Skylar's Intro Exam 2
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Two Types of Ionizing Energy
1. human-made
-medical/dental
-x-ray
2.background
-radium/uranium
-sun
-cosmic
risk must weigh _______ than __________
less
benefit
what kind of effect can radiation cause
biologic
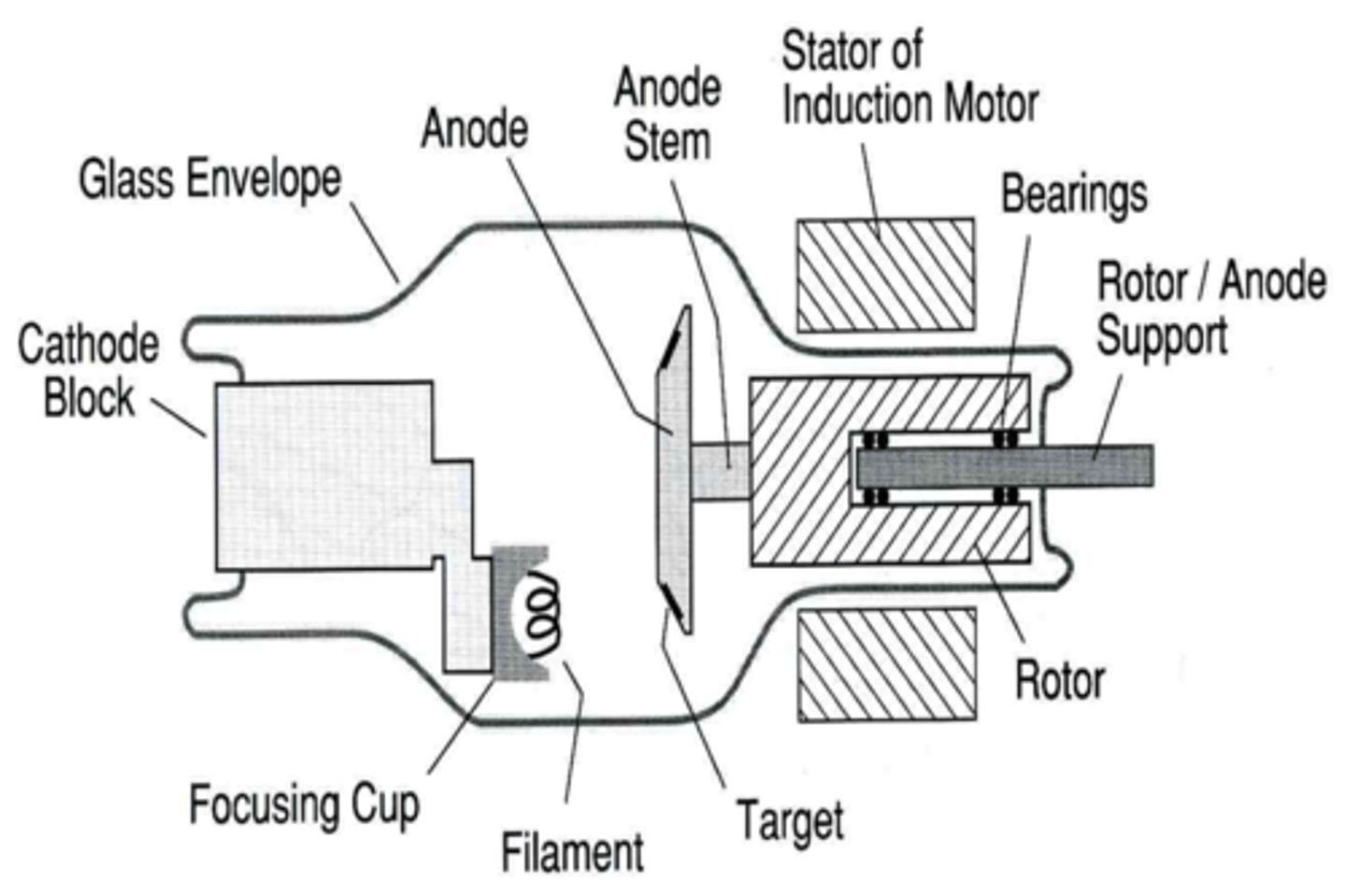
conditions necessary for x-ray production
1. a source of electrons
2. a means to rapidly accelerate the electrons
3. something to rapidly stop this movement
all of this is done by the tube
x-ray tube is a __________ tube
diode
-glass envelope maintains vacuum
is the beam heterogenous and homogenous
heterogenous
how is the energy of the beam expressed?
