2.2 Energy and biomass in ecosystems
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Organic (substance)
Carbon-containing molecules associated with living organisms, for example, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, and hydrocarbon fuels.
Food webs
Two or more food chains linked together and can show that a single species can occupy multiple trophic levels.
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
The total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time fixed by photosynthesis in green plants.
Gross secondary productivity (GSP)
The total gain by consumers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time through absorption.
Net primary productivity (NPP)
The gain by producers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time remaining after allowing for respiratory losses (R). This is potentially available to consumers in an ecosystem.
Net secondary productivity (NSP)
The gain by consumers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time remaining after allowing for respiratory losses (R).
Dry mass
is approximately equal to mass of organic matter (biomass) since water represents the majority of inorganic matter in most organisms
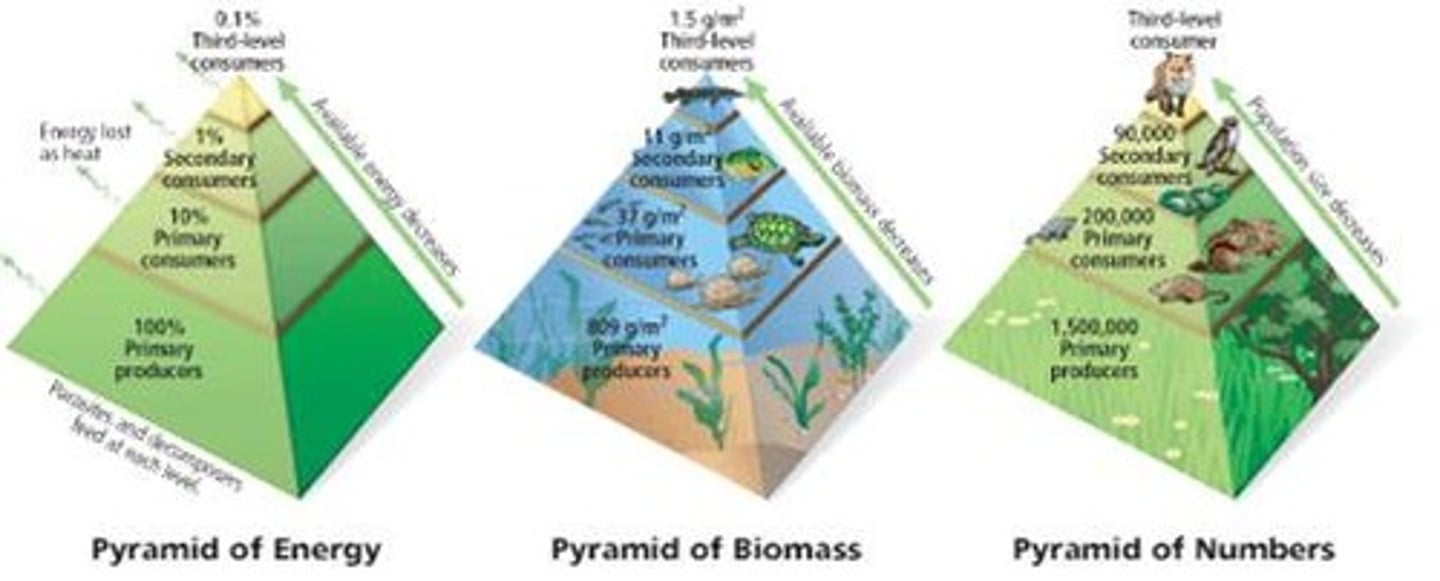
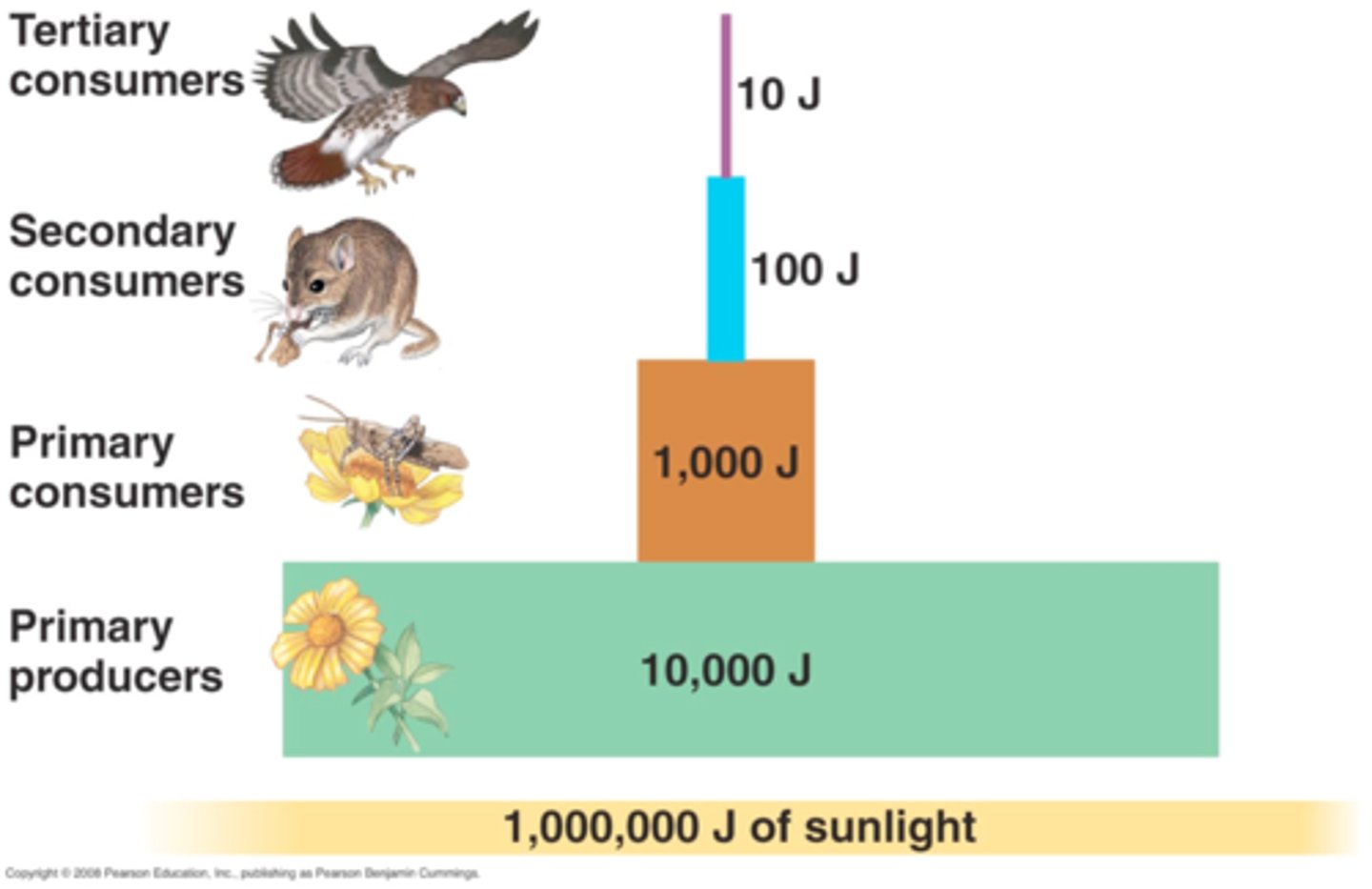
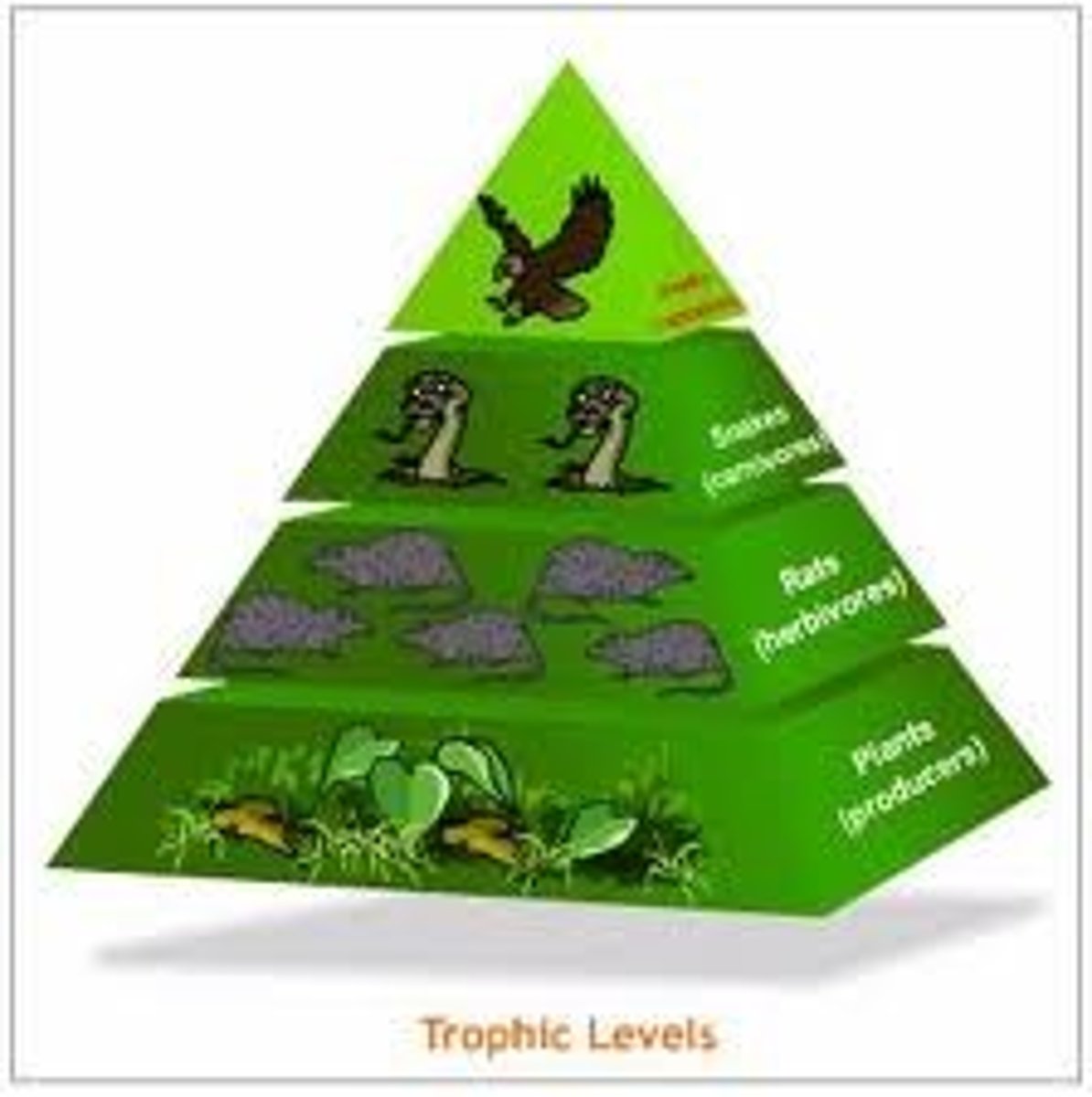
Ecological pyramids
Quantitative models showing changes between organisms at different trophic levels in a food chain. They include pyramids of numbers, biomass, and productivity.
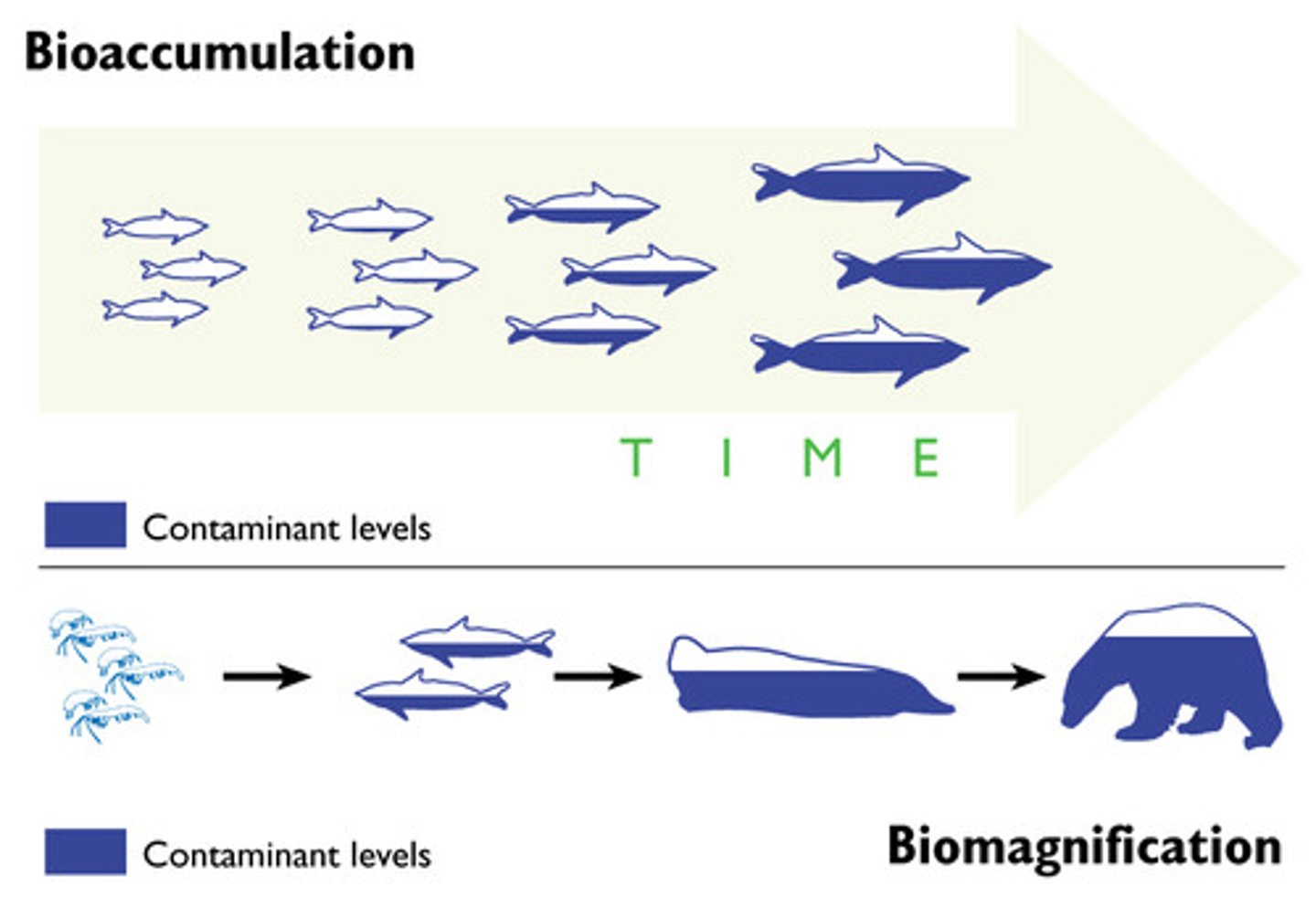
Bioaccumulation
The build-up of persistent or non-biodegradable pollutants within an organism or trophic level because they cannot be broken down.
