Chapter 2: Atomic Structure/Bonding
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Elements in Structure
Atomic structure (s, p, d)
Affects bonding and certain properties (Elastic/Young’s modulus E, coefficient of thermal expansion CTE, and melting temperature Tm)
Crystal Structure (FCC, BCC, HCP, BCT)
affecting mechanical and physical properties (elastic and plastic properties)
Microstructure (grain size, phases, defects)
affects mechanical and physical properties (hardness, strength, ductility, electrical/thermal conductivity)
Macrostructure (pores, cracks - seen visually)
affects mechanical and physical properties (fatigue strength, fracture toughness, strength, ductility)
Electrons and Configuration
Every electron in an atom is characterized by 4 quantum numbers:
Principal quantum number n = 1,2,3,4,5 (K,L,M,N,O) - shell designation
number of electrons per shell: 2,8,18,32
Secondary quantum number l = s,p,d,f - subshell
number of electrons per subshell: 2,6,10,14
Tertiary quantum number ml (number of energy states when magnetic field is applied, 1,3,5,7)
Quaternary quantum number ms (spin moment +1/2, -1/2)
Pauli Exclusion Principle - The Aufbau Principle
s,p,d,f subshells may each accommodate, respectively, a total of 2,6,10,14 electrons
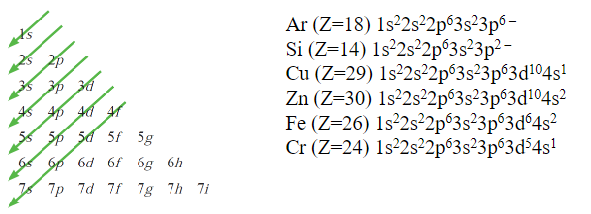
Periodic Table
Transition metals: partially filled d electron states and one or two electrons in the next higher energy shell
Electropositive elements: readily give up electrons to become + ions
Electronegative elements: readily acquire electrons to become - ions
Primary Bonds
All atoms have the tendency to form stable or inert gas electron configurations
This can be achieved by: gaining, losing, or sharing electrons
Primary bonding types:
Ionic bonding
Covalent bonding
Metallic bonding
Ionic Bonding
Metal/non-metal
Atoms of a metallic (donor) element easily give up their valence electrons to the nonmetallic (recipient) atoms
In the process, all the atoms acquire stable or inert gas configurations (ie completely filled orbital shells)
Covalent Bonding
nonmetals, metal + nonmetal, metal
sharing
directional bonding
Metallic bonding
Primary bonding for metals and metal alloys
Arises from a sea of donated valence electrons (1, 2, or 3 from each atom)
The electrons are shared among all
These free electrons act as a “glue” to hold the ion cores together
Mixed Bonding
Ionic-covalent mixed bonding
% iconic character = [1-e-(XA-XB)²/4](100%)
XA and XB are electro-negativities of elements A and B
For two elements with different electro-negativities, there will be some % of ionic bond between them
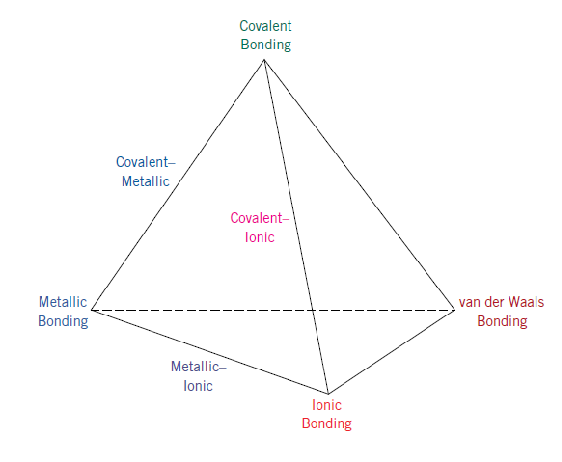
Bonding Tetrahedron
Sometimes it is illustrative to represent the four bonding types - ionic, covalent, metallic, and van der Waals - on what is called a bonding tetrahedron.
