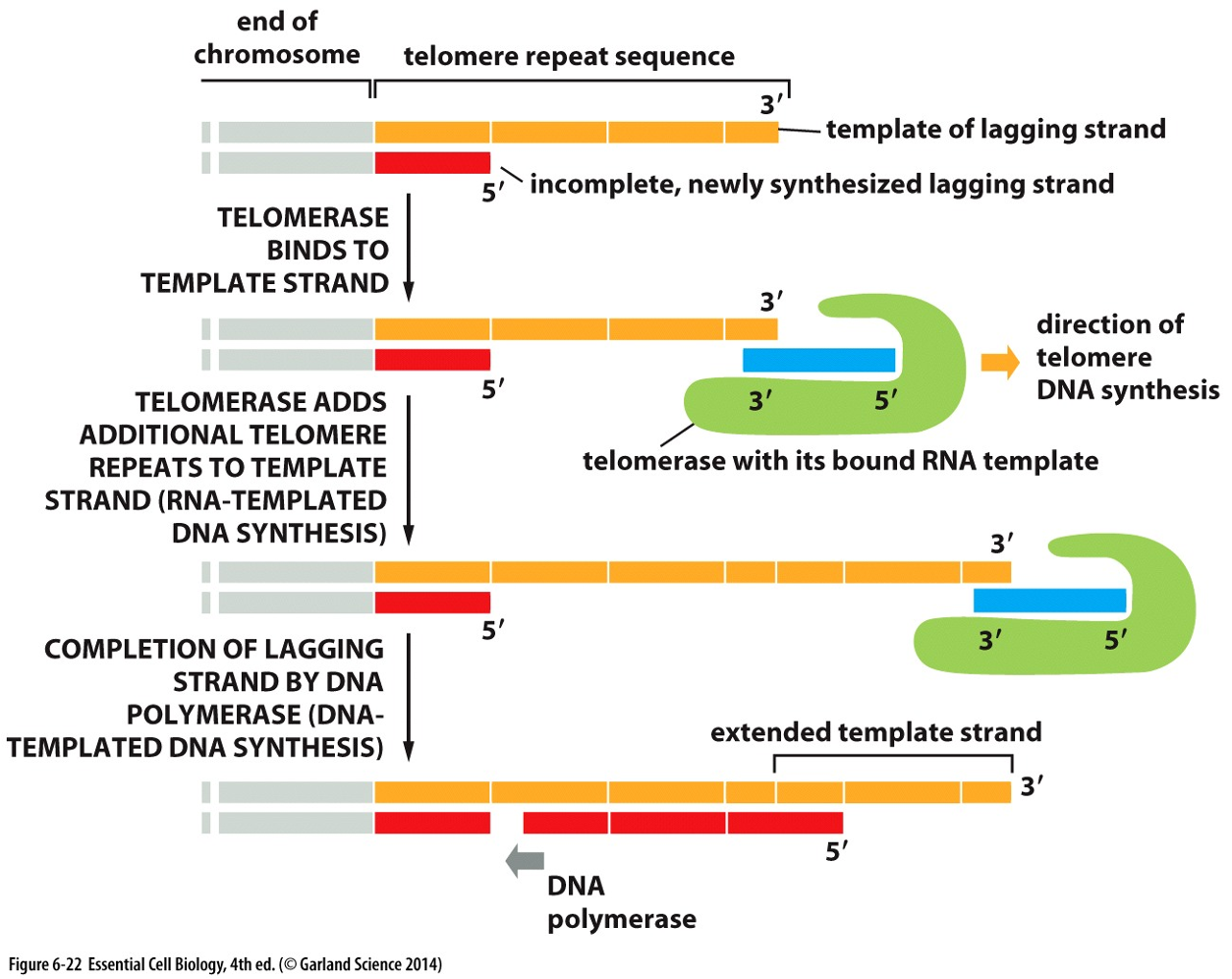
How does the cell prevent shortening of DNA ends during replication?
Telomerase adds repeated sequences to the 3’ end after replication, creating a place for primers to bind, lengthening the lagging strand so genetic info isn’t lost despite RNA primer removal.
