psych 1115 chapter 3 consciousness and two track mind
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is dual processing
the principle that info is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks
what does two-track mind refer to
refers to dual processing
what is blindsight
a condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulus without consciously experiencing it
what is selective attention
focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
what is inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
what is change blindness
failing to notice changes in environment; a form of inattentional blindness
what is circadian rhythm
our biological clock; regular bodily rhythms (for example, of temp & wakefulness) that occur on a 24-hour cycle
how circadian rhythm works
in morning, body temp rises, peaks during day, dips in early afternoon, begins to drop in evening — thinking, memory work best when we are in peak circadian arousal (altered by age, individuals, external factors)
suprachiasmatic nucleus
part of hypothalamus that controls circadian clock
melatonin
sleep-inducing hormone
what is biological rhythm
sleep comprising of 5 stages that are cycled through every 90 min
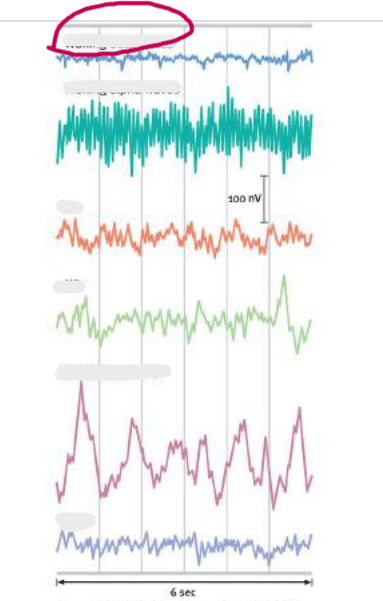
waking beta
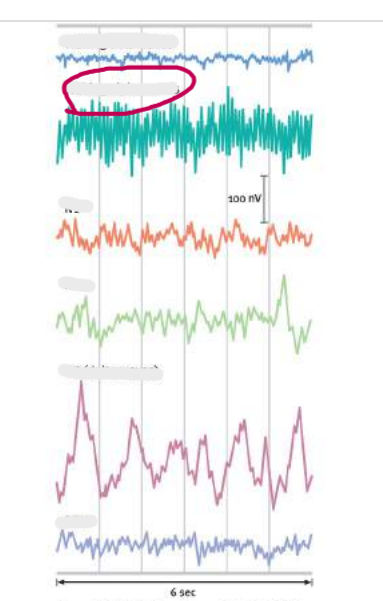
waking alpha
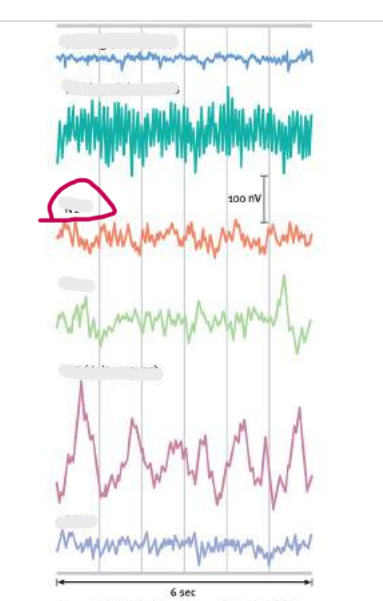
stage 1
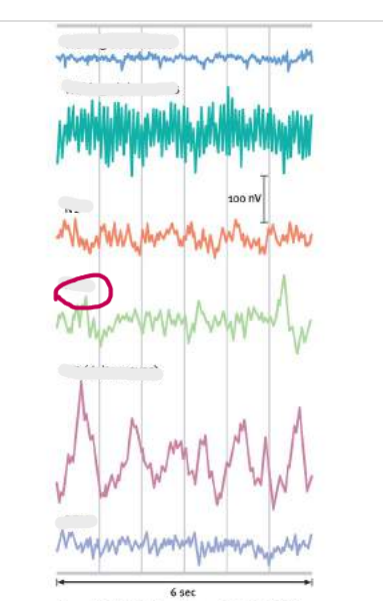
stage 2
stage 3/4
REM sleep
stage 1 of biological rhythm
fleeting images, hypnagogic state; Theta wavers
stage 2 of biological rhythm
Theta waves continues to slow
stage 3/4 of biological rhythm
Delta waves (large, slow) release of human growth hormone
REM sleep of biological rhythm
‘Paradoxical sleep’ — brain is buzzing but body is paralyzed, heart rate rises, breathing is rapid
why we sleep
helps restore & repair damaged neurons, plays a preservative & protective role in human evo, strengthen neural connections, promotes creative problem solving, pituitary gland secretes growth hormone
wish fulfillment theory (why we dream)
a dream’s manifest content is censored version of latent content, dreams are safe outlet to act out unacceptable wishes
information processing (why we dream)
dreams help us sort out day’s events, consolidate memories
activation synthesis (why we dream)
dreams are brain’s attempt to make sense of random neural activity in visual & auditory cortexes, amygdala activities increase during emotional dreams
physiological functions (why we dream)
regular brain stimulation from REM may help develop, preserve neural pathways
cognitive development (why we dream)
dream content reflects dreamer's’ cognitive development — his/her knowledge & understanding
effects of sleep loss
decreased ability to focus/store memories, decreased production of immune cells, increased risk of obesity, increased inflammation, increased risk of high blood pressure, reduced strength/slower reaction time
how hormones are affected by sleep loss
increased ghrelin (hunger), increased cortisol (stress), decreasing metabolics (energy), disrupts gene expression, enhances limbic brain responses
withdrawal
discomfort, distress that follow discontinuing an addictive drug/behaviour (symptoms include physical, psychological dependence)
addiction
compulsive craving of drugs/certain behaviours (gambling) despite known adverse consequences — can be cured
tolerance
tendency for larger does of a drug to be required over time to achieve the same effect
psychoactive drug
chemical substance that alters perceptions, mood
depressant (psychoactive drug)
drugs such as alcohol, barbiturates (tranquilizer), opiates that calm neural activity & slows body function — alcohol acts as disinhibitor (slows neural processing, reduces self-control, memory disruption, cognitive impairment) behaviour is influenced by expectation
stimulants (psychoactive drug)
excite neural activity, speeds up body function — increases alertness & energy (includes caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, ecstasy, metamphetamine)
hallucinogens (psychoactive drug)
distort perceptions, call up sensory images without any input from senses, includes LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide), psilocybin (mushroom), ketamine/marijuana (mild hallucinogen)
alcohol myopia
by focusing on arousing situation at the expense of normal inhibitons and future consequences
biological perspective (brain functioning)
depressants dampen CNS function — loss of reason, caution, inhibitons, fine motor skills, slower reaction — slurred speech, impaired hearing, blurred vision, poor depth perception
biological perspective (neurotransmission)
some stimulants, like cocaine are reuptake inhibitors (blocks reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin), metamphetamine works by increasing release dopamine at presynaptic neurons
psychological perspective (stress response)
addiction is learned response to unpleasant experiences, stress is related to drug addiction/relapse, PTSD & drug abuse often co-occur, young adults who reported higher lvls of meaning life reported lower lvls of alcohol/marijuana use
Social-cultural perspective (media exposure, smoking)
tobacco industry targets toward adolescents/children by featuring themes of masculinity/coolness (psychological motive), claims to persuade adult smokers to switch brands but only 10% of them do
Social-cultural perspective (rat park study)
demonstrates importance of social and structural environment