FHD - microbiology
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
contains FHD topics: introduction to microscopic anatomy, microscopic anatomy: cell types and tissue, fundamentals of molecular cell biology, cells and their organelles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
what are the four body tissue types
epithelial, muscular, connective, nervous
which two body tissue types can self renew
connective and epithelial
what are the four types of epithelial tissue
simple. stratified, pseudostratified, transitional
what are the three types of simple epithelial tissue
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
what is the appearance of squamous cells
flat appearance of cells
what are the functions of squamous cells
diffusion, filtration, secretion
what is the function of cuboidal cells
secretion and absorption
what is the appearance of cuboidal cells
cube like appearance
what is the function of columnar cells
secretion and absorption
what is the appearance of columnar cells
cells have a rectangular appearance
what are simple cells
cells that have a single layer
what are stratified cells
cells that have multiple layers
what are pseudostratified cells
cells that give the appearance of having multiple layers due to their arrangement
what are transitional cells
cells with a variable number of cell layers
what type of cell is a squamous cell
stratified
what is the function of squamous cells
protection against injury
what type of epithelial cell is ciliated
pseudostratified
which type of epithelial cell allows for the stretching of linings
transitional
which type of epithelial cell allows for the propelling of mucous particles
pseudostratified
what are the three (overall) types of connective tissue
fibrous, specialized, fluid
what are the two types of fibrous connective tissue
loose connective tissue, and dense connective tissue
what are the four types of specialised connective tissue
compact bone, spongy bone, adipose tissue, fibrocartilage
what is the fluid connective tissue
blood
how many types of collagen are there
five
what are the fibers like in type I collagen
large fibers
where is type I collagen found
skin, tendon, bones, ligaments
where is type II collagen found
in cartilage
what type of fibers are in type II collagen
small fibers
what are the fibers like in type III collagen
small fibers
where is type III collagen found
in blood vessels, parenchyma organs
what are parenchyma organs
solid organs
what is the structure of IV collagen
a sheet like layer
where is type IV collagen found
in basement membranes
what is the structure of type V collagen
thin fibrils
where is type V collagen found
in basement membranes and smooth skeletal muscle
what are glands comprised of
epithelial cells (which make up glandular tissue)
in exocrine glands what are secretions transported via
ducts
what is autophagy
degrading damaged or dysfunctional organelles and cellular components to help alleviate stress and retain cellular function
what carries out autophagy
lysosomes
when is autophagy non-selective
during starvation
what are melanosomes
specialized lysosomes that hold melanin pigments
how do melanosomes secrete pigment
via exocytosis
what is mitophagy
the removal of damaged mitochondria
when are Endolysosomes formed
lysosomes fuse with entities that enter the cell via endocytosis
how does apoptosis occur
If present, microvilli contract and intercellular junctions break, chromatin condenses and cell fragments into membrane enclosed apoptotic bodies
what is fixation
a treatment used to preserve a sample in a life-like state
what are the two procedures involved in sample processing
embedding and sectioning
what type of dye is haematoxylin
a basic dye
what does haematoxylin stain
acidic/ basophilic structures