KeV
source of electrons
mA
high speed motions
potential difference (KvP)
does muscle or fat need a higher KvP
muscle
does bone or muscle need higher KvP
bone
deceleration
target
-anode
anode
positive end
cathode
negative end
thermonic emission
the release of electrons from the tungsten filament when the electrical current passes through it and heats the filament
when is the x-ray produced?
when it strikes the anode
what is the x-ray
the primary beam
what are the 3 paths of the x-ray beam
1. can be absorbed
2. transfer energy and scatter
3. pass through unaffected
Classic Coherent Scattering
no energy transfer
Photoelectric Interaction
greatest hazard to patient
complete energy absorbed
Compton Interaction
greatest hazard to worker
scatters in random direction until energy is gone
Pair Production Interaction
radiation therapy
high energy photon
Photodisintegration
nuclear energy
Roentgen
Coulomb per Kg
Air
Radiation Absorbed Dose
Gray
RAD energy absorbed
Radiation Equivalent Man
Sievert
REM
different types of biologic effects
Curie
Becquerel
activity of radioactive
-nuclear med and radiation therapy
Standards
FDA
ALARA
The annual dose limit for occupationally exposed individuals is valid for
50 mSv (5 REM)
annual dose for public
5 mSv (0.5 REM)
monthly dose for embryo-fetus
0.5 mSv (0.05 REM)
dose for lens of eye
15 msV
-can get cataracts
2 class of radiation
1. nonionizing
2.ionizing
examples of nonionizing
-radio waves
-micro
-infrared
-visible
examples of ionizing
-moving electrons
-ultraviolet
-x-ray/gamma
-alpha particles
-beta particles
-protons
-neutrons
lead apron requirement
0.5mm
thyroid shield requirment
0.5mm
lead gloves
.25-0.5mm
lead eye glasses
.35-.5mm
does the dosimeter protect you from radiation?
no
Radiation Syndromes
bone marrow
GI
Central Nervous
True or False: Any extraneous information on an image that does not reflect the patient's true medical condition detracts from diagnostic efficacy
True
diagnostic efficacy
The degree to which the diagnostic study accurately reveals the presence or absence of disease in the patient
should you mask an image
no
PBL
positive beam limitation
automatically reduces collimation to IR levels
Tabletop is highly radiolucent
little absorption
can penetrate
radiolucent high or low absorption?
low
radiopaque high or low absorption?
high
IR Technology
receives remnant radiation from patient and captures x-ray energy for processing
Classes of Diagnostic Imaging
1. Film-screen radiography
2.Flouroscopic imaging
3.Digital/computerized imaging
penetrating ability and quality
KvP
the only radiation that has any clinical value is...
- the radiation that is absorbed in the detector
- able to be converted to a radiographic
image for interpretation
latent image
invisible image created after exposure but before processing
cord attached to IR
tether
static radiographic image
SPOT film
X-ray production requirements
vacuum tube
source of electrons
high voltage
target
vacuum
removes all of the air so gas will not interfere with the production of x-ray
what is a primary factor of density?