Secondary Bonding
aka van der Waals bonding
arises from interaction between dipoles
Fluctuating dipoles - asymmetric electron clouds
Permanent dipoles - molecule/geometry induced
Hydrogen Bond
HF, H2O, NH3
F, O, and N strongly pull single electron from H leaving a bare proton which bonds strongly
Strongest secondary bonding type
Permanent dipoles - molecule induced (due to asymmetrical arrangement of positive and negative regions)
Ionic Bonding Summary
Bond energy
Large
Found in
Ceramics
Covalent Bonding Summary
Bond energy:
Variable
Large - diamond
Small - bismuth
Tm = 270*C
Found in:
Semiconductors
Ceramics
w/in polymer chains
Metallic Bonding Summary
Bond energy:
Variable
Large - Tungsten
Small - Mercury
Found in:
Metals
Secondary Bonding Summary
Bond energy:
Smallest
Found in:
Inter-chain (polymer)
Inter-molecular
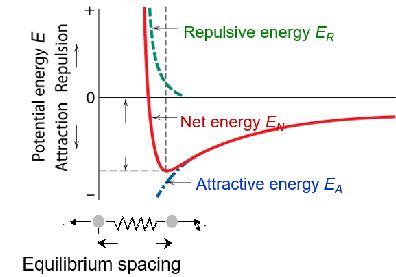
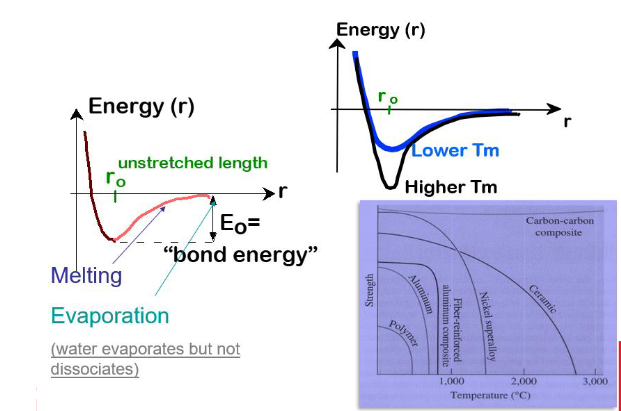
Bonding Energy, E0
Energy balance of attractive (-) and repulsive (+) terms
(at equilibrium spacing)
EN = EA + ER = -A/r + B/rn
EN = Net energy
EA = attractive energy
ER = repulsive energy
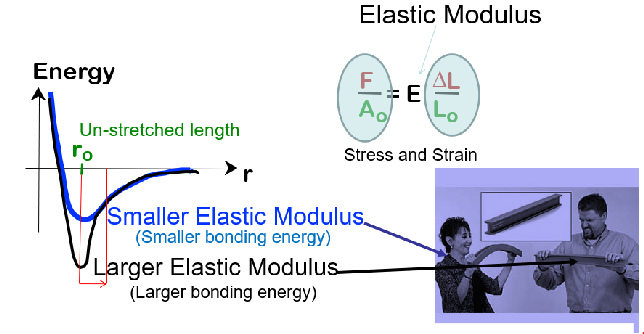
Importance:
Stiffness
melting point
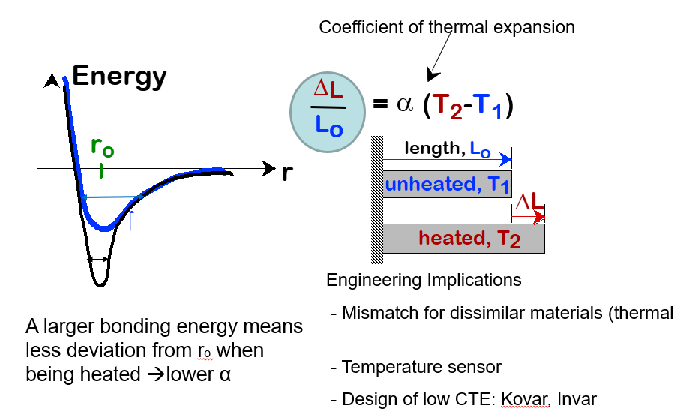
coefficient of thermal expansion of pure substances
Bonding Energy/Elastic Modulus
Bonding Energy/Melting Temp
Bonding Energy/Elastic CTE α
Ceramic Material Class Summary
Bonding type
Ionic
Covalent
Properties
Large bond energy
large Tm
Large E
Small α
Metals Material Class Summary
Bonding type
Metallic
Properties
Variable bond energy
Moderate Tm
Moderate E
Moderate α
Polymers Material Class Summary
Bonding type
Co
Properties
Directional properties
Secondary bonding dominates
Small Tm
Small E
Large α