Monohybrid Inheritance
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
State Mendel’s law of segregation.
‘The characteristics of an organism are determined by factors which occur in pairs.
Only one member of a pair of factors can be represented in a single gamete'.
What is monohybrid inheritance?
The inheritance of a single gene.
What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring of 2 heterozygous individuals?
3 dominant, 1 recessive.
Describe how you would carry out a monohybrid cross.
Find the phenotypes of the parents and whether they are homo/heterozygous.
Choose suitable letters for the alleles e.g. T for tall, t for short.
Represent the parental genotypes with the appropriate pairs of letters
State the gametes produced by each parent. Circle the gametes and label them clearly.
Use a matrix, called a Punnett square, to show the results of the random crossing of the gametes.
State the phenotype of each different genotype and indicate the numbers of each type.
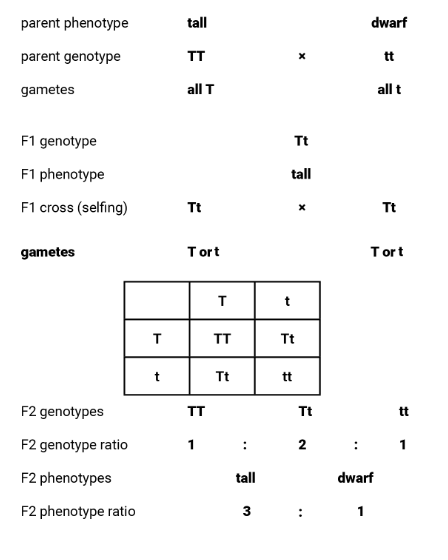
Why is a back cross / test cross useful?
Used to determine whether an individual is homozygous or heterozygous for a dominant characteristic.
How is a back cross carried out?
Cross the individual with the unknown dominant phenotype and a known recessive genotype.
What is co-dominance?
When both alleles in the heterozygote are expressed individually.
Give an example of co-dominance.
Human ABO blood group system- the I gene has 3 alleles, IA, IB and IO.
Homozygous parents who have the genotype IAIA have the A antigen on their red blood cells and are blood group A.
Homozygous parents who have the genotype IBIB have the B antigen on their red blood cells and are blood group B.
Their offspring has the genotype IAIB. Both alleles are expressed; they both have A and B antigens on their red blood cells so are blood group AB.
What is incomplete dominance?
When the phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate between the 2 parental phenotypes.
E.g. red flowered carnations crossed with white flowered carnations have an F1 of pink flowers. Neither the alleles for red petals nor white petals is completely dominant.