NUCLEIC ACID
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are the 2 types of nuclei acid?
DNA
RNA
What is a nuclei acid made from>
Large polymers formed from many nucleotides
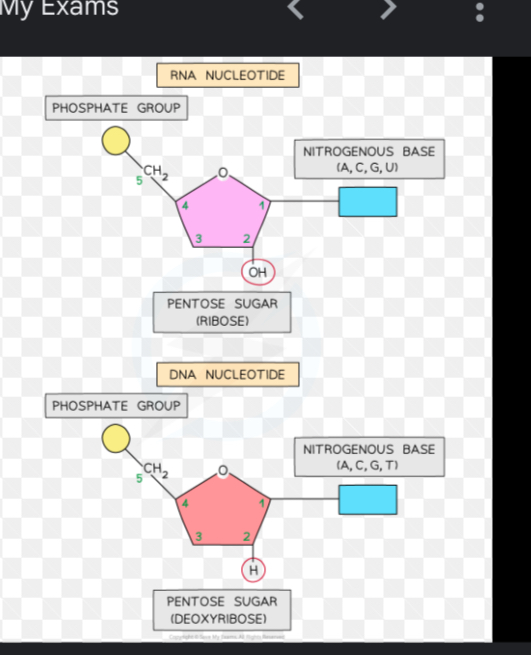
What is an individual nucleotide made of?
PO4²- phosphate group
Inorganic
Acidic
Negatively charged
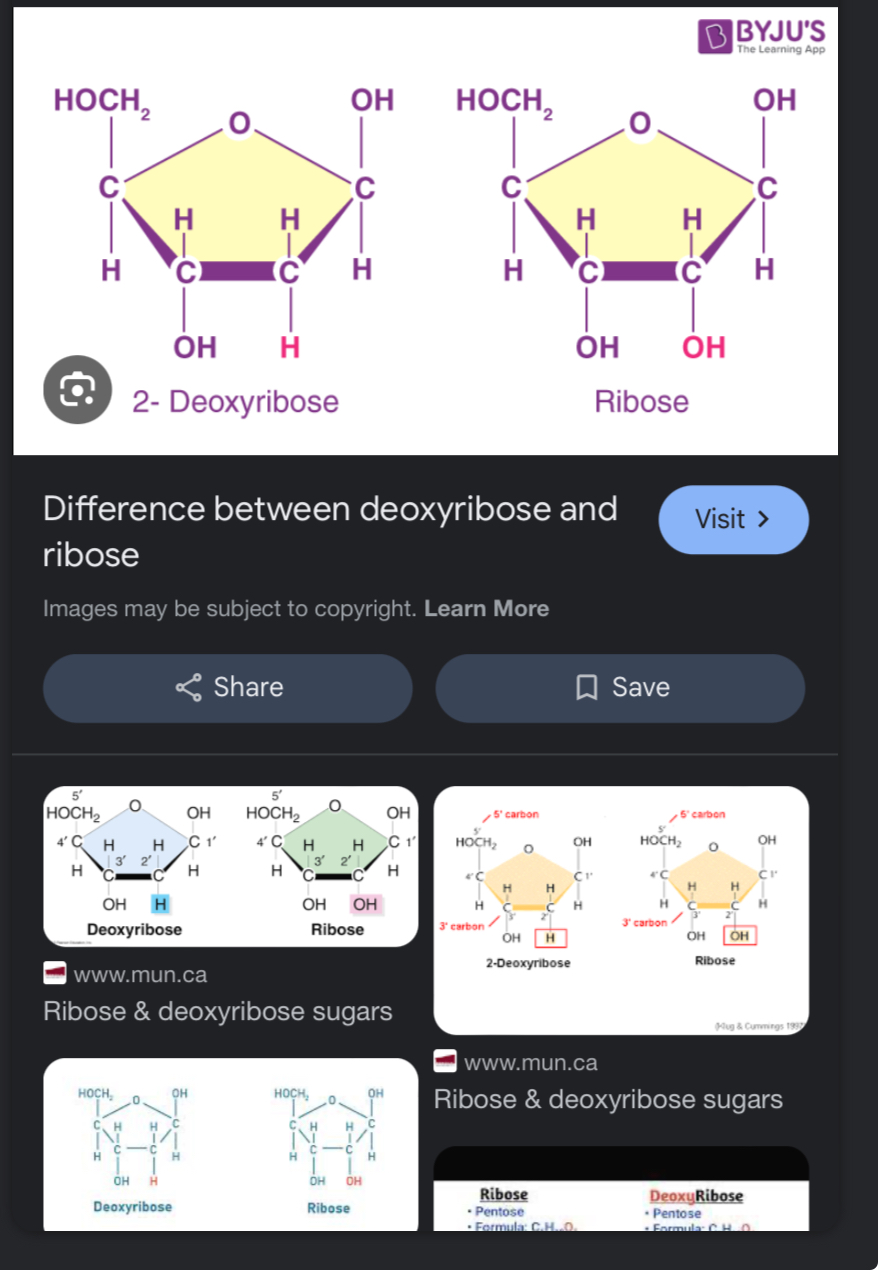
PENTOSE SUGAR (ribose etc)
Nitrogenous base which is an organic molecule with 1-2 carbon rings
What are nucleotides linked together by
Condensation reaction to form polynucleotides (polymer)
How is a phosphodiester bond formed
The phosphate group of 5th carbon of pentose sugar of one nucleotide forms a covalent bond with OH group of 3rd carbon of another pentode of an adjacent nucleotide
What does the phosphodiester bond form and how is it broken
The sugar phosphate backbone
Broken by hydrolysis releasing individual nucleotides
What does DNA stand for
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Te sugar is deoxyribose
How many nucleotides are there and what are they divided into
PYRIMIDINES - thymine and cytosine
smaller bases
PURIE - adenine and guanine
larger bases
What forms 2 hydrogen bonds and what forms 3
Thymine and adenine - 2 hydrogen bonds
Guanine and cytosine - 3 hydrogen bonds
PURINES PAIR WITH PYRAMIDINES
What forms the double helix
2 strands of polynucleotides coiled into a helix
What are the 2 strands held together by
Hydrogen bonds
What are the 2 strands called due to their position
ANTI PARALEL
Run in opposite directions
Each strand has what one what end
A phosphate group on one end
OH group on the other
Why is pairing important. In DNA
Allows DNA TO BE COPIED AND transcribed
What is so important about complementary based pairing
DNA always has equal amounts of adenine and thymine and equal amounts of cytosine and guanine
What is the strutcu`re of RNA
Nucleotides are penates suaar is ribose rather than deoxyribose (meaning it has one less oxygen)
Thymine is replaced with uracil which is a pyrimadine that forms 2 hydrogen bonds with adenine (base pairing still happens).
What happens after protein synthesis with RNA
RNA degrades into cytoplasm
Phosphodiester bonds are hydrolysed and RNA nucleotides ar released and reused