Physiology: Lab Practical #1
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 1760
1.76 × 10³
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 2,200,000
2.2 × 10^6
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 0.00064
6.4 × 10^-4
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 304,000
3.04 × 10^5
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 0.00003
3 × 10^-5
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 43.125
4.3125 × 101
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 0.0056
5.6 × 10-3
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 0.0000073
7.3 × 10-3
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 2.750
2.75 × 10-3
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 4.300
4.3 × 10³
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 0.02
2 × 10^-2
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 0.0000535
5.35 × 10^-5
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 0.00234
2.34 × 10^-3
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 8900
8.9 ×10³
Express numbers in the form of scientific notation: 5.600000
5.6 × 10^6
Abbreviation for decimeter
dm
Abbreviation for milimeter
mm
Abbreviation for nanometer
nm
Abbreviation for miligram
mg
Abbreviation for deciliter
dL
Abbreviation for micrometer
um
Abbreviation for centimeter
cm
Abbreviation for gram
g
Abbreviation for Angstrom
Å
Abbreviation for cubic centimeter
cm³/cc
Express the following numbers exponentially: 0.0000034
3.4 × 10^-6
Express the following numbers exponentially: 72.00000
7.2 × 10^7
Express the following numbers exponentially: 6050
6.05 ×10³
Express the following numbers exponentially: 0.00348
3.48 × 10^-3
Convert: 3.65 grams to milligrams
3650mg
What is the name for the Red objective lens: 4x
Scanning power
What is the name for the Yellow objective lens: 10x
Low power
What is the name for the Blue objective lens: 40x
High power
What is the name for the White objective lens: 10x
Oil Immersion
What is the micrometers for the 100x total magnification of view?
1600 uq
What are the monomers that construct proteins
Amino Acids
What are the monomers that construct carbohydrates
Glycogen
What are the monomers that construct nucleic acids
Nucleotides
Carbohydrates are under what test(s)?
Benedict’s and Lugol
Lipids are under what test?
Grease
Proteins are under what test?
Biuret and Ninhydren
Beer’s Law states…
The absorptive capacity of a dissolved substance is directly proportional to its concentration in a solution.
Transmittance def
How much light is going through.
Absorbance def
How much light is being blocked.
Spectrophotometer def
To determine light absorbance measurement.
How to calculate protein concentration
Volume of Albumin x 2.5 mg/mL = answer mg of protein / 8 = protein concentration.
Balanced equation
2H2O2
Net diffusion
Uniformed distribution of solute molecules.
Net Osmosis
Net movement of water molecules from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration.
Osmotic Pressure
Concentration of dissolved particles.
Diffusion
The spreading of molecules
Osmosis
Movement of water from high concentration to low concentration.
Brownian Movement
Random movement of solutes in a solution.
Tonicity
Concentration of a solution as compared to another solution.
Isotonic
Solution having equal osmotic pressures.
Hypertonic
Solution with a high osmotic pressure.
Hypotonic
Solution with a low osmotic pressure.
Understand what occurred in sheep blood cell experiment.
Hemolysis and crenation occurred. We aw the isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic measures in the blood.
Understand the purpose behind the great osmosis race experiment.
To see the movement of water from high concentration to low.
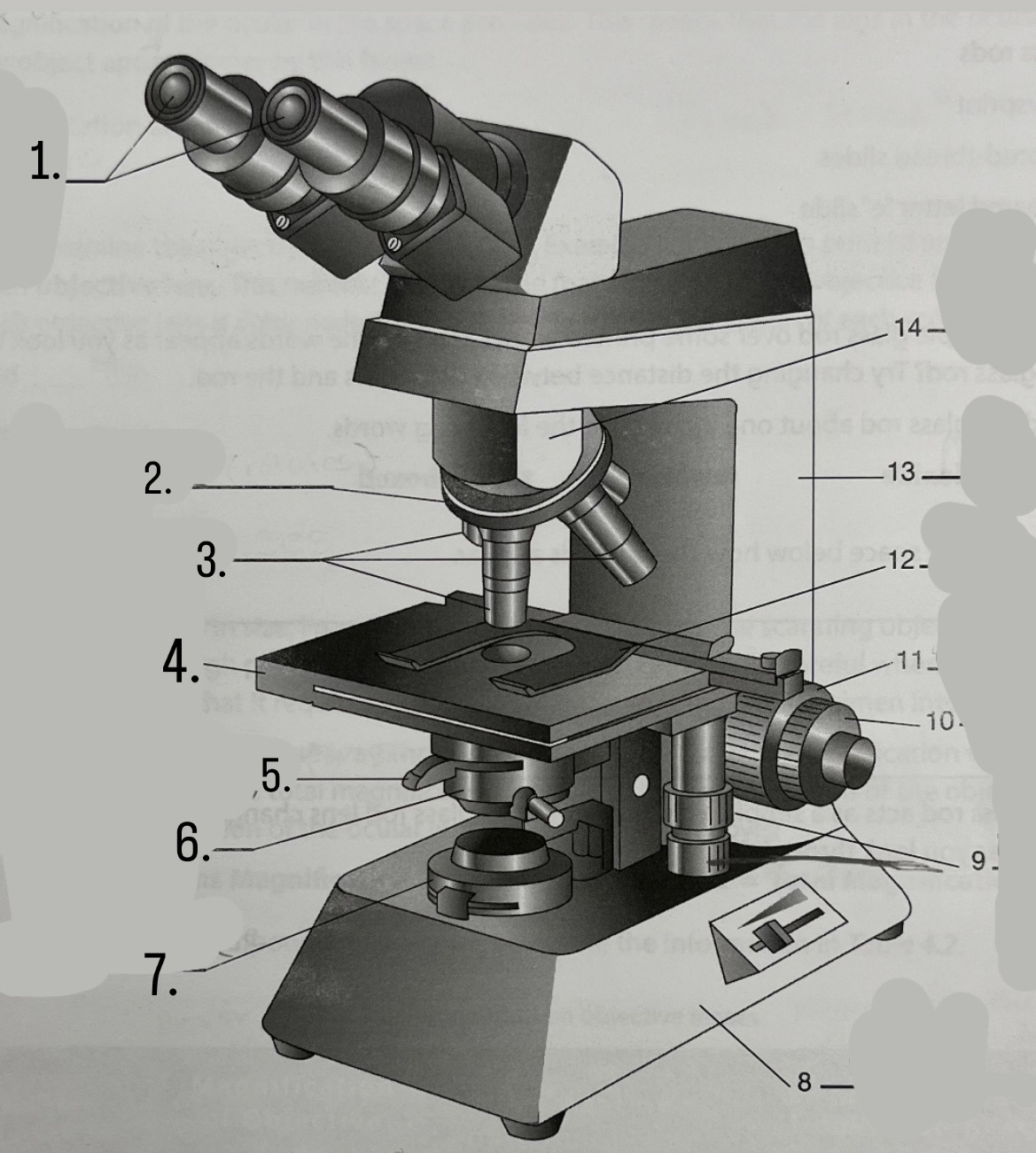
What is #1?