Biodegradable
When something is capable of being broken down by natural biological processes; for example, the activities of decomposer organisms.

Biomagnification
The increase in concentration of persistent or non-biodegradable pollutants along a food chain due to the decrease of biomass and energy.
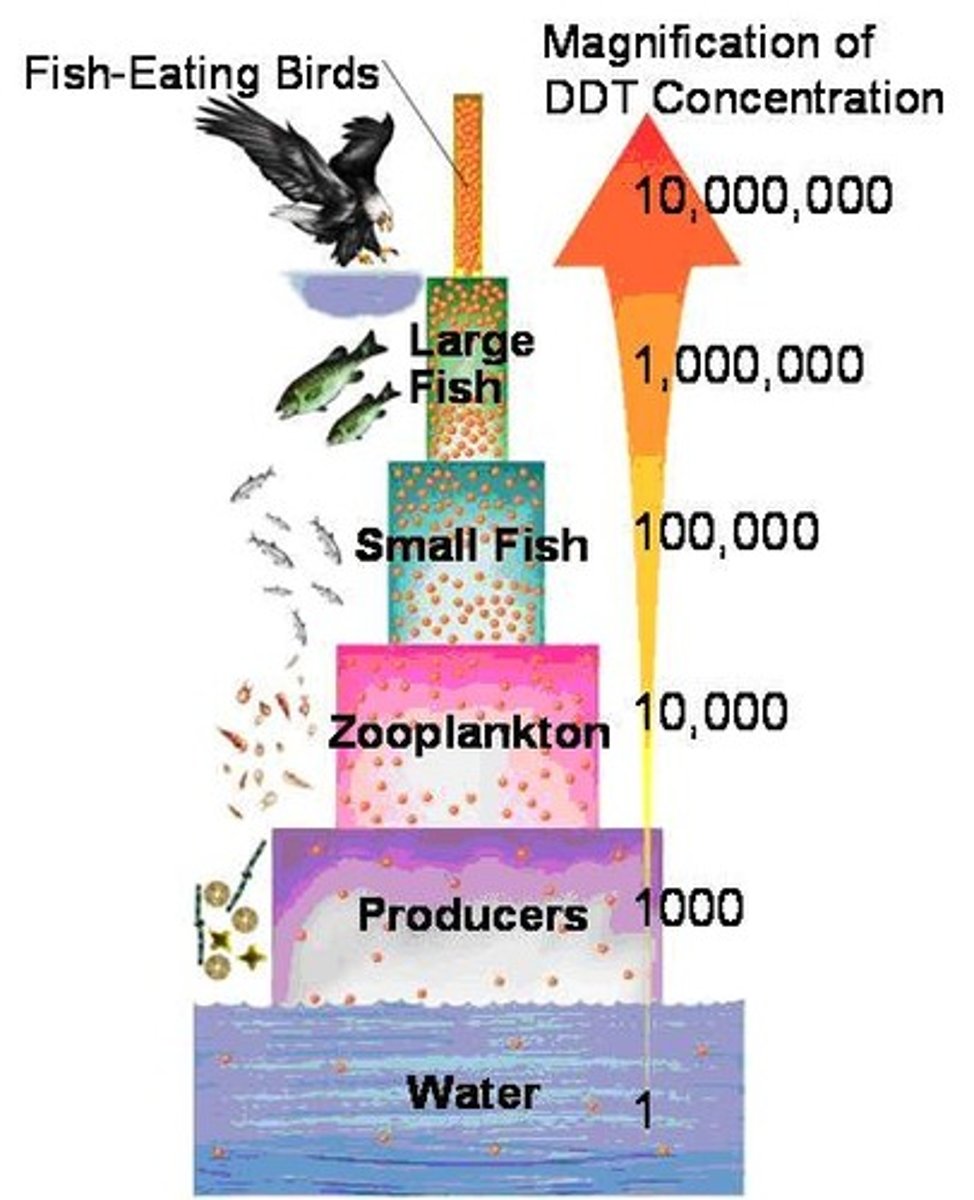
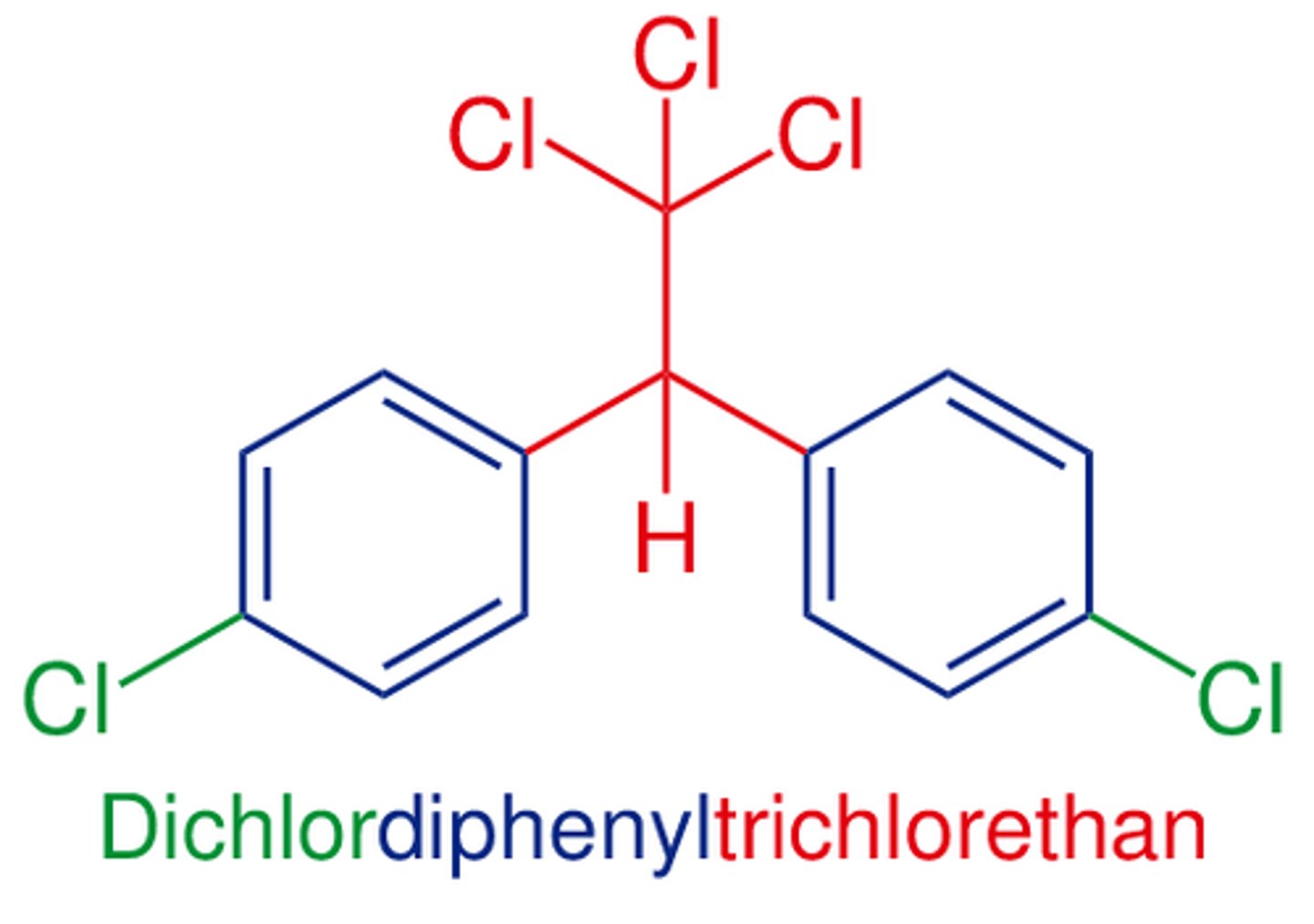
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is an insecticide that was used in agriculture. There is a worldwide ban for agricultural use, however some countries still use it to control the spread of malaria.