which dye stains DNA
haematoxylin
which dye stains cartilage molecules
haematoxylin
what type of colour does haematoxylin stain
purple
what type of dye is eosin
an acidic dye
what structures does eosin stain
basic/ acidophilic structures
which dye stains cytoplasmic proteins
eosin
which dye stains extracellular fibres
eosin
what colour does eosin stain
pink
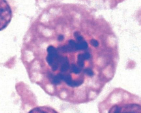
which stage of mitosis is shown here
prophase
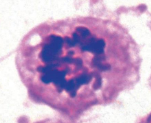
which stage of mitosis is shown here
metaphase
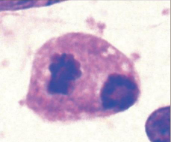
which stage of mitosis is shown here
anaphase
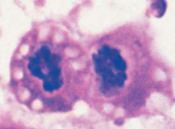
which stage of mitosis is shown here
telophase
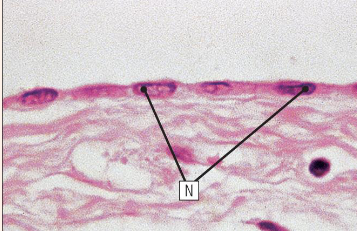
what type of epithelium is shown here
simple squamous epithelium
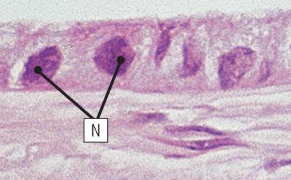
what type of epithelium is shown here
simple cuboidal epithelium
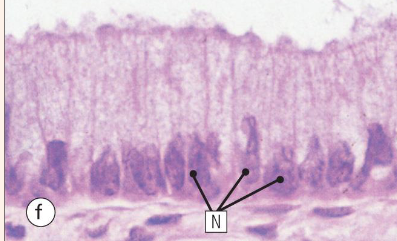
what type of epithelium is shown here
simple columnar epithelium
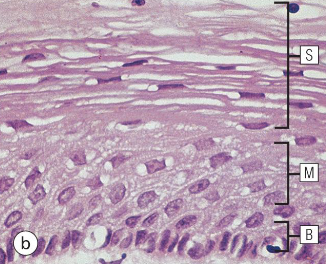
what type of epithelium is shown here
stratified squamous epithelium
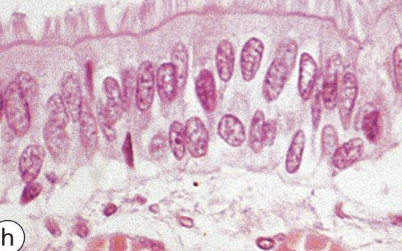
what type of epithelium is shown here
pseudostratified epithelium
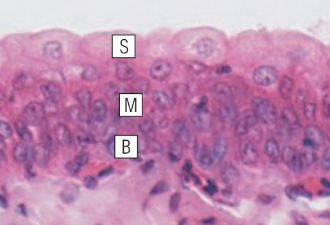
what type of epithelium is shown here
transitional epithelium
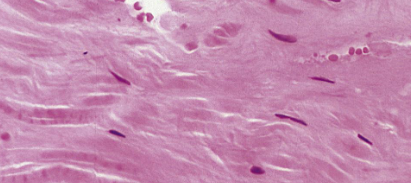
what type of fibres are shown here
collagen fibres
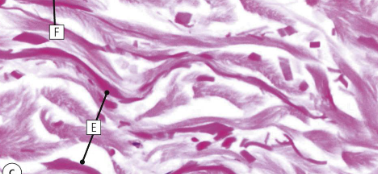
what type of fibres are shown here
elastic fibres
what is a biomarker
a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated
what can a biomarker an indication of (3 points)
normal biological processes, pathogenic responses, pharmacological responses to therapeutic intervention
what is translational research
the application of basic research to clinical settings
what does TNF stand for
tumour necrosis factor
what is Tumour necrosis factor (TNF)
a cytokine involved in inflammation
what does TNF bind to
the cell surface receptors TNFR1 and TNFR2
what is interleukin 1 and what is it involved in
a cytokine involved in inflammation
where is interleukin 1 generated
primarily in macrophages, but also in endothelial and epithelial cells
what is antibody drug conjugates
an approach used to improve drug delivery via targeting
what is the protocol CRISPR used for
gene editing
what are the two components of the CRISPR system
DNA binding protein (Cas9), RNA guide molecule
what is the DNA binding protein used in CRISPR
Cas9
what pH do lysosomes have
5
what does a peroxisome contain
enzymes that break down fatty acids and amino acids, and a crystalline array of catalase
what does the peroxisome break down fatty acids and amino acids into
hydrogen and peroxide
what occurs to the by product peroxide
it is neutralised by large amounts of catalase within the peroxisome
What are protein bio markers used for in a clinical setting
as part of the diagnosic process
what percentage of total body fluid is intracellular
67%
what reaction does carbonic anhydrase catalyse
the reaction of carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid (or the reverse)
What is the main function of the Golgi
to post translationally modify and sort proteins to specific regions of the cell
what are microtubules
cytoskeletal structures involved in cell division, muscle contraction and vesicular transport
Which cell type lacks internal compartments
prokaryotes
what component of gram negative bacteria trigger an innate immune response
lipopolysaccharides
on average, when testing bacteria to determine susceptibility to antibiotics, how long does it take to generate definitive results that can influence treatment results
48 hours
What do macrolides to
inhibit folic acid synthesis and metabolism