Hearing Anatomy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:31 AM on 8/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
Helix
the outer posterior superior rim of the ear and curves slightly inward towards the external auditory meatus
3
New cards
Stapes
part of the middle ear that is most medial and is connected to the oval window of the cochlea
4
New cards
Travelling Wave Theory
states that there is a coding system in the cochlea
5
New cards
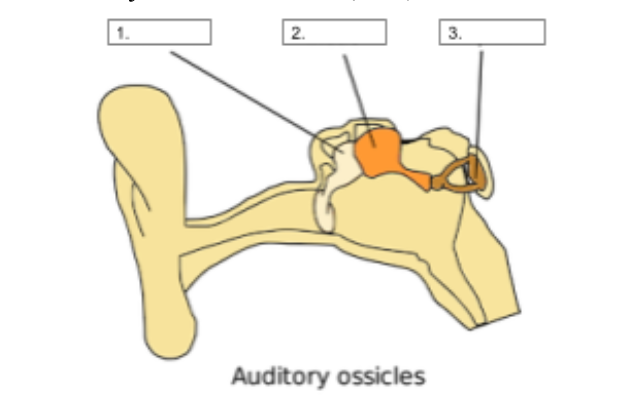
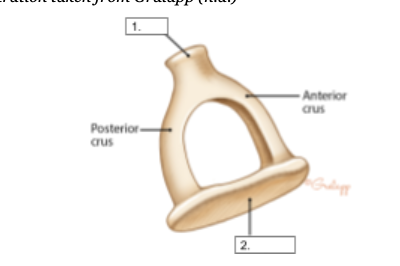
Malleus
identify structure #1
6
New cards
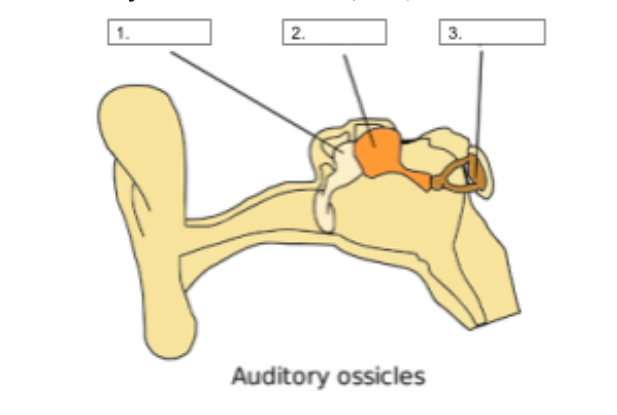
Incus
identify structure #2
7
New cards
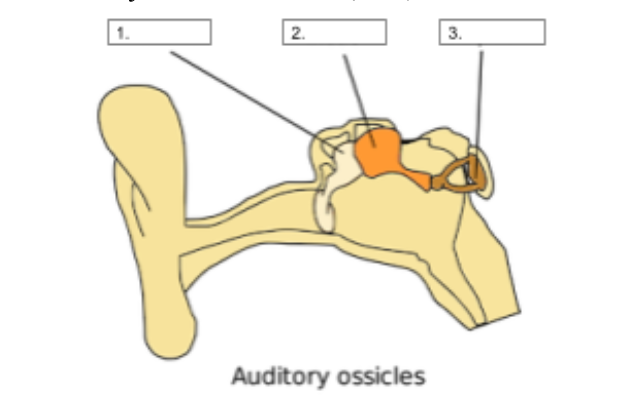
Stapes
identify structure #3
8
New cards
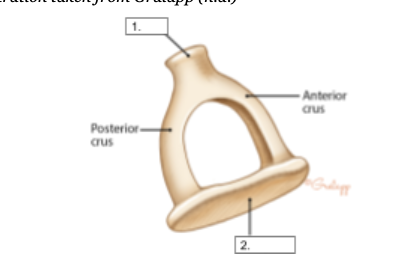
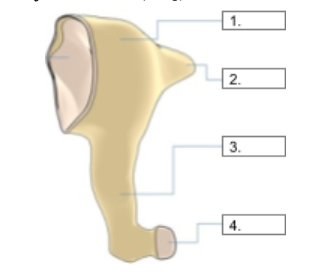
Head
identify structure #1
9
New cards
Footplate
identify structure #2
10
New cards
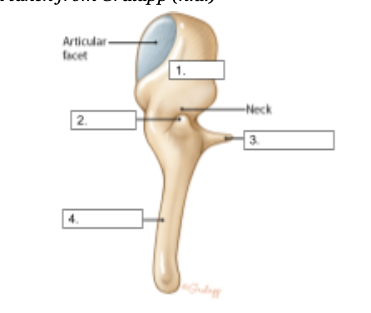
Body
identify structure #1
11
New cards
Head
identify structure #1
12
New cards
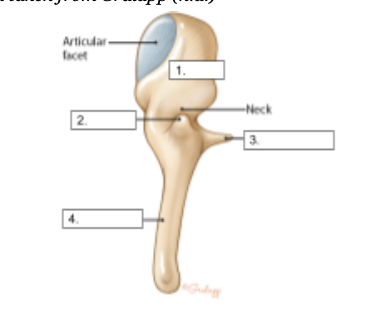
Lateral Process
identify structure #2
13
New cards
Endolymph, Perilymph
the scala vestibuli and scala media contain perilymph, while the scala media contain endolymph. High concentration of potassium ions and low in sodium is found in ________, while low concentration of potassium and high concentration of sodium is found in _________.