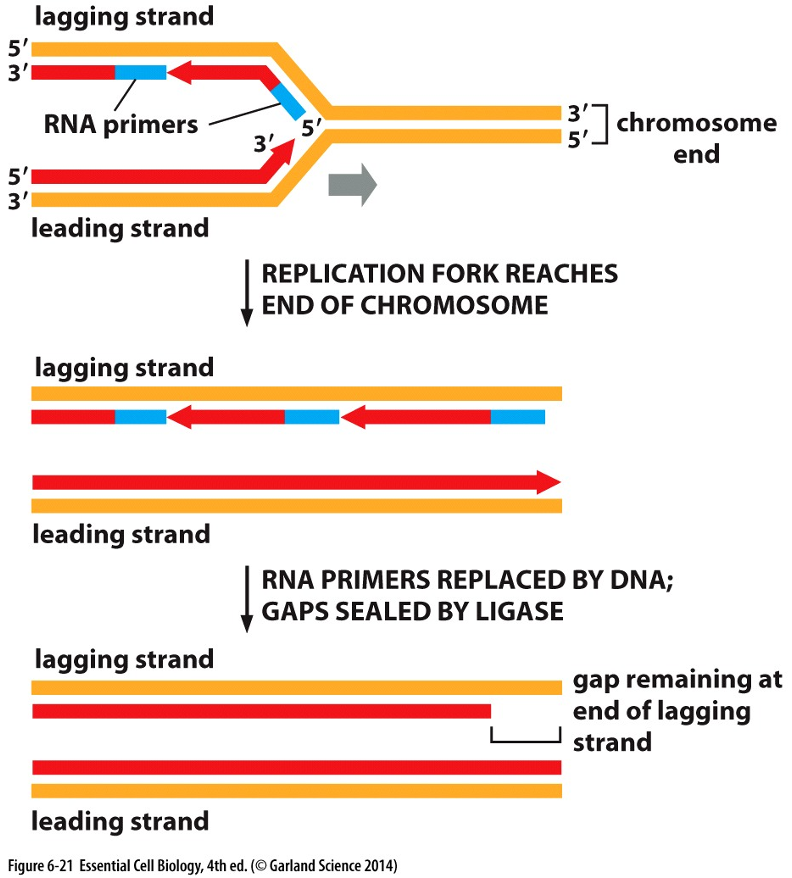
What is telomere replication and why is it important?
Telomere replication involves telomerase adding repeated sequences to chromosome ends to prevent loss of genetic information during DNA replication.
Why do organisms look so different if they all have the same nucleotides?
Because the order of nucleotides (the genetic code) is different, creating different organisms despite having the same types of nucleotides.
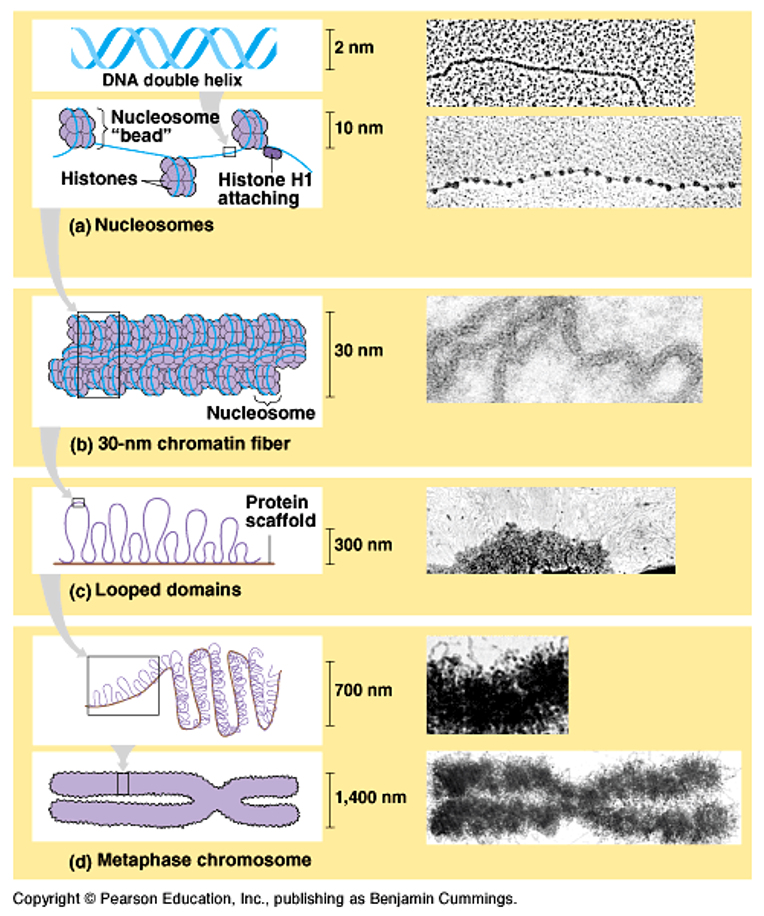
What is a chromosome in eukaryotic cells?