Ocular Lens
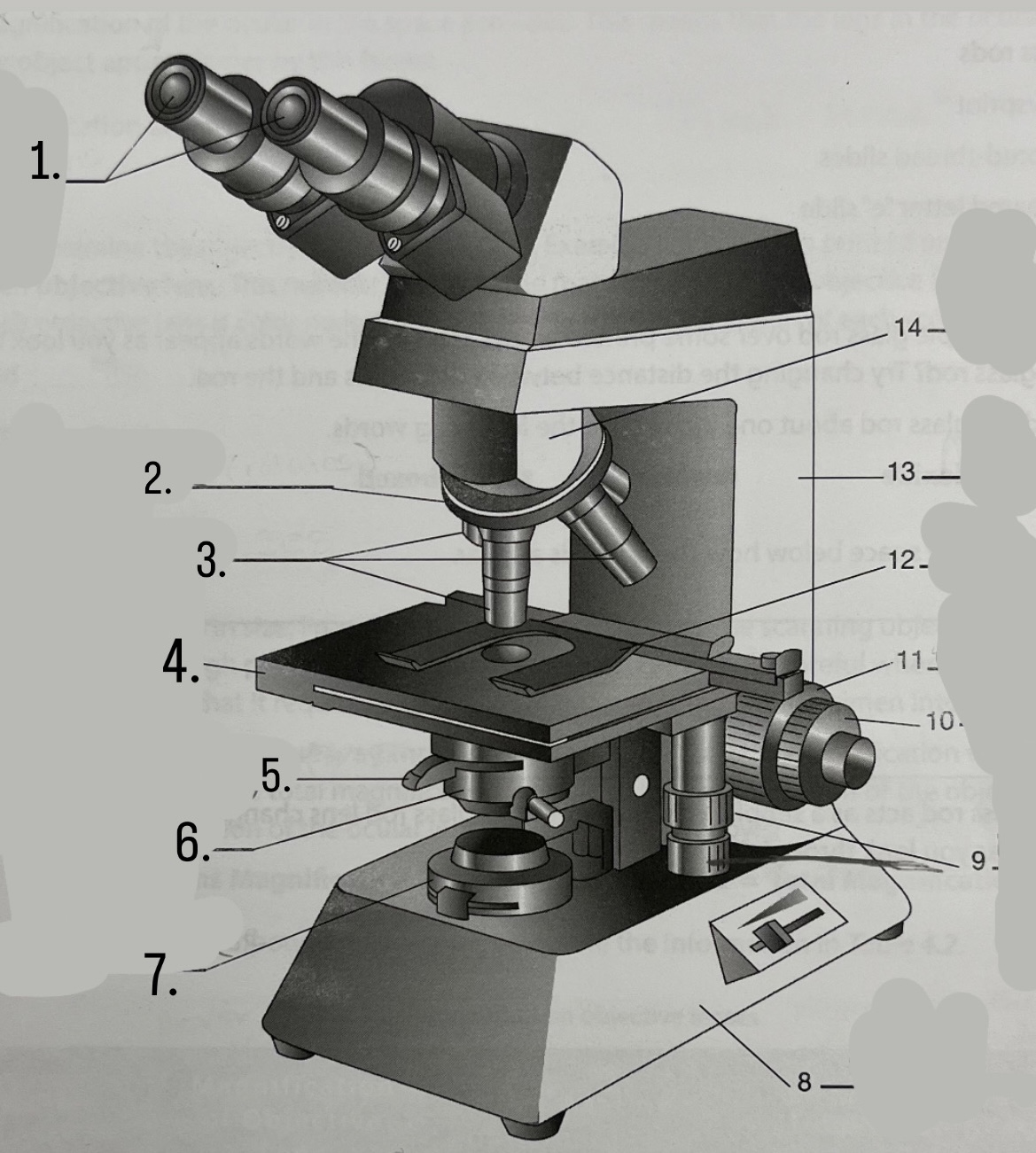
What is #2?
Nosepiece
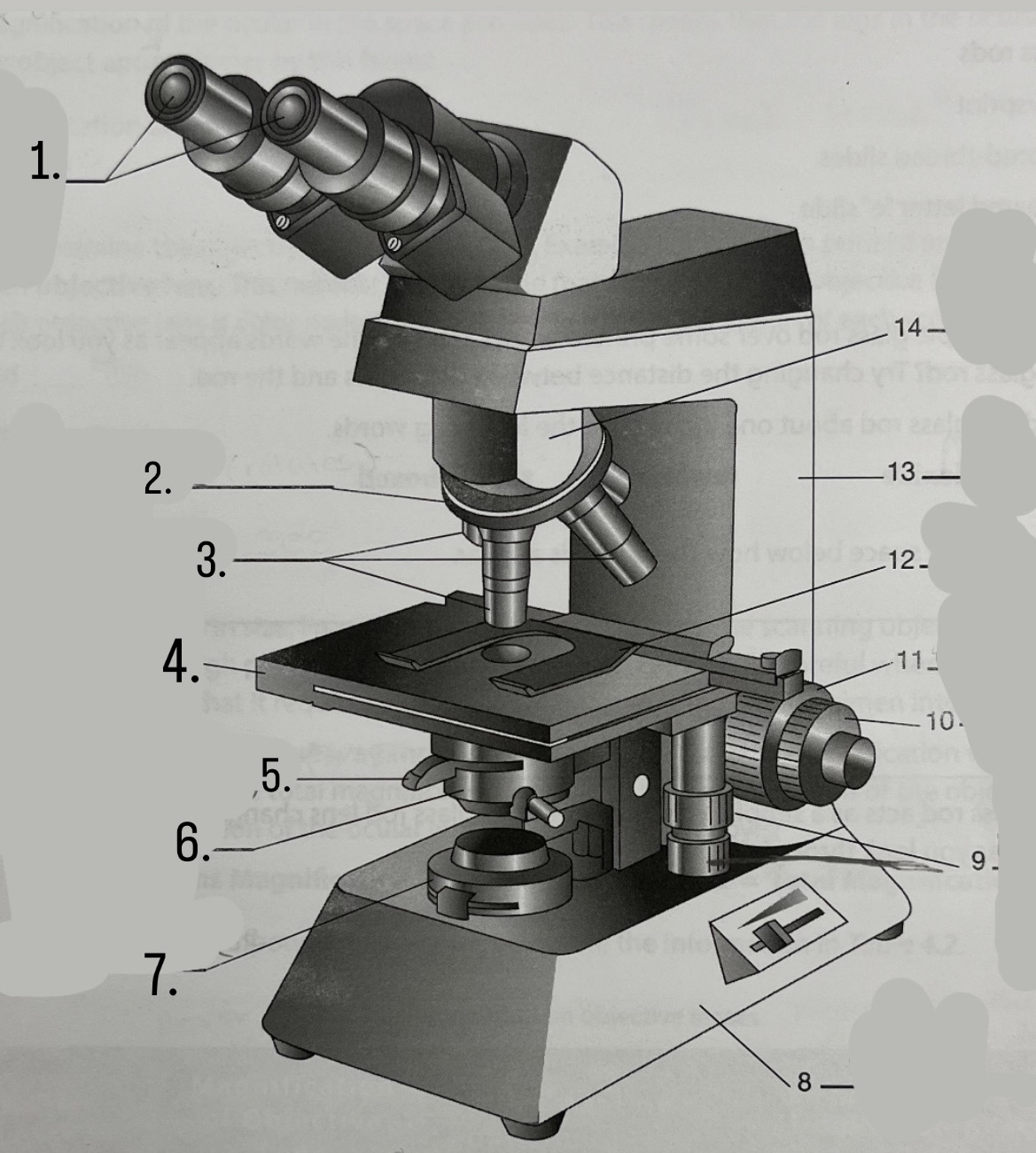
What is #3?