14
New cards
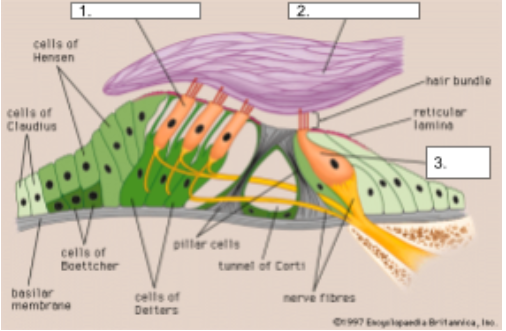
Outer Hair Cells
structure #1
15
New cards
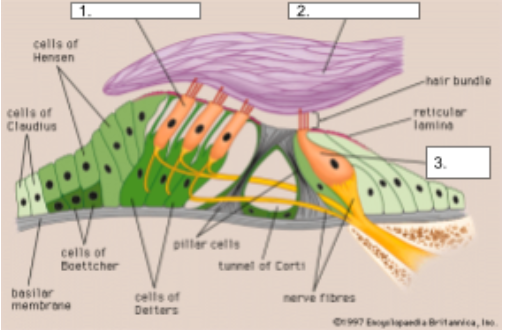
Tectorial Membrane
structure #2
16
New cards
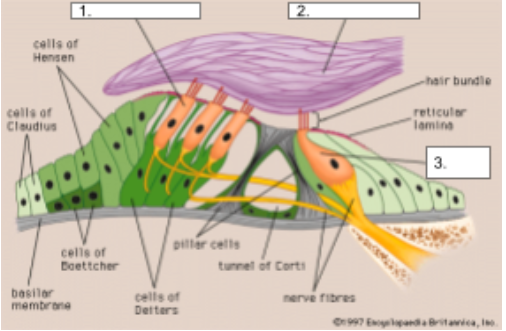
Inner Hair Cells
structure #3
17
New cards
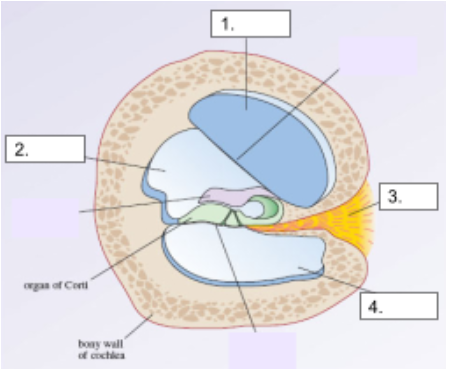
Scala Vestibuli
structure #1
18
New cards
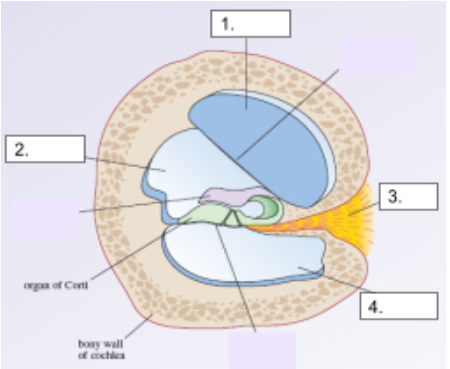
Scala Media
structure #2
19
New cards
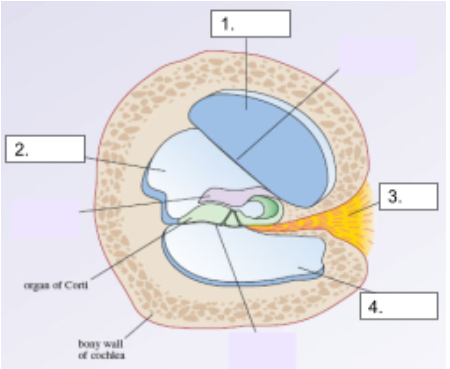
Cochlear Nerve
structure #3
20
New cards
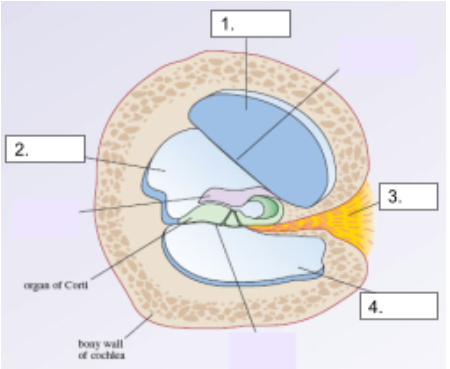
Scala Tympani
structure #4
21
New cards
Cochlear Nuclei
a more analysis of the frequency in the sound stimulus happen in the ______
22
New cards
Cochlea
which of the following is affected if a patient has an inner ear infection?