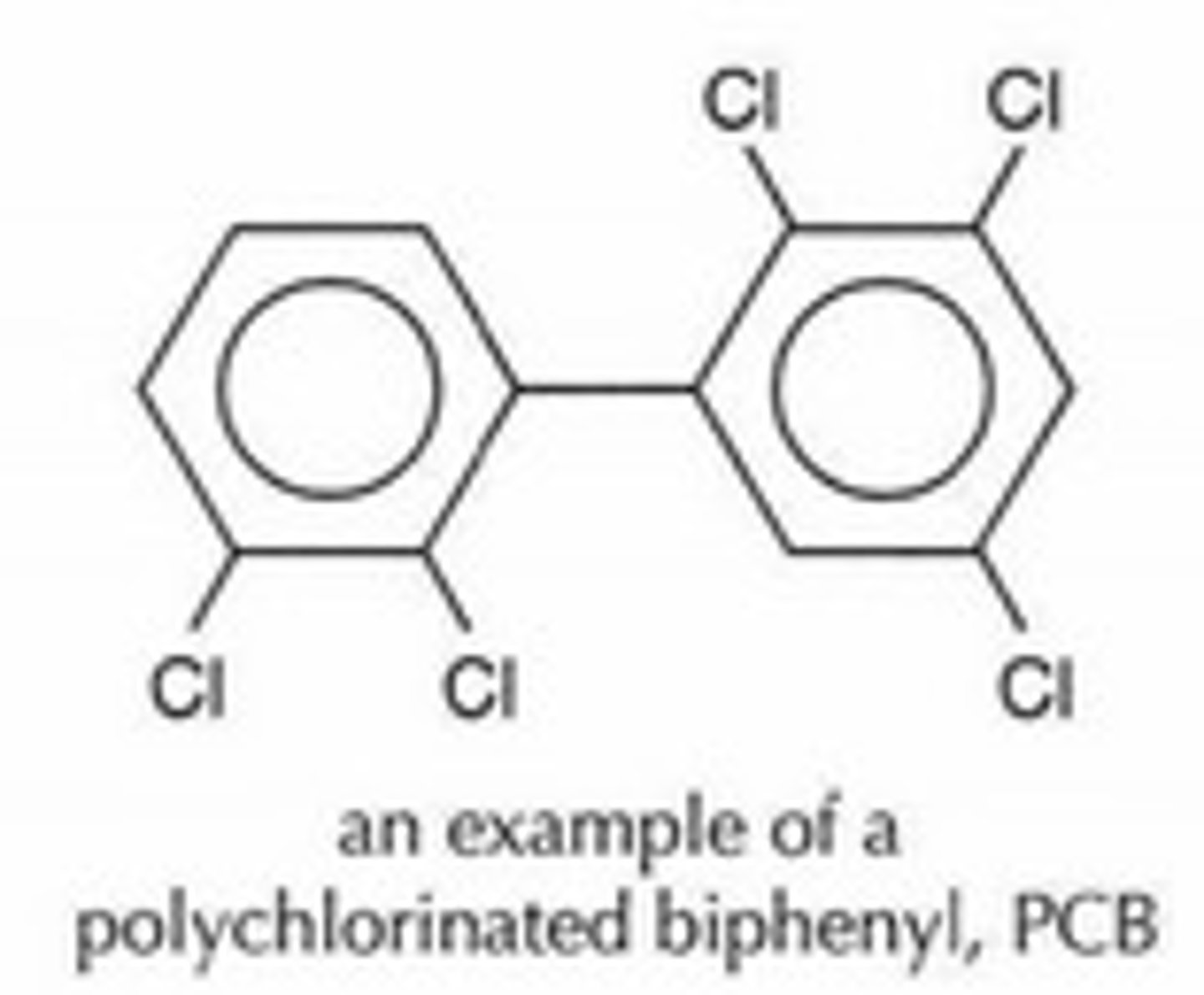
Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)
Chemicals that affect innate immune functions in humans.