Objective lenses
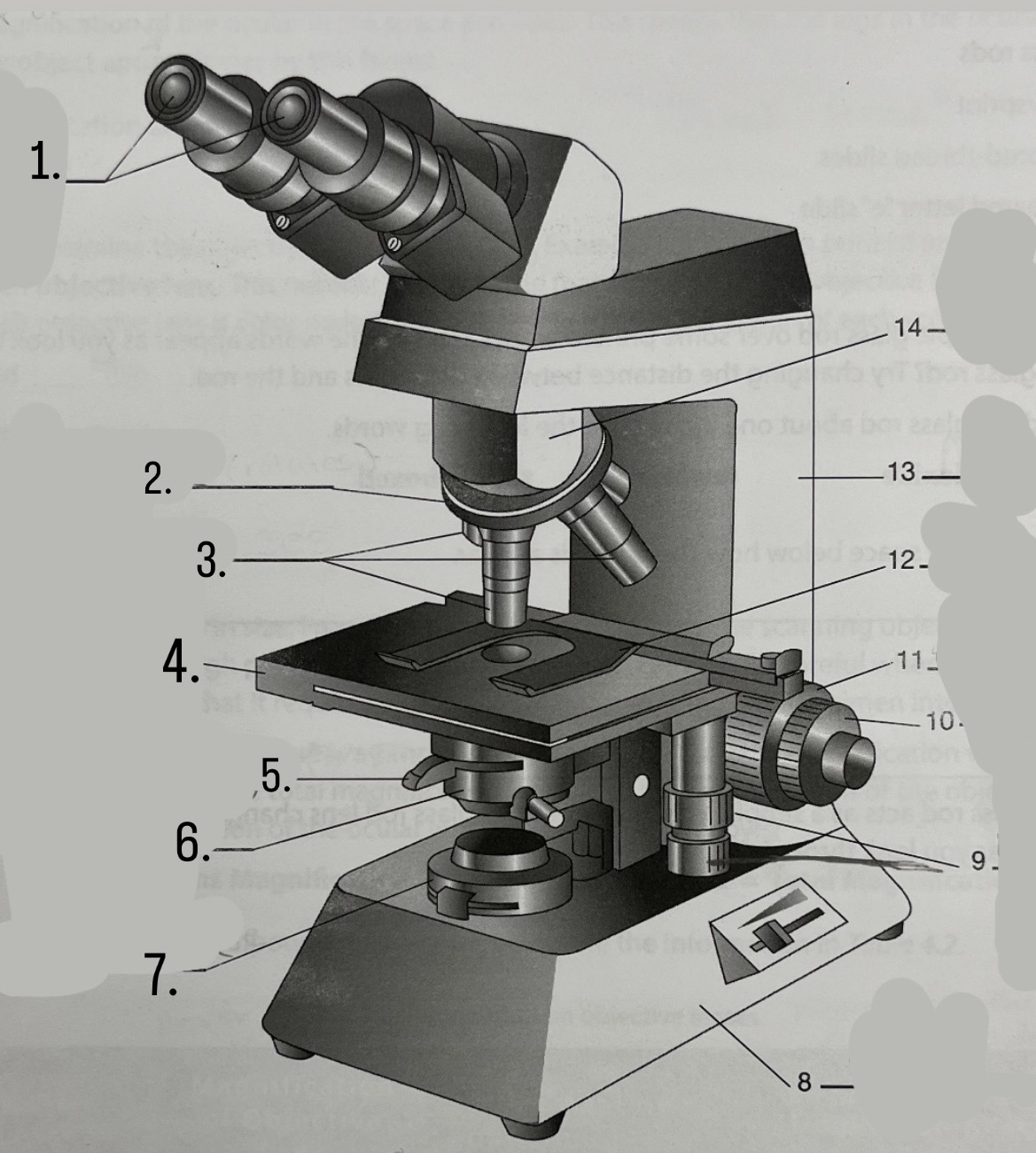
What is #4?
Stage
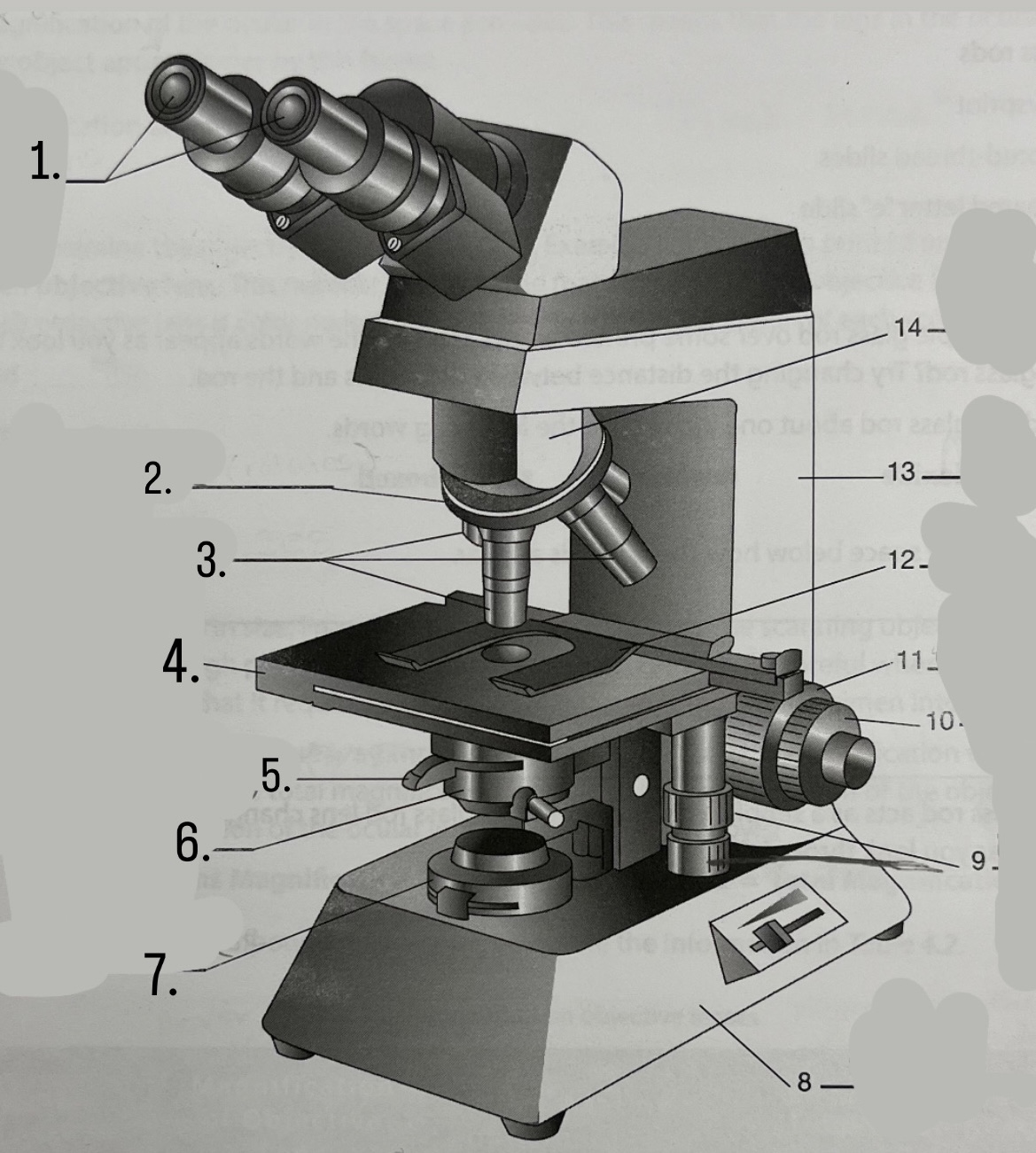
What is #5?