23
New cards
Semicircular Canals
the fluid moving in the _______ causes an individual to feel dizzy after she/he stops spinning
24
New cards
Perilymph and Endolymph
vestibule controls the sense of equilibrium in the ___ __*____*__
and __________
and __________
25
New cards
Organ of Corti
located on the basilar membrane of the cochlea is the _____, which contains hair cell sensory receptors for the sense of hearing
26
New cards
Middle Ear
converts acoustic energy to mechanical energy
27
New cards
Auditory Nerve
fluid from the inner ear stimulates nerve endings called hair cells. These send electrical impulses along the _______ to the brain.
28
New cards
Inferior Colliculus
the site where the frequency and intensity information of the sound stimulus is put together in the __________
29
New cards
Primary Cortex
the site where 2 stimuli can be discriminated happens in the _________
30
New cards
Superior Olivary Complex
analysis of the loudness of the sound happens in the ________
31
New cards
Cochlea ; Nervous System
the afferent nerve supply is made up of ascending sensory neurons that send signals from the ______ to the _________.
32
New cards
Sensorineural
type of hearing caused by damage in the inner ear
33
New cards
Outer and Middle Ear
structures affected when a person has a conductive hearing loss
34
New cards
Cranial Nerve VII
cranial nerve affected when a person has sensorineural hearing loss
35
New cards
Sudden
a rapid onset of hearing loss
36
New cards
Avulsion
an outer ear trauma wherein the ear is detached from the head, either partially or completely
37
New cards
Subperichondrial hematoma/Boxer’s ear
this injury results from the trauma to the exterior ear wherein blood pools under the skin and cuts off the blood supply to the cartilage which causes the cartilage to die
38
New cards
Otitis Media
inflammation located in the middle ear which results in a malfunction of the eustachian tube which prevents normal drainage of fluid from the middle ear
39
New cards
Otitis Media with Effusion
a type of otitis media where fluid remains in the middle ear for a prolonged period and can result in difficulty fighting new infection
40
New cards
Barotrauma
the medical term for that uncomfortable sensation that hits when we’re in an airplane and our ears suddenly feel like they’re stuffed with cotton
41
New cards
Cholesteatoma
benign growth that starts within the retracted section of the eardrum which was brought about by a sustained, abnormal middle ear pressure
42
New cards
Otosclerosis
causes mild to severe hearing impairment but it rarely results in total deafness; abnormal hardening of body tissue of the ear
43
New cards
Stapes
structure affected when a person suffers from otosclerosis
44
New cards
Presbycusis
the most common hearing loss that affect the majority of those over 60 years old
45
New cards
Measles
this type of infectious disease can cause possible central auditory damage
46
New cards
Tumor
it normally grows slowly, gradually compressing the auditory nerve, and may also affect the nearby vestibular nerve which results in both hearing loss and balance problems.
47
New cards
Auditory Brain Response
a 5-month-old baby was referred for an audiometric assessment as recommended by the SLP. What type of instrumental assessment may be suggested with this age?
48
New cards
Sensorineural
the results of the audiometry shows that the results from bone conduction and air conduction are both poor. With this, what type of hearing loss would be possibly diagnosed?