mAs
Label the x ray tube
increase kVp
lowers contrast
images few grey tones
short scale (high contrast)
seeing black and white
images many grey tones
long scale (low scale contrast)
Direct Square Law
increase distance
increase technique
Inverse Square Law
decrease distance by 1/2
increase intensity by 4x
OR
increase distance by 2x
decrease distance by 1/4
Classes of Radiation
Primary radiation
Scatter radiation
Absorbed radiation
Remnant radiation
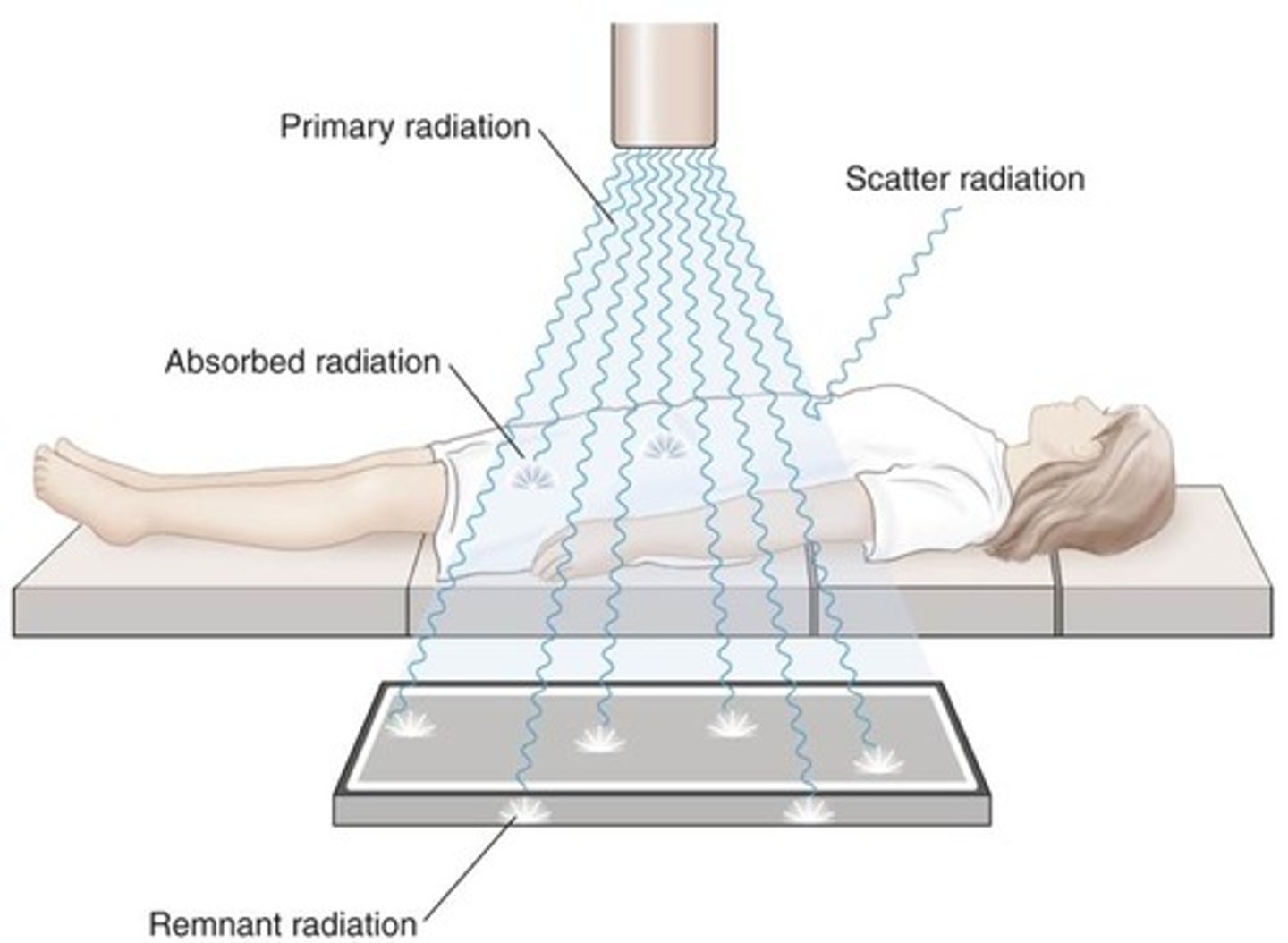
attenuation
absorption of radiation in the body
loss of radiation energy as result of passing through an absorbing material
high attenuation
radiopaque
low attenuation
radiolucent
scatter control
occupational worker receives their dose from
retracts from image quality
can create fog
fog
exposed IR
how to control scatter
lead blocker on side of patient
IR
detect remnant radiation from patient and convert it into chemical or electrical charges
digital receptor systems (DR)
computerized radiography
cassette
exposed plate and ran through reader with latent image
Computed Radiography (CR)
exposure to plate
Exposure Index
a numeric representation of total x-ray exposure to the receptor
differs among manufacturers
geometric qualities of image
affects resolution, size, and shape of image
what controls size of image
SID and OID
What can affect the detail
motion
unsharpness
focal spot size
SID
OID
distortion
what is the most common cause of image unsharpness
motion
voluntary or involuntary
unsharpness
loss of resolution
OID
patient and image receptor
distortion
any misrepresentation of patient's true size and shape
size distortion
image always slightly larger than objects actual size
can use longer SID or minimize OID
shape distortions
Central Ray (angling)
Patients' anatomy (rotation)
IR
deliberate distoration
angling tube on purpose
density
mAs
contrast
kVp