Iris Diaphragm
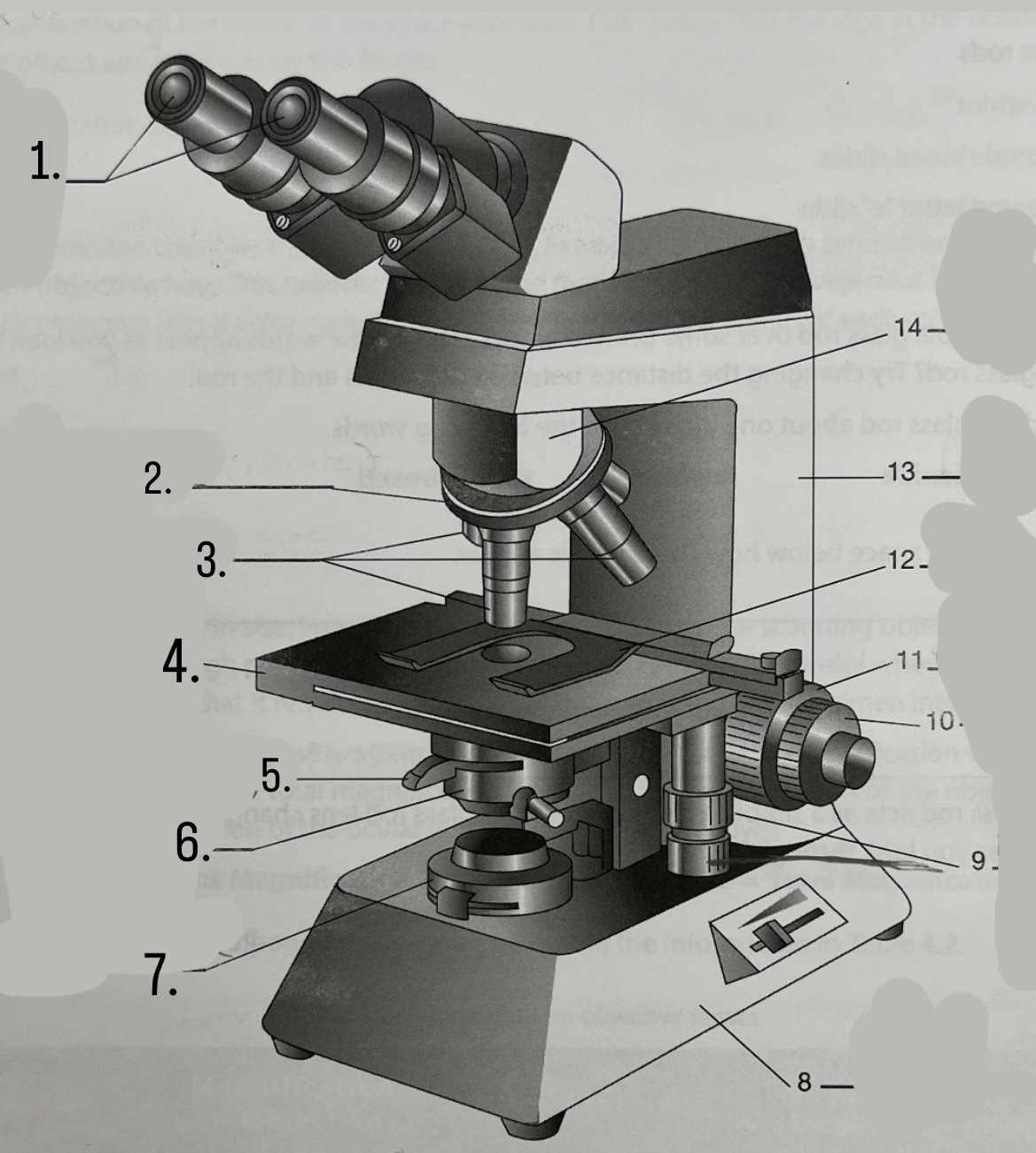
What is #6?
Condeser
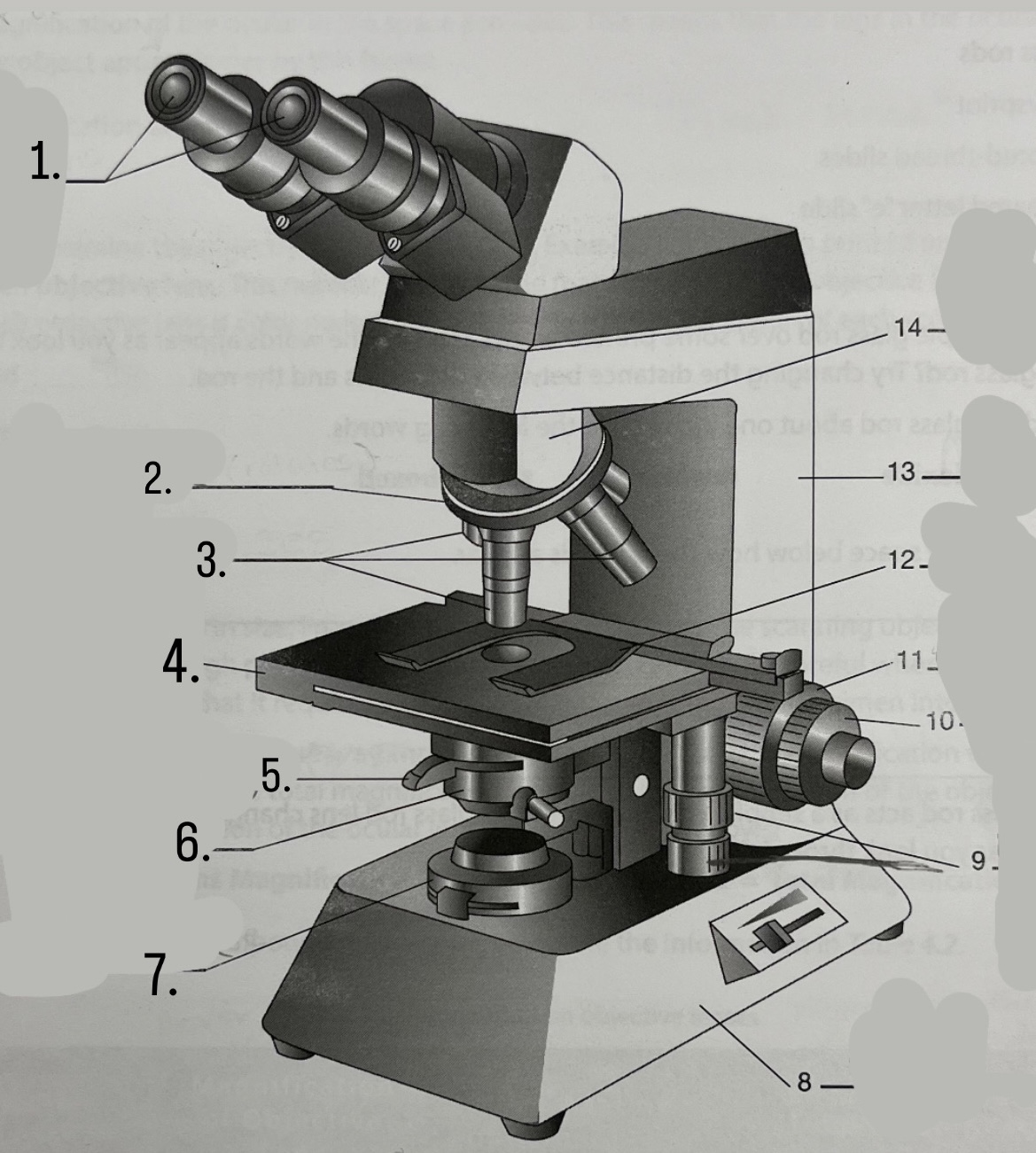
What is #7?