Tightly coiled DNA wrapped around proteins during cell division.
What is chromatin and what are histones?
Chromatin is loosely packed DNA around proteins; histones are proteins that DNA wraps around.
What are heterochromatin and euchromatin?
Heterochromatin is tightly packed chromatin (no transcription); euchromatin is loosely packed chromatin (transcription occurs).
What is histone acetylation and its effect on transcription?
It loosens DNA packing, creating euchromatin, allowing transcription factors to bind and transcription to occur.
What is DNA methylation and when does it occur?
DNA methylation happens after DNA synthesis and lowers transcription rates.
How does DNA methylation affect female mammals and what enzyme works with it?
One X chromosome in females is highly methylated (inactivated), and it works with a deacetylation enzyme in some species.
Levels of DNA packing
DNA wraps around histones → forms nucleosomes → nucleosomes coil into chromatin → chromatin condenses into chromosomes during cell division.
RNA and DNA

RNA (RiboNucleic Acid)
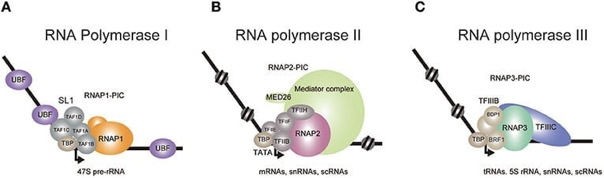
What role does RNA Polymerase II play in transcription?
It attaches to the promoter (TATA box) with transcription factors to begin transcription.
What are control elements in transcription?
Non-coding DNA sequences where transcription factors bind to regulate gene expression.
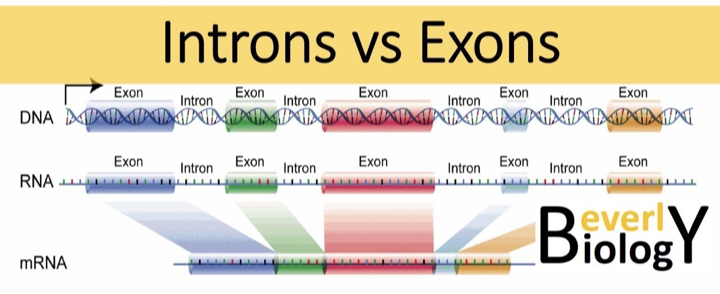
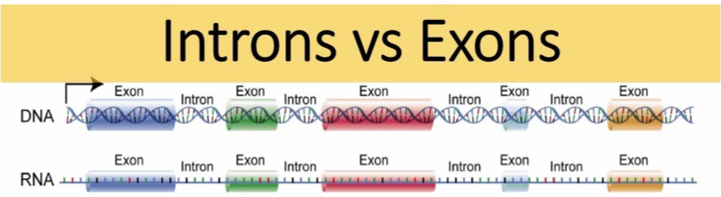
What are introns and exons?
Exons are coding regions of a gene that remain in mRNA; introns are non-coding regions that are removed during RNA processing.