49
New cards
Air Conduction Test
Pure Tone Assessment wherein the sound is presented via headphones through outer and middle ear
50
New cards
Outer Ear
localizes the sound
51
New cards
External Auditory Meatus
provides a sticky trap for foreign bodies and repels insects
52
New cards
Umbo
where the tip of the malleus is attached
53
New cards
Auditory Ossicles
chain of the three tiny bones that transmit sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window
54
New cards
Malleus
outermost, most lateral and the largest of the ossicles
55
New cards
Incus
located at the manubrium of the malleus to the lenticular process
56
New cards
Stapes
smallest bone in the human body
57
New cards
Mastoid Air Cells
a collection of air-filled spaces in the mastoid process
58
New cards
Endolymph
receives the motion of the waves
59
New cards
Anterior Semicircular Canals
detects forward and backward head movement
60
New cards
Posterior Semicircular Canals
detects head tilt
61
New cards
Inner Hair Cells
convert sound vibrations from the fluid in the cochlea into electrical signals that are transmitted via the auditory nerve to the brain
62
New cards
Outer Hair Cells
amplify low level sounds that enter into the fluids of the cochlea
63
New cards
External Auditory Meatus
protects the middle and inner ears from external traumas by impeding the entry of foreign objects
64
New cards
Tensor tympani
pulls the malleus anteromedially
65
New cards
Stapedius
stabilizes the stapes by rotating the footplate
66
New cards
Eustachian Tube
equalizes pressure in the middle ear with external air pressure
67
New cards
Tympanic Cavity
transmits sound energy from the external ear to the inner ear by the oval window
68
New cards
Semicircular Canals
associated with balance or equilibrium
69
New cards
Utricle
plays a vital role in orientation and static balance, particularly horizontal tilt
70
New cards
Saccule
has a role in vertical acceleration
71
New cards
Organ of Corti
receptor organ for hearing
72
New cards
External Auditory Meatus
acts as a quarter wave resonator and has its own resonant characteristics
73
New cards
Middle Ear
matches low-impedance airborne sounds to the higher-impedance fluid of the inner ear
74
New cards
Protection Theory
suggests that acoustic reflex protects the inner ear from intense sound levels that may be damaging to the ear.
75
New cards
Fixation Theory
suggests that the middle ear muscles maintain the appropriate positioning and rigidity of ossicles
76
New cards
Travelling Wave Theory
suggests that there is a coding system in the cochlea; the fundamental cochlear response to acoustic stimuli consists of a displacement wave which propagates along the basilar membrane from base to apex
77
New cards
base of the cochlea
resonates high frequency sounds
78
New cards
apex of the cochlea
resonates low frequency sounds
79
New cards
Afferent Auditory Pathway
send signals from the cochlea to the nervous system
80
New cards
Superior Olivary Complex
localizes where the sound is coming from
81
New cards
Ipsilateral
stays on the direction of the original pathway
82
New cards
Contralateral
decussate or cross over the other side
83
New cards
Inferior Colliculus
integrates the sound signals and receives all the information signal in the body
84
New cards
Medial Geniculate Body
plays a role in the emotional responses to auditory stimuli
85
New cards
Primary Auditory Cortex
responsible for discrimination of frequency and intensity of the incoming auditory stimulus
86
New cards
Efferent Auditory Pathway
starts at the auditory cortex
87
New cards
Rostral or Centrifugal Pathway
starts from the auditory cortex down to the inferior colliculus
88
New cards
Corticothalamic System
where messages in relation to tonotopic frequencies and spatial topography are sent from the auditory cortex to different parts of the medial geniculate body
89
New cards
Corticollicular System
comprises the efferent pathways to the midbrain and inferior colliculus
90
New cards
Hearing Loss
a condition that happens when the transmission of sound from the outer ear to the brain is disrupted
91
New cards
Hard of Hearing
people with hearing loss ranging from mild to severe
92
New cards
Deaf
these people mostly have profound hearing loss, which implies very little or no hearing
93
New cards
Conductive Hearing Loss
occurs when sounds are unable to pass through the outer and middle ear
94
New cards
Conductive Hearing Loss
soft sounds may be difficult to hear, while louder sounds may be muffled
95
New cards
Sensorineural
occurs when there is a damage in the inner ear
96
New cards
Mixed Hearing Loss
occurs when there is a damage in the outer, middle or inner ear
97
New cards
Avulsion
the ear can detach partially or completely from the head
98
New cards
Subperichondrial hematoma
occurs as a result of trauma to the external ear; frequently obtained in contact sports
99
New cards
Otitis Externa
an inflammatory condition that causes redness and swelling of external ear canal
100
New cards
Osteoma
a slowly growing, benign tumor made of mature bone