Light source
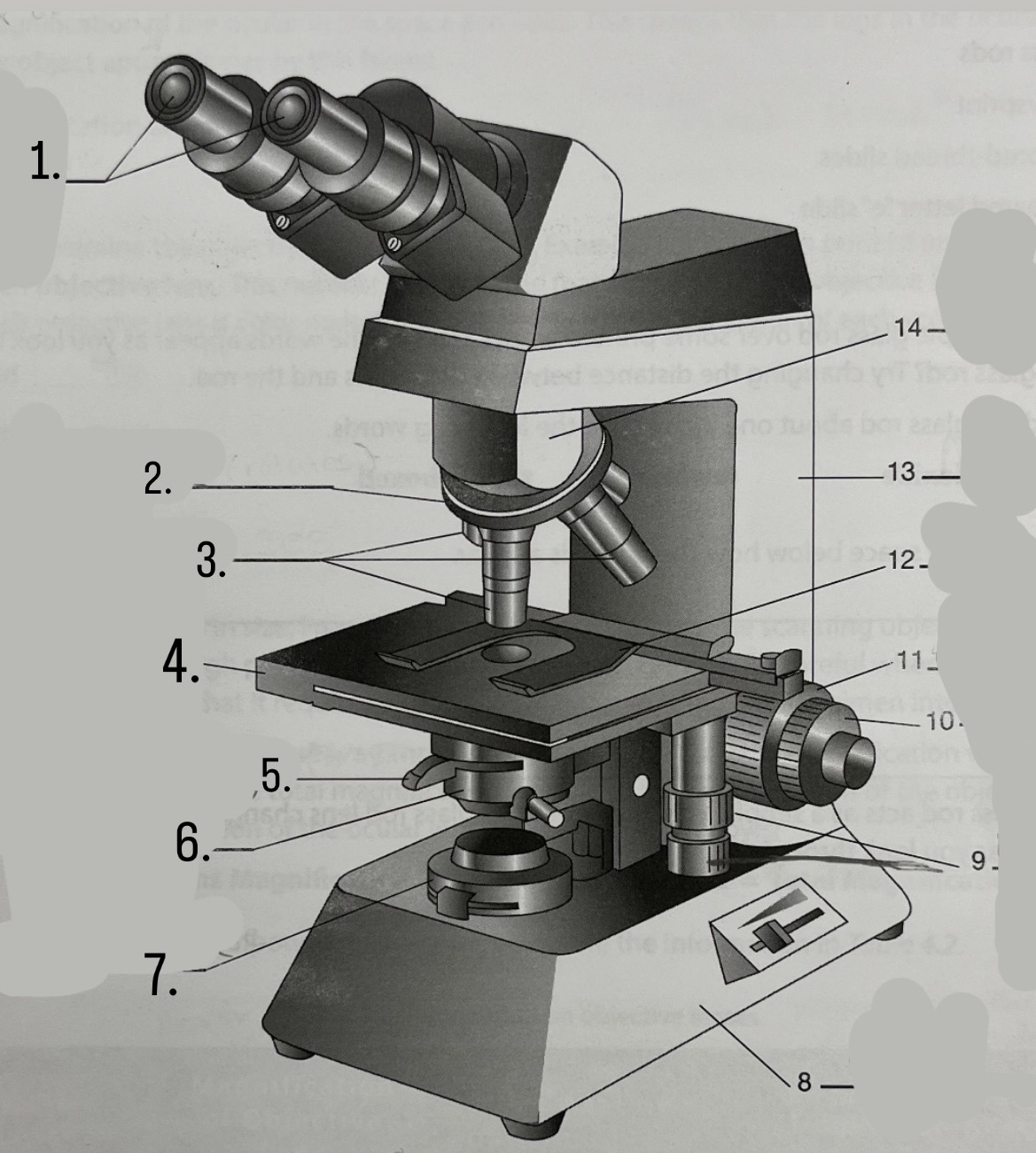
What is #8?
Base
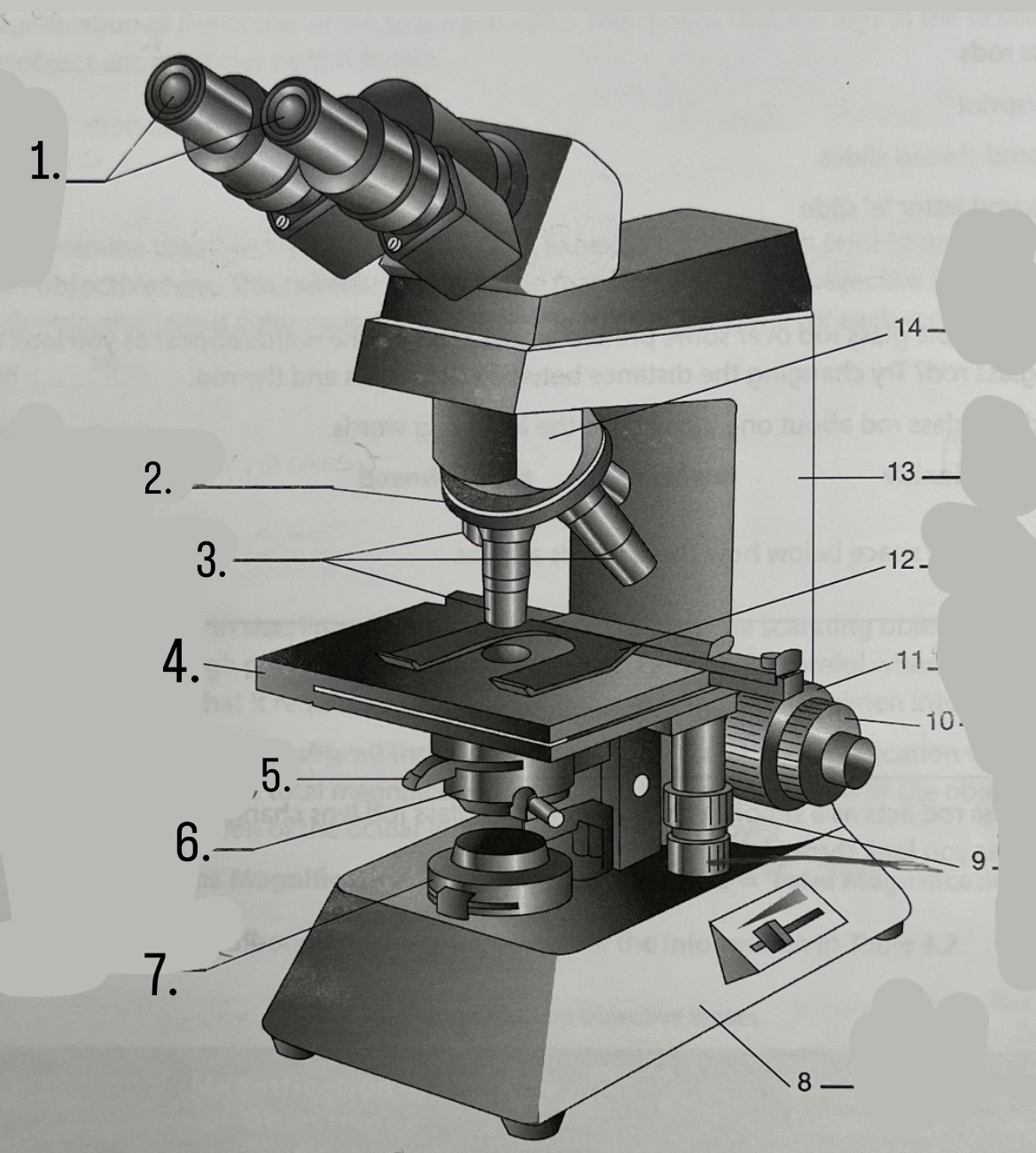
What is #9?