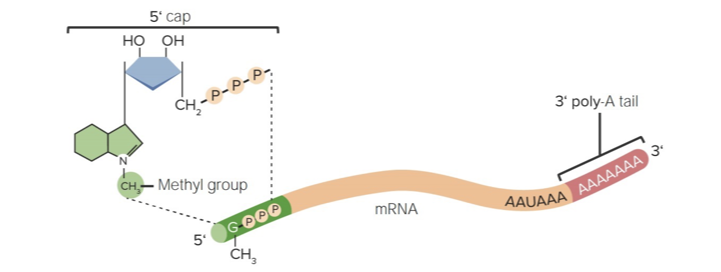
RNA modification
The pre-mRNA undergoes processing where introns are removed (splicing), a 5’ cap is added, and a 3’ poly-A tail is attached to stabilize the RNA and prepare it for translation.

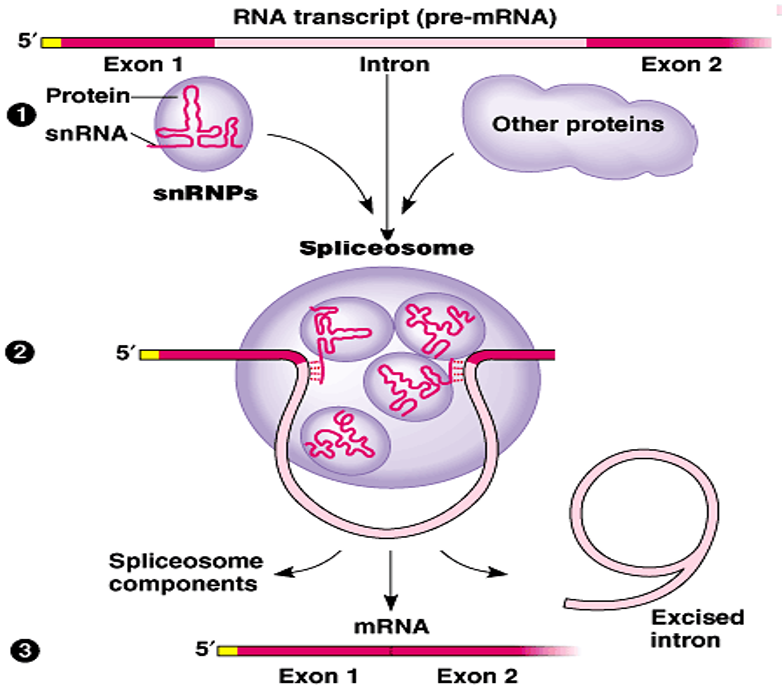
How are introns removed during RNA processing?
A spliceosome, made of snRNPs (proteins + snRNA), cuts out introns by splicing at specific sequences, releasing the intron as a "lariat" RNA.
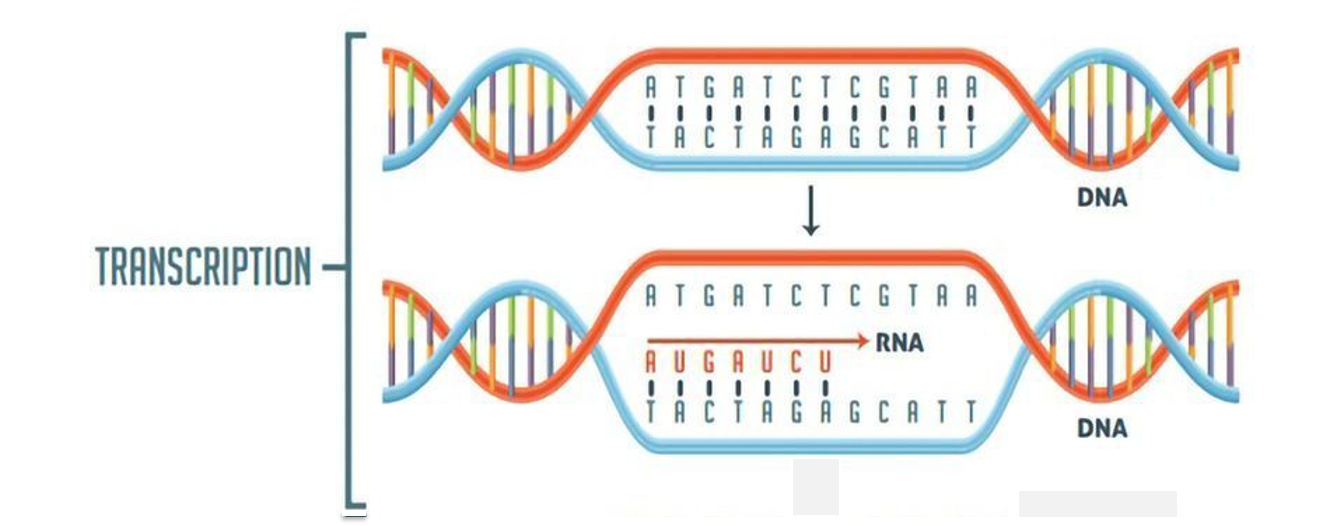
What happens during transcription in RNA?
