The Business Environment
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Business
Any activity that seeks to provide goods and services to others while operating at a profit.
Goods
Tangible products.
Services
Intangible products.
Entrepreneur
A person who risks time and money to start and manage a business.
Revenue
Represents the funds an enterprise receives in exchange for its goods or services.
Profit
What's left (hopefully) after all the bills are paid or the cost of doing business.
Stakeholders
All the people who stand to gain or lose by the policies and activities of a business and whose concerns the businesses need to address.
Functional Areas of Business
Introduction to the various activities in which businesspeople engage.
Management
Managers are responsible for the work performance of other people.
Operations Manager
The person who designs and oversees the transformation of resources into goods or services.
Marketing
Everything that a company does to identify customers' needs and design products to meet those needs.
Four P's of Marketing
Price, Product, Promotion, Place.
Accounting
Managers need accurate, relevant and timely financial information, which is provided by accountants.
Financial Accountants
Prepare financial statements to help users assess the financial strength of the company.
Managerial Accountants
Prepare information for internal use only, such as reports on the cost of materials used in the production process.
Finance
Involves planning for, obtaining, and managing a company's funds.
Financial Managers
Address questions such as how much money the company needs.
Types of Businesses
Includes hotels, airlines, law firms, hospitals, and various products like Mac, iPhone, iPod, iPad, and Apple Watch.
Not-for-Profit (Nonprofit)
Organizations like United Way of America and Habitat for Humanity that provide services without profit motive.
Car Dealership
Sells goods (cars) and provides services (automobile repairs).
Colleges and Universities
Provide educational services.
Globalization
The spread of products, technology, information, and jobs across national borders and cultures, fostering interdependence of nations through free trade.
Absolute Advantage
A nation has an absolute advantage if it is the only source of a particular product or can produce more of a product using fewer resources than other countries.
Comparative Advantage
Exists when a country can produce a product at a lower opportunity cost compared to another nation.
Opportunity Cost
The products that a country must forego making in order to produce something else, often associated with specialization.
Licensing Agreements