Mechanical Stage Knobs
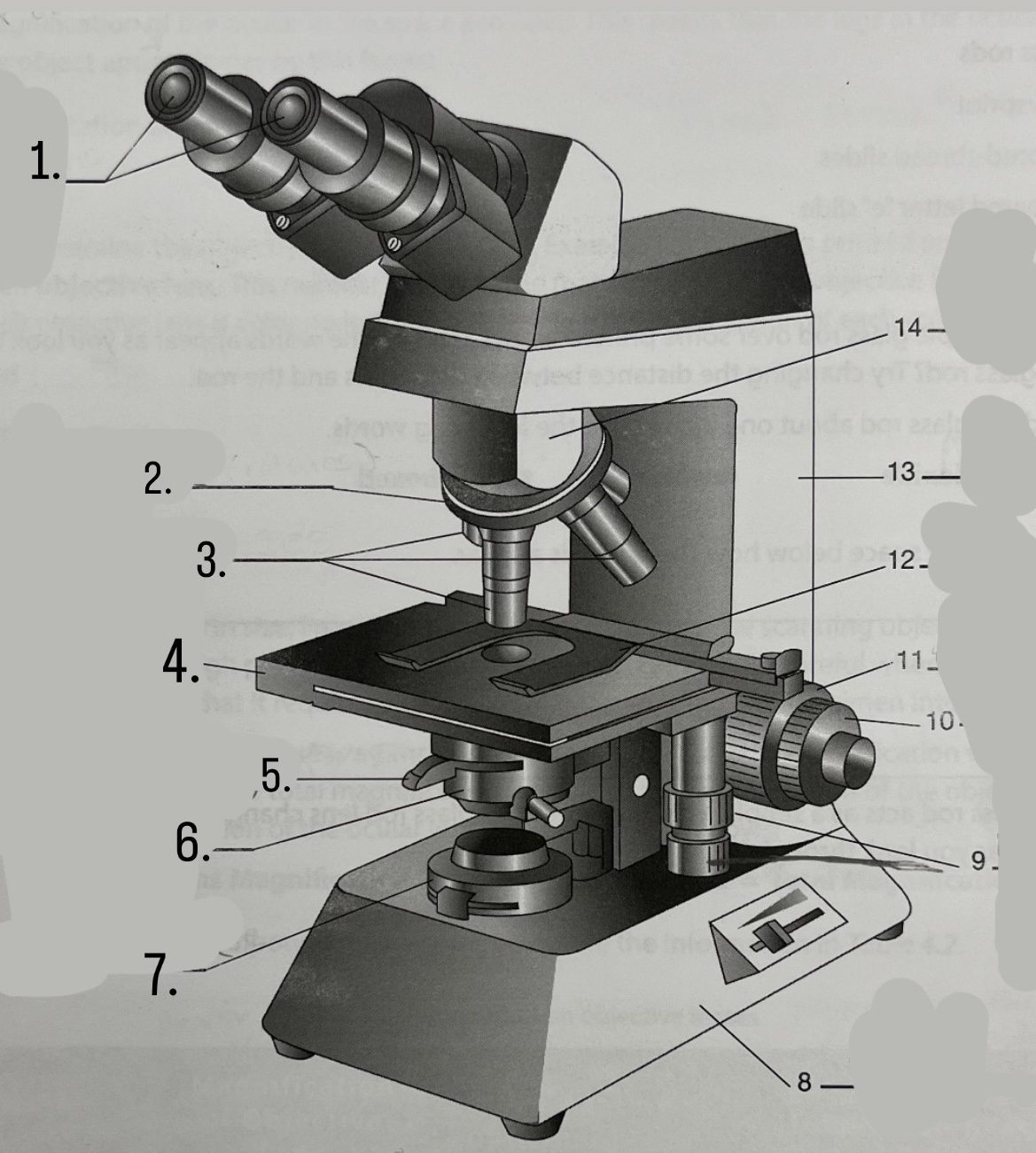
What is #10?
Fine Focus Knob
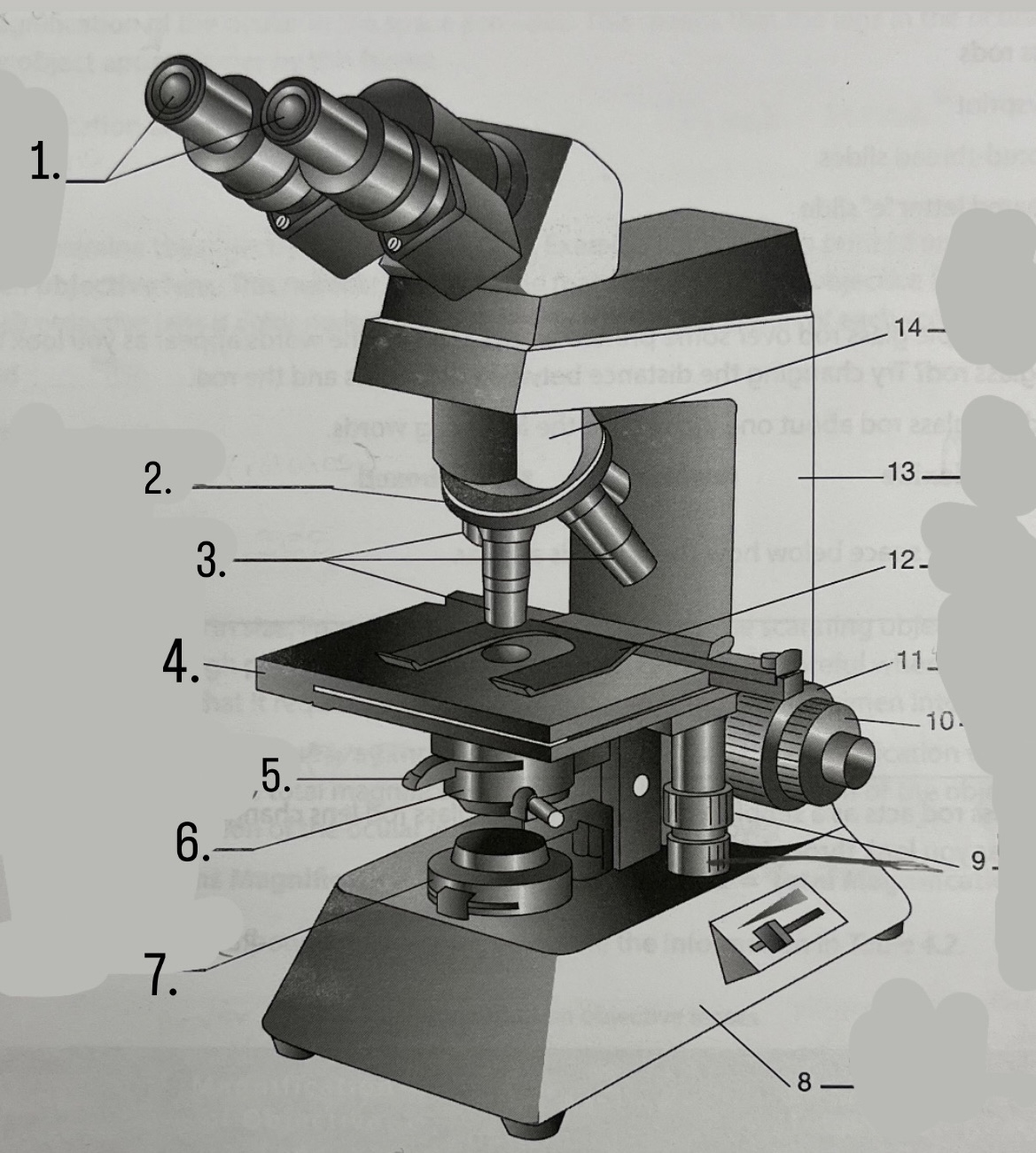
What is #11?