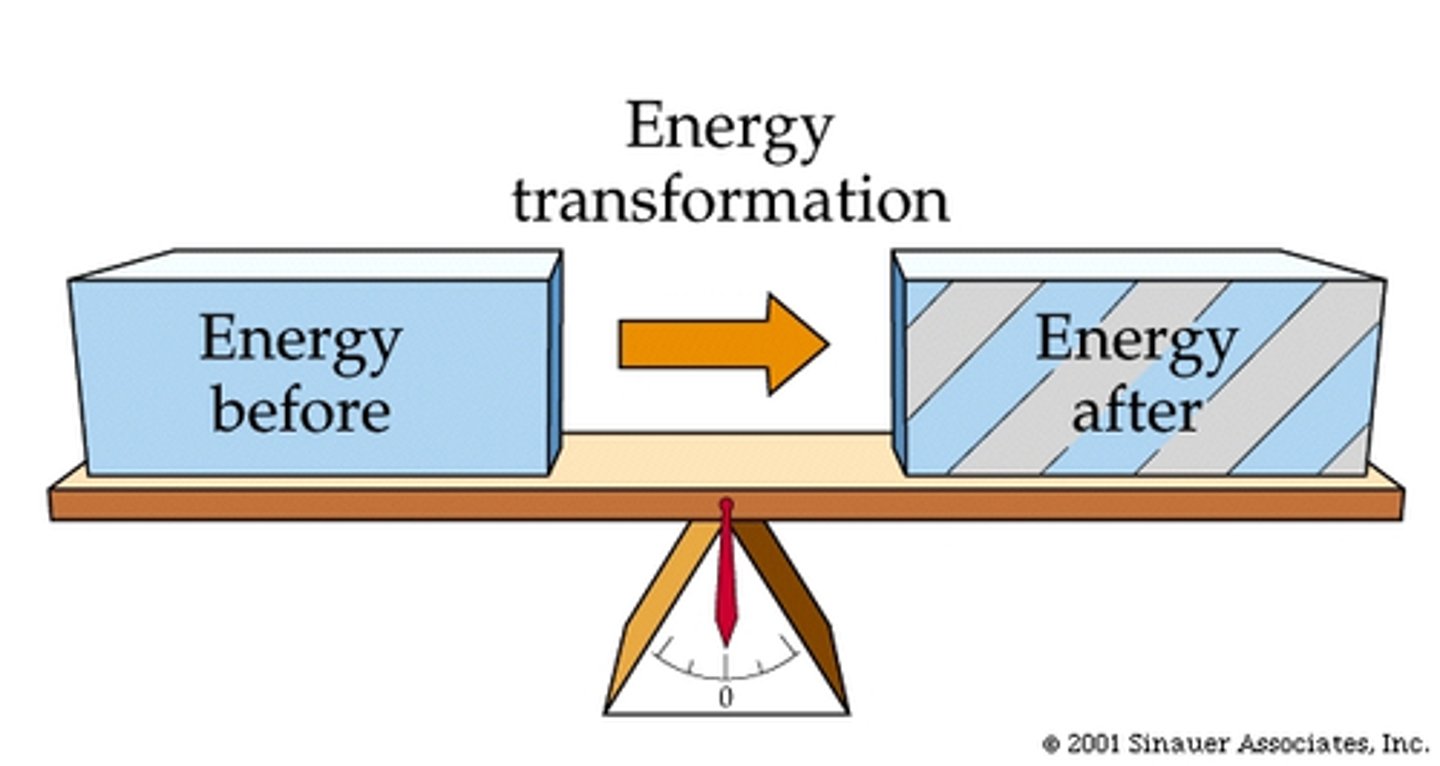
First law of thermodynamics
The principle of conservation of energy, which states that energy can be transformed but cannot be created or destroyed.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that obtain their organic nutrients from other organisms.

Chemoautotrophs
Organisms that use chemical oxidative processes to synthesize organic nutrients from inorganic sources.

Photoautotroph
Organisms which use sunlight to synthesize organic nutrients from inorganic sources.

Primary productivity
The gain by producers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time. This term could refer to either gross or net primary productivity.
Secondary productivity
The biomass gained by consumers, through feeding and absorption, measured in units of mass or energy per unit area per unit time.
Ecological efficiency
the percentage of energy received by one trophic level that is passed on to the next leve