An international agreement allowing a foreign company (the licensee) to sell the products of a producer (the licensor) or to use its intellectual property in exchange for royalty fees.
Franchises
An agreement where a company (the franchiser) grants a foreign company (the franchisee) the right to use its brand name and sell its products or services, with the franchisee responsible for operations.
Market Growth
Strategies aimed at expanding revenue by reaching new global markets.
Balance Payments
A financial statement that summarizes a country's transactions with the rest of the world, including trade, investment, and transfer payments.
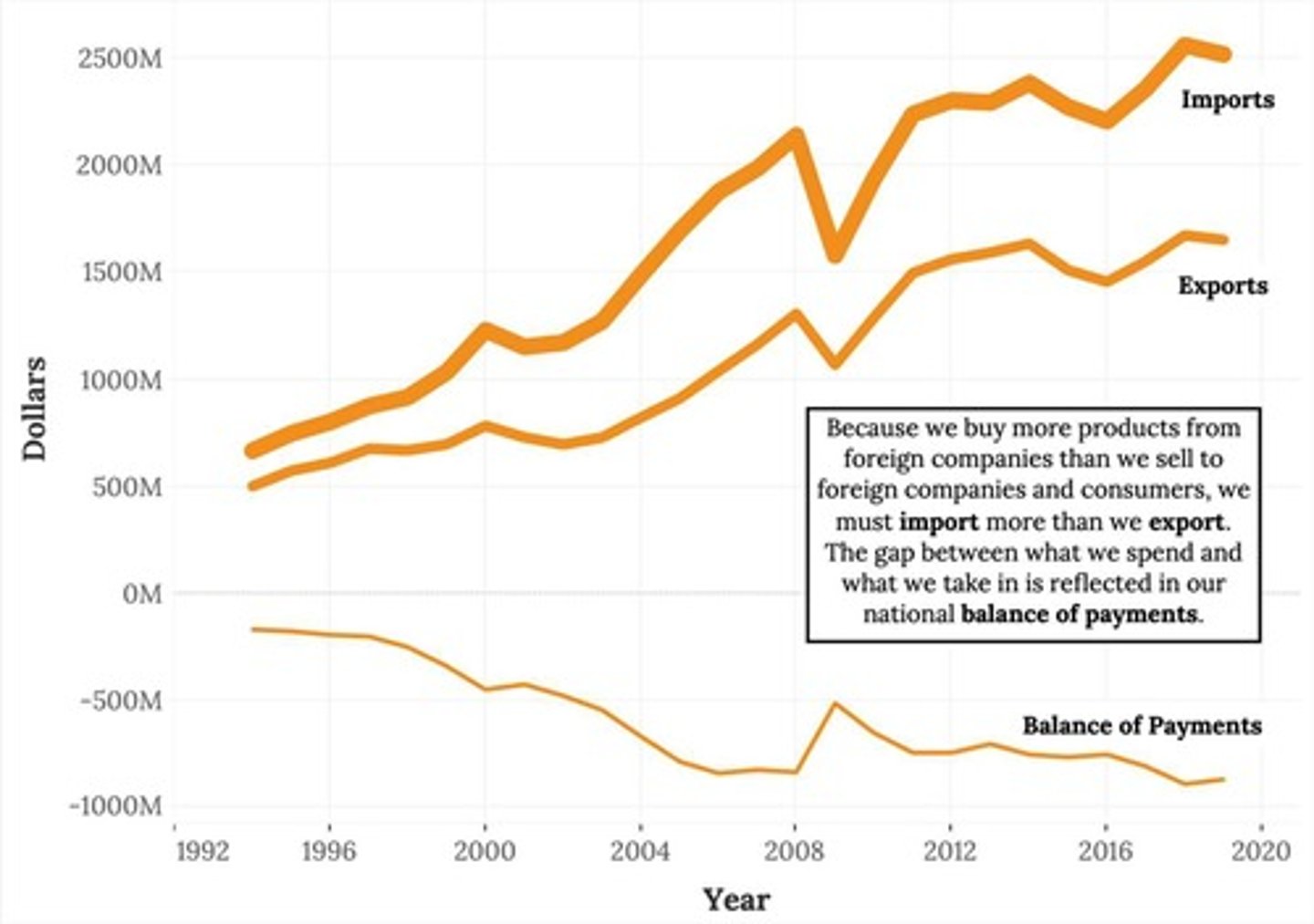
Trade
The exchange of goods and services between countries, critical for economies.
Consumer
An individual who purchases goods and services for personal use.
International student
A student who is studying in a country other than their home country.
Future manager
An individual preparing for a managerial role, potentially dealing with international colleagues, suppliers, and customers.
Audit
A systematic examination of financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Planning
The process of setting goals and outlining steps to achieve them in a business context.
Analyst
A professional who evaluates data and trends to inform business decisions.
Budget
A financial plan that outlines expected revenues and expenditures over a specific period.
Consultant
An expert who provides professional advice in a particular area of business.
Research and Development
The activities associated with the innovation and improvement of products and services.
Plant and Equipment Investments
Financial expenditures made by a company to acquire or upgrade physical assets used in production.
Revenue Expansion
The process of increasing the income generated from business activities.
Licensing
Sign a contract with a company in another country to give them the right to manufacture your product.
Franchising
Most often used in restaurants and hotels, permits the franchisee to use brand name and other aspects of the business model.
Pros of Franchising
Expertise, Marketing, and sometimes financial help from the parent; nationally known name, but you own the outlet and therefore the profits.
Cons of Franchising
Big upfront investment in time and money; share profit through royalties; mistakes of others may impact the whole chain.
Contract Manufacturing
A form of outsourcing where a U.S. company contracts with a local company in a foreign country to manufacture one of its products.
Joint Venture
Typically results in the formation of a new company jointly owned by the companies involved.
Strategic Alliance
Involves two companies pooling limited resources to work on a given opportunity.