Coarse Focus Knob
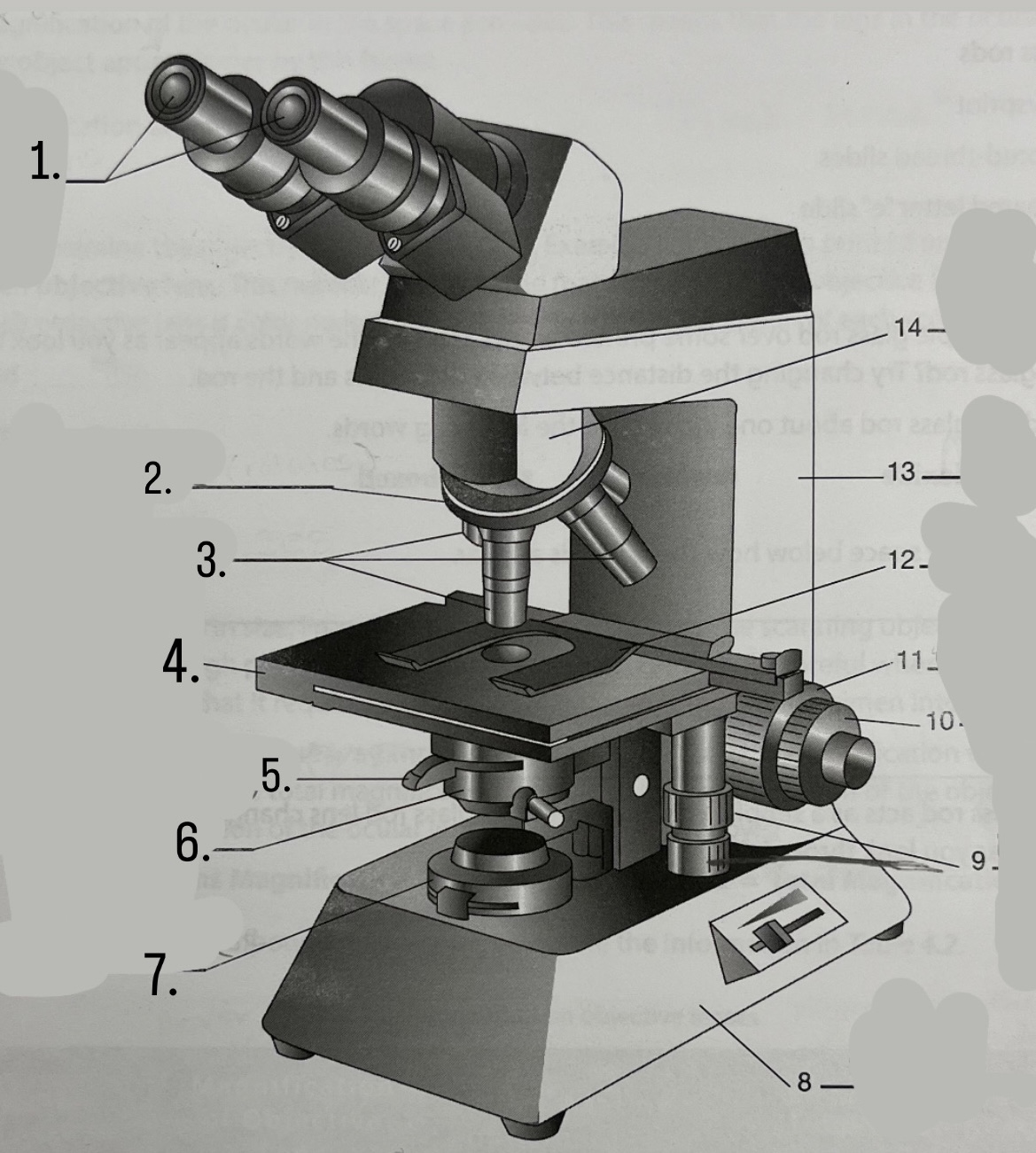
What is #12?
Stage Clips
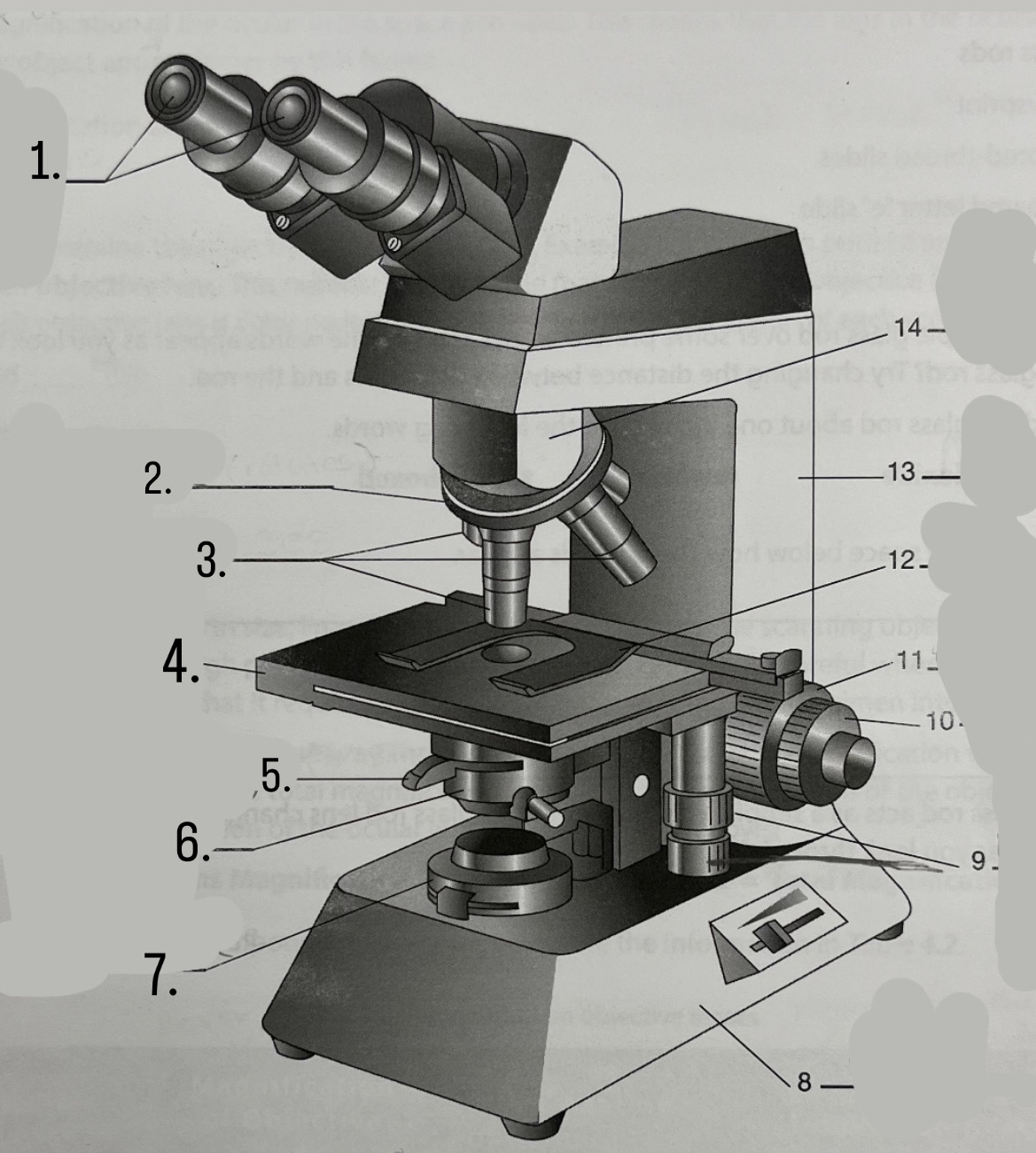
What is #13?
