2.5 Databases and distributed systems
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
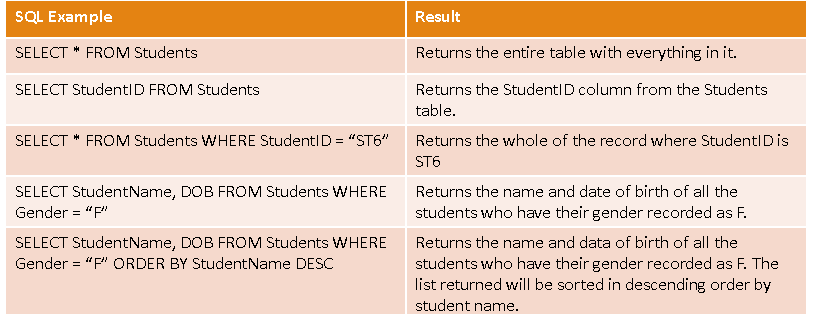
What are databases?
Organised collections of data, which allow for easy storage, management, and retrieval of data
What is it important for databases to have?
Data redudancy - The same piece of information is stored multiple times in different rows (This wastes storage, reduces integrity, and increases chance of inconsistencies as data is changed)
Data consistency - Data is accurate in all stored areas (Data doesnt conflict as it gets updated which would lead to unreliability and poor integrity of data)
Data integrity - Accuracy and reliability of data (no errors/duplicates/missing data) (Unreliabilitys can spread reducing integrity and can lead to communication errors)
What is the structure of a flatfile database
Data is stored in rows and columns
Each row represents one records
Each column is a field
All data is in one table
What is referal integrity?
A validation method for databases that is used when linking tables a record is required to exist in both. (For example primary and foreign keys and these prevent records being added that are not part of the relationship)
It ensures connecting data exists and you cannot delete data that is connected to other data
What are relational databses
They were introduced to solve the problem with flatfile
They have multiple tables linked together with primary keys
Characterisitcs
-Entities (each table in the database)
-Primary key (unique identifier for each record)
-Foreign key (these keys link tables)
-Composite key (Primary key of 2 or more fields)
No two records can have the same primary key
What are benefits of electronic databases?
Easier to add/delete/modify data
Data is easily backed up/copied
Acessibile by multiple people in diff locations at the same time
Less mistakes (spelling and copying error etc)
Storage is smaller physcially
What are types of database relationships?
One-to-One (Like person to student ID as one field represents one other field)
One-to-Many (Like School to student
Many-to-Many (Like student to classes but will create reduancies so will need to add a new table)
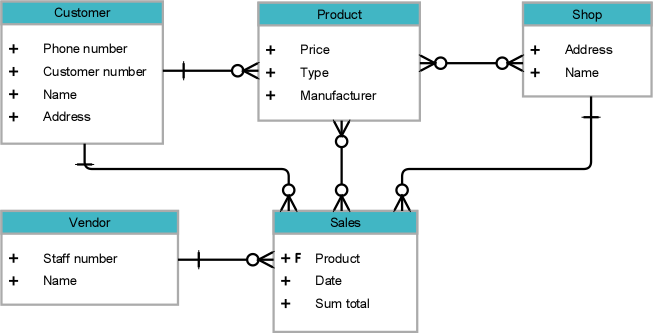
Whats an ERD
Shows how data is organised with entities, atribute and relationships (Like a shop can have many sales)
What is indexing
Used to speed up data retrieval by indexing a column by associating an index with certain characters (Like names starting with T)
Pros and cons of indexing?
+Faster retrieval
+Efficient sorting/filtering
+Improve performance
-Overheads
-More storage
-Needs updating with changes
What is normalistation?
Organising data in a relational database to reduce redudancy and improve data integrity.
There are 3 Levels (1NF, 2NF, 3NF)
What is 1NF and its Rules
1s Normalised Form.
It ensures data in a table is organised clearly and efficiently so each value is atomic (cannot be split)
Rules:
-Each column contains 1 value (no lists)
-Each record is unique (each row has primary key)
-Each field is dependant on the primary key
What is 2NF and its rules
2nd normalised form.
Rules:
-It is already in 1NF
-All-non key attributes depend on the whole primary key (Not on a composite)(For example spliting an order table with each product having a product ID and its details so you dont have to repeat them)
What is 3NF Rules
-Must be in 2NF
-Every non-key attribute depends on the primary key and not a non-key attribute
This removes repeated data by creating new tables
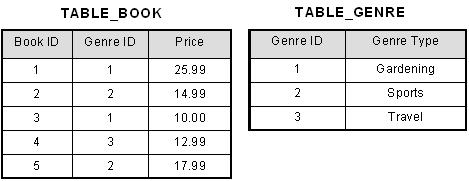
What is a data dictionary?