Autotrophs
Organisms that make their organic nutrients from inorganic sources.

Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen.
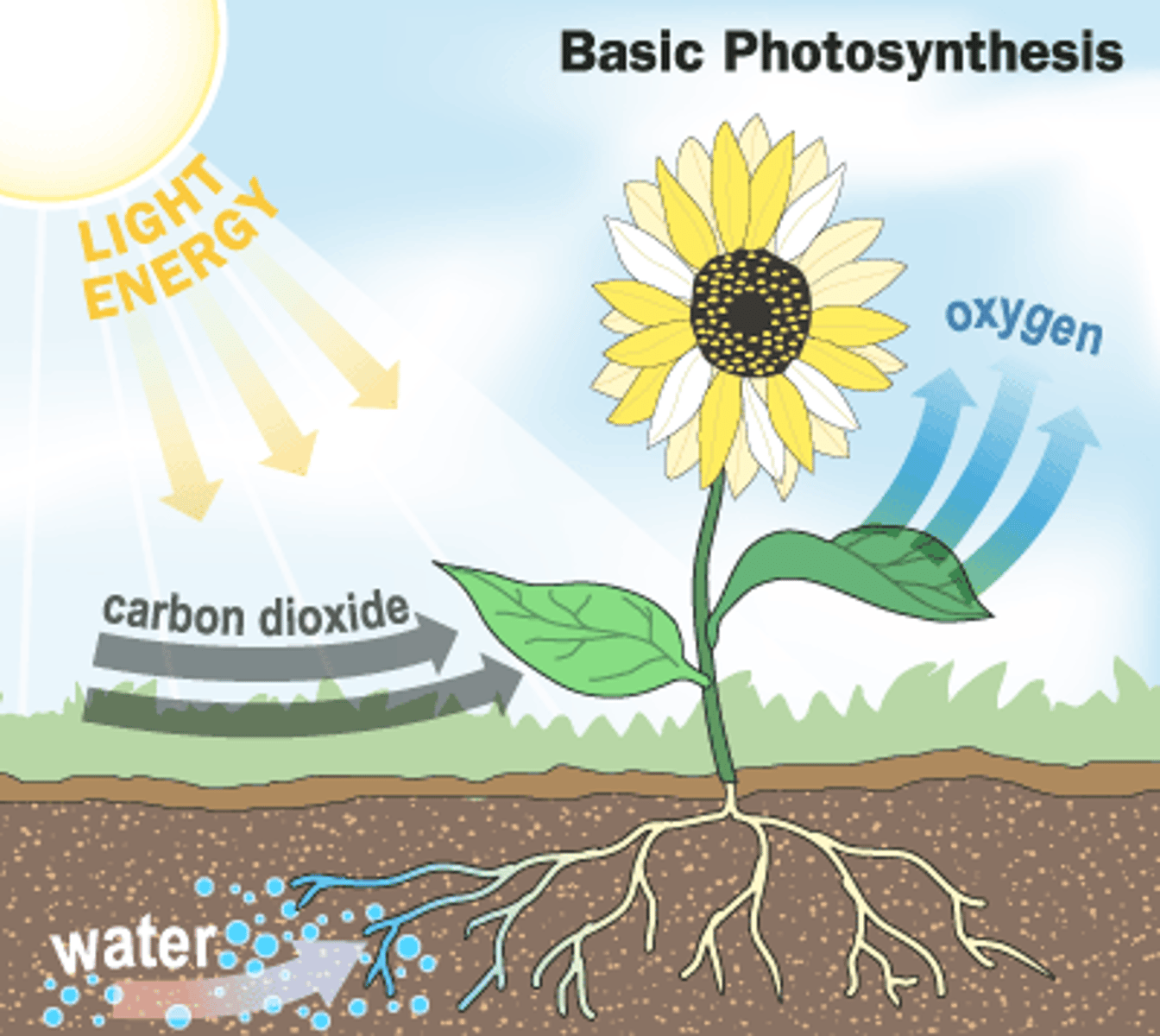
Producers
Typically, plants or algae that produce their own food using photosynthesis and form the first trophic level in a food chain.

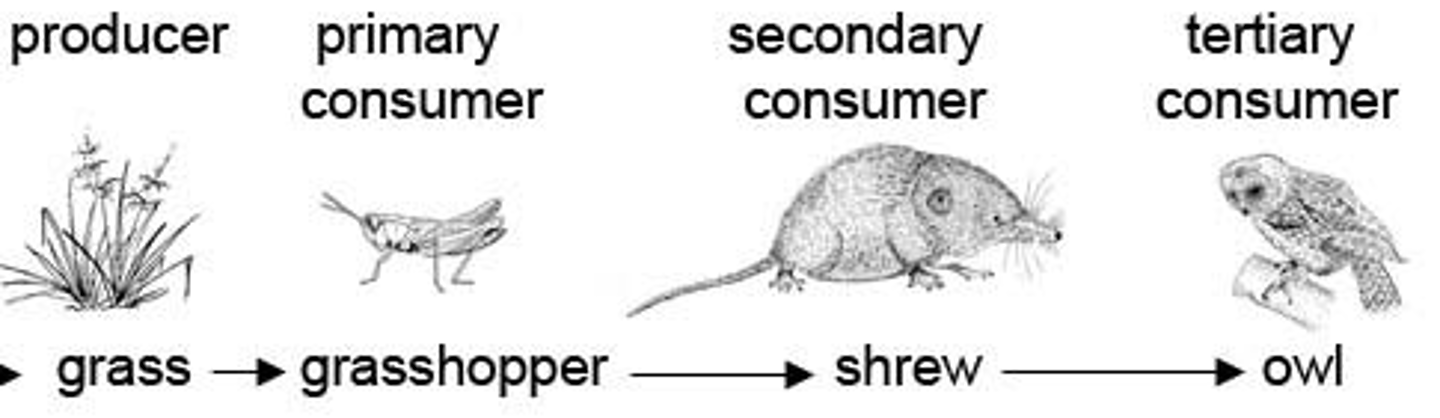
Trophic level
The position that an organism occupies in a food chain, or the position of a group of organisms in a community that occupy the same position in food chains.
Respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.

Second law of thermodynamics
This law states that the quality of energy changes as it is transferred or transformed, from useful energy (for example, solar radiation) to low-quality energy (e.g., heat).
Consumers
Organisms that ingest live or recently dead organisms, and are further classified as herbivore, carnivore, or omnivores.