Arm
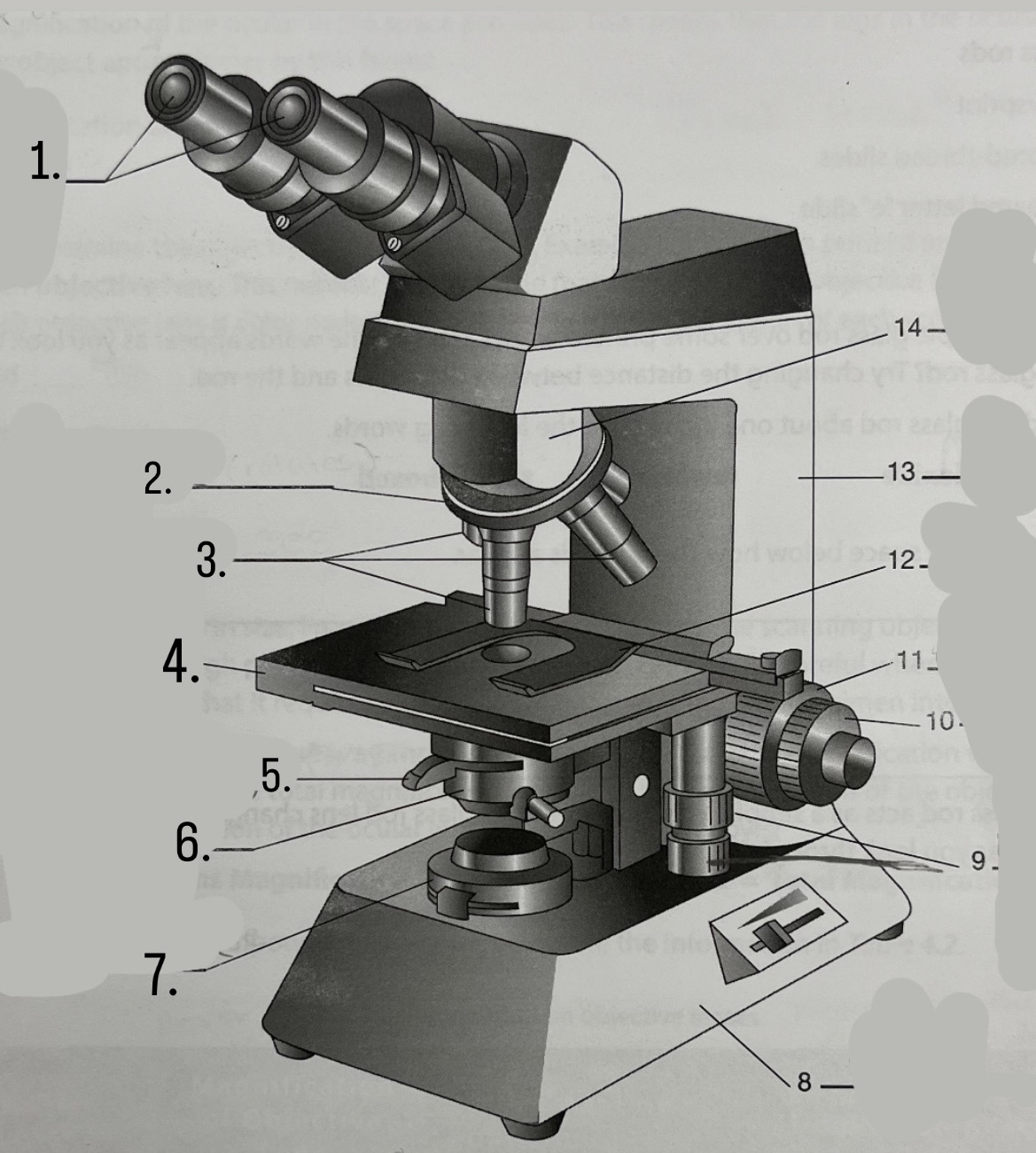
What is #14?
Body Tube
Monomers that construct: Proteins
Amino Acids
Monomers that construct: Carbohydrates
Glycogen
Monomers that construct: Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
What were the four tests that was applied carbon compounds?
Benedict, Lugol, Grease, and Biuret.
What did Lugol’s test determine?
Complex Carbohydrate
What did Benedict’s test determine?
Simple Sugars
What did Grease’s test determine?
Lipids
What did Biuret’s test determine?
Proteins
The 3 rules that govern the rate of diffusion
The greater the concentration difference, the faster the rate of diffusion. 2. The high the temperature the greater the rate of diffusion. 3. The lighter the molecule, the greater the rate of diffusion.
What does transmittance mean in terms of a spectrometer?
How much light is going through.
What does absorbance mean in terms of a spectrometer?
How much light is being blocked.
What are the 6 receptors
Photoreceptors 2. Mechanoreceptors 3. Thermoreceptors 4. Osmoreceptors 5. Chemoreceptors 6. Nociceptors.
Photoreceptors
Responsive to light.
Mechanoreceptors
Sensitive, tendons and muscles. Stretch.
Thermoreceptors
Sensitive to heat and cold.
Osmoreceptors
Detects increase of salt concentration.
Chemoreceptors
Sensitive to specific chemicals. In the taste buds and nose.
Nociceptors
Pain receptors. In the skin.
Two receptors we looked at
Pacinian Corpuscle and Meissner’s Corpuscle
Pacinian Corpuscle
Deep pressure. Located in Subcutaneous tissue
Meissner’s Corpuscle
Light touch. Located in the Dermal Papillae.
Referred pain experiment
Elbow in ice. Pain felt at the fingers because that’s where the pain receptors are located.
Taste buds experiment (4)
Bitter 2. Sour 3. Salty 4. Sweet
Accommodation problems
Emmetropia 2. Myopia 3. Hyperopia 4. Nystagmus
Emmetropia
Normal shaped eye
Myopia
Eye too long (nearsightness)
Hyperopia
Eye shape too short (Farsightness)