from chromosomes to genomes
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter. 6: genomes, genes and alleles; chromosomes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, contains genetic information, common to all species
DNA structure
macromolecule in form of double polymer, 2 long strands of nucleotides wound together in a double helix
nucleotide structure
5 carbon (pentose) deoxyribose sugar, negatively charged phosphate sugar, nitrogenous base
nucleotide bonds
sugar molecule bonds to phosphate group of next nucleotide in strand, nitrogenous base is hydrogen bonded with corresponding nitrogenous base
Complementary Base Pairing
nitrogenous base pairing, adenine bonds with thymine, cytosine bonds with guanine
Genes
sections of DNA/ sequence of nucleotides that code for a specific protein
Alleles
alternative forms of genes, have same gene locus on chromosome but different nitrogenous base sequences
allele origin
two alleles for each gene in an organism, one from each parent
genome
sum of all DNA, measured in number of nucleotide bases in haploid set of chromosomes
genomics
study of genomes
Human genome
mapped in 2003 by human genome project, 20,000 to 25,000 genes in human
bioinformatics
science of analysing biological data using advanced computing techniques
chromosomes
one DNA molecule, found in nucleus, made of tightly coiled DNA
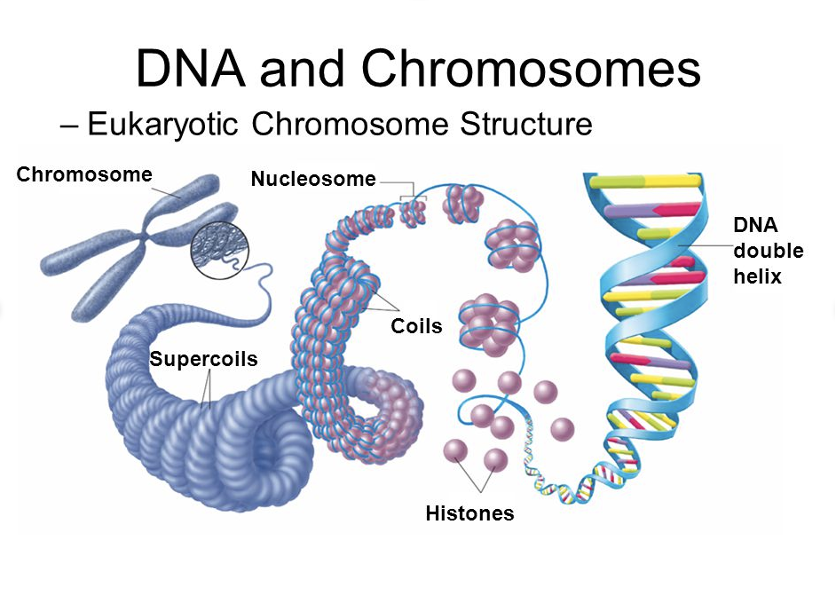
histones
proteins that DNA wraps around to become a chromosome
heredity
study of inheritance; how genes pass from one generation to next
karyotype
photograph of chromosomes, arranged in homologous pairs from largest to smallest, show size, centromere location and banding patterns
homologous
chromosomes with similar size and shape, but potentially different base sequences
autosome
first 22 pairs, homologous, code for physical characteristics
sex chromosome
code for sex and some other traits, match in females(XX), don’t match in males(XY)
haploid
represented by n, amount of chromosomes in gametes, 23 in humans, half of chromosomes in somatic cells
diploid
number of chromosomes in somatic cells, represented by 2n
gene locus
particular position of a gene along length of chromosome, homologous chromosomes have same gene loci
linked genes
genes on the same chromosome, tend to be inherited together
sex determination
sperm gametes determine sex of offspring
sex-linked
genes on sex chromosomes, far more genes on X, meaning sex linked conditions often come from the X chromosome
aneuploidy
addition or loss of one chromosome in a cell
polyploidy
extra sets of homologous chromosomes(4n, 6n), common in plants and some amphibians, does not always result in disease, lethal in humans
non-disjunction
incorrect separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, causes aneuploidy
trisomy
one extra chromosome e.g down syndrome, klinefelter syndrome
monosomy
one less chromosome e.g turner syndrome
meiosis
cell division that produces gametes, creates genetically unique offspring
meiosis location
gonads (ovaries, testes) in animals, anther and ovary in plants
Meiosis I
reduction division, homologous pairs seperate
Interphase I
chromosomes replicate, normal cell processes
Prophase I
centrioles move to opposite poles, spindle forms, homologous pairs synapse
Synapsis
the joining of homologous chromosomes together during prophase I, pair is called a bivalent
Crossing over
exchange of genetic information between synapsed chromosomes, occurs at chiasmata
Metaphase I
synapsed homologous chromosomes move to spindle equator
Anaphase I
homologous chromosomes seperate and move to opposite poles
telophase I
new nucleus forms with one chromosome from each homologous pair, spindle breaks down
Meiosis II
chromatids from each chromosome seperate, similar to mitosis
Interphase II
brief, no dna replication
prophase II
chromosomes re-condense, new spindles form, no synapsis or crossing over
Metaphase II
chromosomes align along equator
Anaphase II
sister chromatids seperate to opposite poles
telophase II
four haploid cells produced, spindle disappears, nuclear envelopes form, cytokinesis
independent assortment
homologous chromosomes line up independently of each other during meiosis I, meaning assortment of alleles in resulting gametes is random
monoploidy
fully functional organisms with only one copy of each chromosome, produced by parthenogenesis (no fertilisation). common in males of colony insects e.g bees
prokaryote chromosomes
DNA found in cytosol, usually as a single circular chromosome, can be condensed, said to be haploid
plasmids
small rings of DNA in prokaryotes, replicate independently
chloroplast DNA
single circular chromosomes (similar to prokaryotes), contains roughly 100 genes coding for proteins needed in photosyntheis
mitochondrial DNA
similar to chloroplast DNA, codes for some proteins needed to make up mitochondria, comes only from the mother (sperm has no mtDNA)
endosymbiosis
theory explaining eukaryotic cell evolution, mitochondria evolved from aerobic bacteria and chloroplasts evolved from cyanobacteria, both of which were engulfed by an ancestral host cell