A document or table that describes the structure of a database (contains information about how data should be)
Its a reference that says:
-What data exists
-Where it exists
-How its used
What will a data dictionary store for each field?
-Field name
-Data type
-Size
-Constraints (Like if its a key and if it should contain letter ‘s’)
Why are data dictionaries important?
It outlines rules to allow for accuracy and consistency of data.
How is validation used in a database?
It is designed into a data dictionary when creating the table. Restrctions can be set during declaration with constraints
How would i create a new column in a table?
You would:
-Set the data type (like an int would reject a string)
-Reject null values (NOT NULL or instead just keep them)
-Set length checks (truncate data)
How would I format check in a database?
The database does not do that so it needs to be separately implemented
What is data redudancy?
When there are duplicate data in different tables (this compromises consistency as data may not be updated everywhere and also wastes storage)
What is data consistency?
The accuracy of data (all occurances of the same field data are the same value)
What are the benefits of a relational database?
Avoids redundancy
Easily edited
Supports complex queries
Consistnet records
Data is easily added and deleted
What is SQL
Structures Query Language. Is a general purpose language used to manipulate data in databases and tables
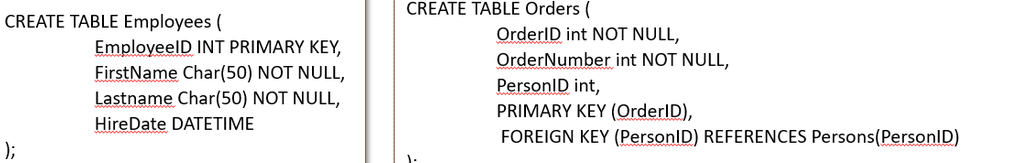
Create table query?
make sure to define NOT NULL, primary keys, foreign keys ,etc
With structure:
<name><data type (char(50) or int)><Primary key/Foreign key><NOT NULL (optional)>
What is numeric data type for create table
numeric(x,y)
x is total digits
y is digits to right of decimal (use 2 for money)
Insert Into [Table] Values[]

select query
where… IN
e.g. WHERE name IN (‘Pete’,’steve’)
instead of where name == pete
AND
where name = ‘peter’ and age = 12
OR
Similar to and but can allow one or both conditions
ORDER BY
ASC
DESC
BETWEEN
BETWEEN ID = 1 AND ID = 2
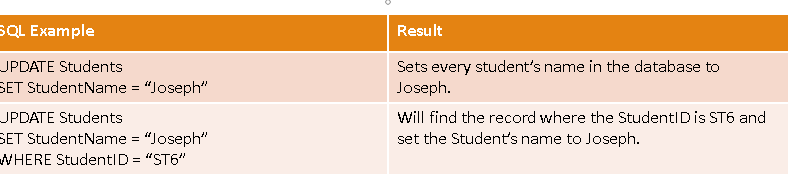
UPDATE query
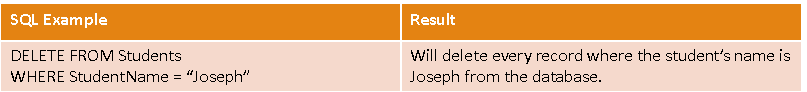
DELETE query
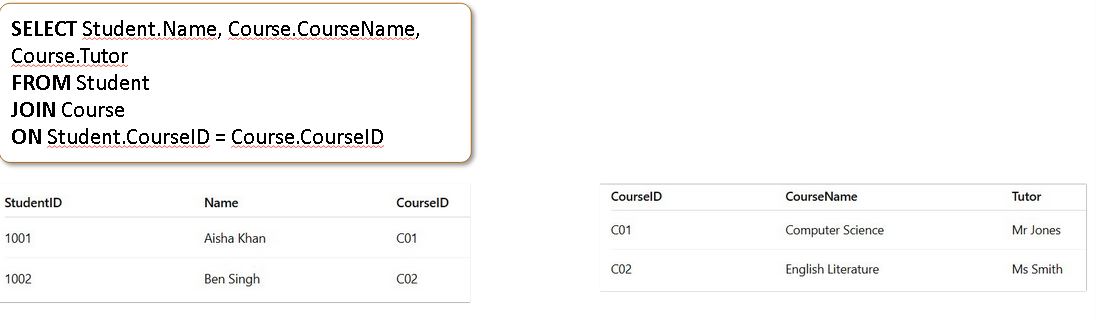
Join query
can use where instead of join on
GROUP BY [Field];
You would use this to group data that is associated (such as associating all the cash payments associated with one person and grouping it by cash payments to add all up)
Make sure to end with semi colon
What is data?
