auditory perception
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Azimuth
Horizontal angle
elevation
Vertical angle
ITD
The difference in time between sound arriving at one ear vs the other; good for low frequencies, accurate localization for low frequencies, processed in the medial superior olive (MSO)
interaural time difference
Itd
azimuth, elevation, distance
elements to localize sound
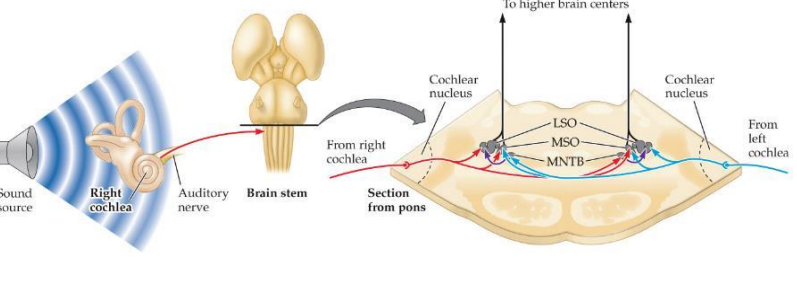
MSO
relay station in the brain stem where inputs from both ears contribute to detection of ITDs
Medial superior olive
Mso
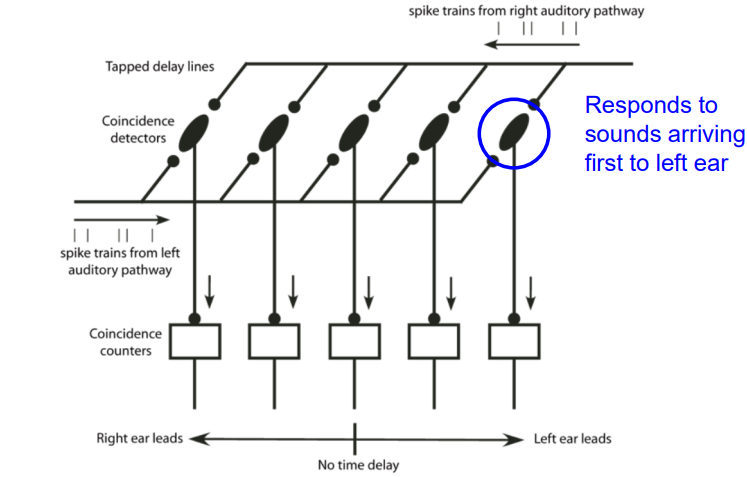
jeffress model
coincidence - detector model; responds to sounds coming from opposite ear neurons that respond maximally when inputs arrive from the two ears simultaneously – innervated from each ear by a series of delay lines – axons of variable path length
ILD
the difference in intensity (loudness) between a sound arriving at one ear versus the other; not very accurate for localizing stationary sounds, processed in lateral superior olive (LSO)
Interaural level difference
Ild
LSO
relay station in the brain stem where inputs from ears contribute to the detection of ILDs
lateral superior olive
lso
ipsilateral ear
excitatory connections to LSO come from…
contralateral ear
inhibitory connections to LSO come from …
cones of confusion
positions in space where all sounds produce identical ITDs and ILDs
head-related transfer functions (HRTF)
describes how pinnae, ear canals, head, and torso change the intensity of sounds with different frequencies as the sound location changes (aka DTF)
inverse square law
intensity decreases as the square of distance (quieter = farther away)
spectral composition
higher frequencies decrease in energy more than low frequencies as sound waves travel (like scattering of short vs. long wavelengths of light) - distant v. nearby thunder; cue only works for long distances (> 1km)
reverberant energy
whether sound is arriving directly (nearby source) or from reverberations is conveyed by timing info
harmonics
objects tend to vibrate at multiple “resonant frequencies” that are integer multiples of some fundamental frequency
timbre
psychological sensation by which a listener can judge that two sounds with the same loudness and pitch are different
attack
part of a sound during which amplitude increases (onset)
decay
part of a sound during which amplitude decreases (offset)
missing fundamental
structure of harmonic sounds causes listeners to hear a low frequency that is absent