RNA polymerase synthesizes a complementary RNA strand from a DNA template, copying the gene’s code into pre-mRNA.
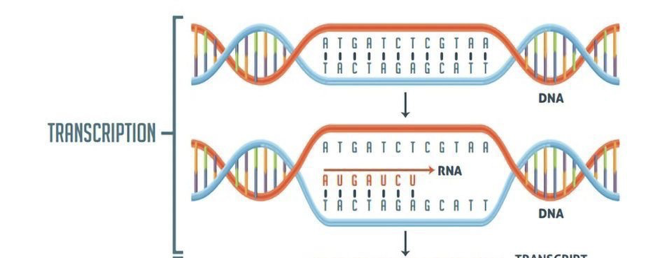
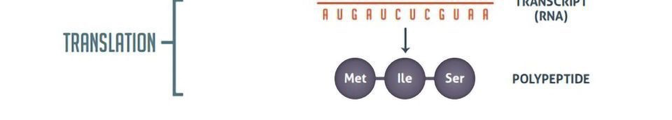
What happens during translation in RNA?
The mRNA sequence is decoded by ribosomes to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide (protein).
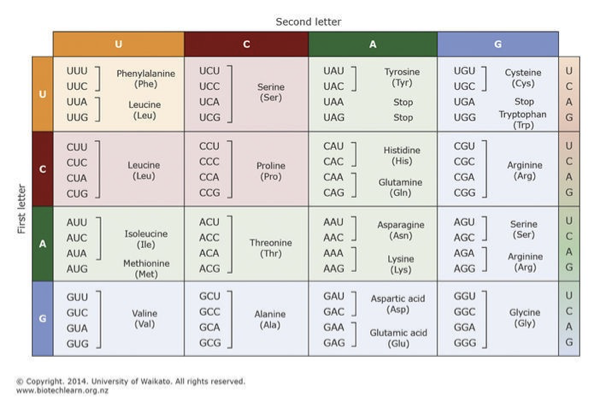
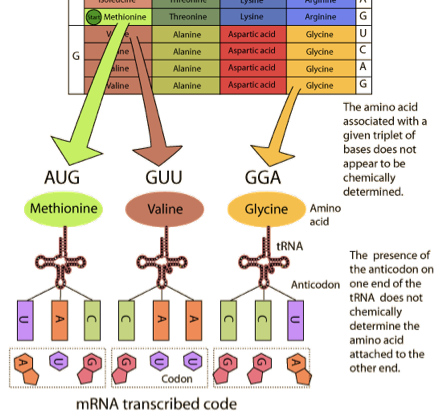
How is transcription activated in eukaryotic cells?
Activators bind to enhancers (control elements far from genes), and together with transcription factors and RNA Polymerase II, form the transcription initiation complex to start transcription.
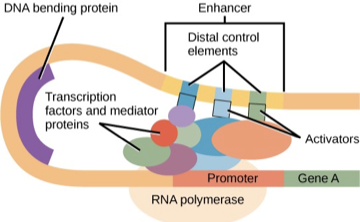
What is the role of repressors in transcription?
Repressors inhibit gene expression by blocking activators from binding to enhancers, turning off transcription.
Gene regulation the third dimension