Facts and figures that represent data (comes in various forms such as images, video, text, audio, video)
What is big data?
Extremely large data sets that can be used to analyse computationally to reveal patterns/trends in behaviour (like consumer purchasing patterns)
What are the characterisitcs of big data?
Volume - large amounts of data too big to fit on a single server
Velocity - data has to be accessed an processed quickly (a query to repsonse needs to be about 1ms)
Variety - in many different formats (like strucutred CSVs, plain text, video, images etc)
Veracity - data is quality, accurate and trustworthy (reliable to use for analysis)
What is a key issue with big data analysis?
The lack of structure (millions of sources) mean that it is hard to extract important data
Where is big data used?
Hospitals - analyse to predict illnesses, treatments, A&E demand
Education - identify at risk students, improve curriculum
Weather predictions - better
What is data warehousing? Issue?
A central repository where data is stored from multiple sources and in multiple formats.
It is time consuming and expensive to build, design, and maintain
Data may become obselete or inaccurate
What do data warehouses do to improve efficiency?
Optimise data for querying and reporting for predictive analysis
What is datamining?
Looking for patterns and information within large data sets (identify relationships between different sets of data). This requires large amounts of storage, processing power, and complex algorithms so can be expensive.
What are the main purposes of data mining?
To categorise data and give it context
To model data in a way that can be used for predictions
What is predictive analysis?
The process of using data held in a data warehouse ahnd apply statistical methods and algorithms to predict the likelihood of an event happening
How is predictive analysis different to data mining?
Data mining looks at relationships between data (correlation, etc) and identifies patterns. Whereas pred analysis makes predictions with that data
What is a distributed database
Data is stored across multiple different sites/locations but to the user it appears as one
What are benefits of distributed systems?
Reduce data each server has
Improve performance (faster local access)
Queries handled locally (less data sent on network so faster)
Scalable (paritions can be added)
Added security as sensitive data can be stored in one location
Drawbacks of distributed systems
Can be more expensive with more servers
If a server fails then data may be lost (more servers to fail)
Can be complex to handle transactions
What is a data transaction?
A single database operation such as insertion/deletion. It must be completed as one action in a distributed system as errors can occur (like transaction in payment system)
What is a two phase algorithm?
Used in distributed systems to ensure transactions are properly handled. (Agreements are met before a commitment)
Phase 1: Prepare
Phase 2: Commit
What is the steps of Phase 1?
One site acts as a coordiantor
The coordiantor sends a message to all participating sites to find out if a transaction can be done
Each participant
Tries to peform the operation (like inserting data)
Votes to commit if there are no issues)
Votes abort if an issues occurs
The coordiantor collects all votes
What is Phase 2 steps?
If all participants vote to commit the coordiantor will send a message to every server. Then each participant commits to the transaction
If any particiapnt votes abort the coordiator sends a message to every server to abort. Then all participants undo the action
What is distributed processing?
Work (processing) of data is shared accross several application servers instead of one single machine doing it all. (A database server will store required data and an application server will communicate with the database server to process data when required)
How can application servers be used?
Multiple applications servers can use the same database server to improve speeds (like one server handling an transaction and one server updating stock for the same database)
Benefits of separating data from processing?
Application servers have smaller storage requirements
Server redundancy + disaster recovery - if the database goes down it can be replaced by a backup server without changes to the application server
Additional security - application servers dont contain data
What are the 3 database level?
Application
Conceptual
Physcial (Schema)
What is the application level?
It defines how data is presented to individual users. Different users can have different views of data depending on access rights and needs.
e.g. Student VS Teacher a grade spreadsheet
What is the conceptutal level?
It defines the structure and organisation of data for the whole database. It describes what data exists and how it is related.
-Focus is on design oof database (relationships, tables, fields)
-ERD, Data dicitionaries are used to design this level
What is the physical level?
Deals with storage of data (How and Where data is stored on disk or memory (sever)).
This isnt concerned with meaning just efficiency and performance
What is data independance?Example?
You can change the way data is stored or organised in a database (modifying schema/physical) without affecting how it is used (if we modify collumns location user view shouldnt change and application server programs dont need to be rewritten if structure changes)
Changing one view in a 3 view system (attendence, grades, payslips) should not affect the other views so users wouldnt notice chages
When are conceptual level changes required?
modifications of the conceptual (logical) level are necessary whenever the conceptual structure of the databse is changed
What is a database view?
A virtual table that looks and behaves like a table but doesnt store the data. It just shows data from a query