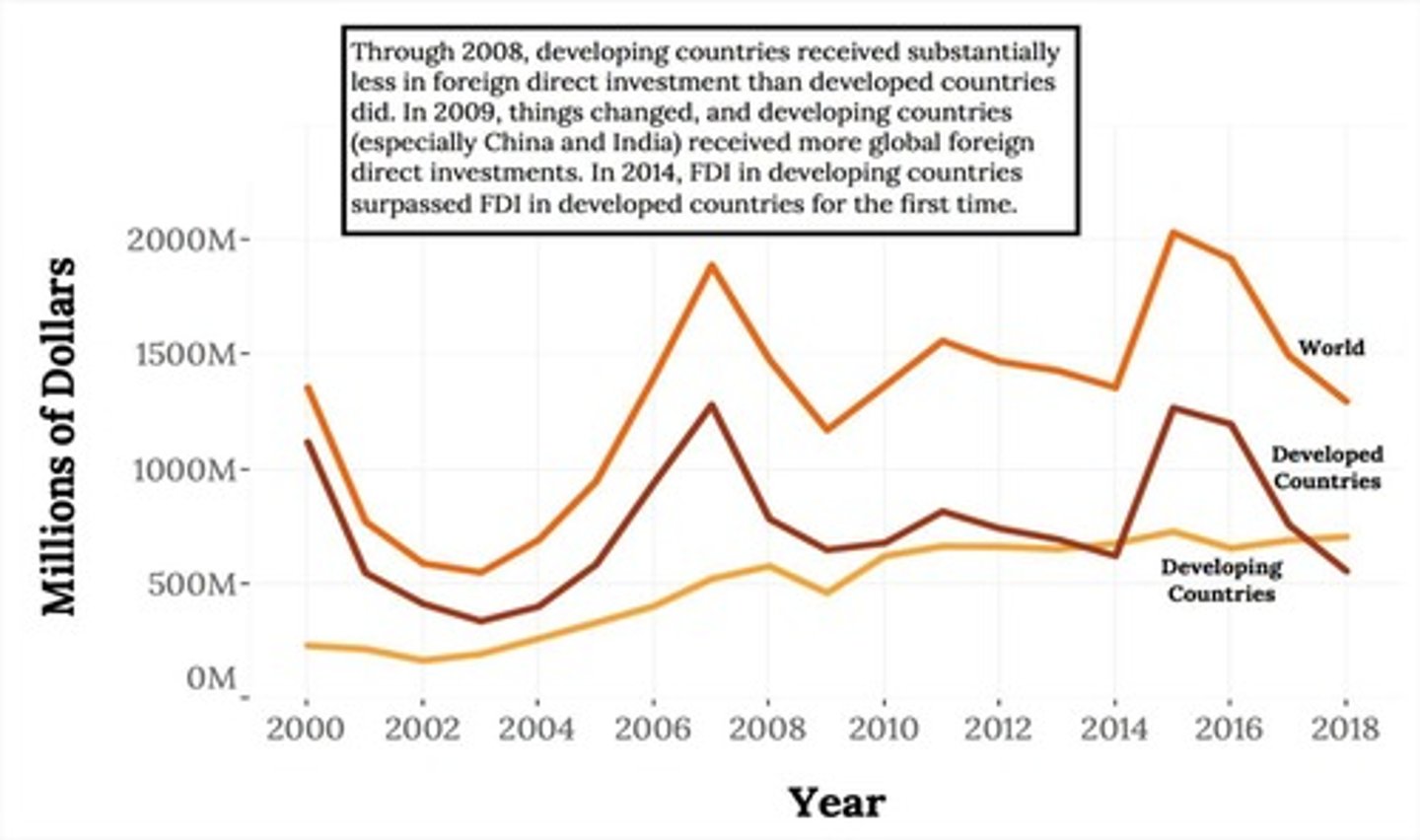
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
The formal establishment of business operations on foreign soil—the building of factories, sales offices, and distribution networks to serve local markets.
Offshoring
Occurs when facilities set up in the foreign country replace U.S. manufacturing facilities and are used to produce goods that will be sent back to the United States for sale.
Outsourcing
Obtaining any product or service from an outside party rather than making the product or performing the service internally.
Trade Controls
Includes subsidies, tariffs, quotas, embargoes, and dumping.
Subsidies
Government support that helps a certain group or product more cheaply by giving them financial help to defray their costs.
Quotas
Imposes limits on the quantity of a good that can be imported over a period of time.
Embargo
An extreme form of quota that bans the import or export of certain goods to or from a specific country.
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
An international treaty aimed at reducing trade barriers.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
An organization that regulates international trade.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Provides financial support for emerging economies.
World Bank
Provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries.
North American Free Trade Association (NAFTA)
A trading bloc that promotes free trade between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
European Union (EU)
A political and economic union of member states located primarily in Europe.