Peri-anesthesia Monitoring and Complications V
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
ETCO2
Ventilation status
CO
RR
What does a capnograph tell you?
0
What should CO2 readings be at during intubation?
ETCO2 - End of expiration where co2 is coming from alveolar
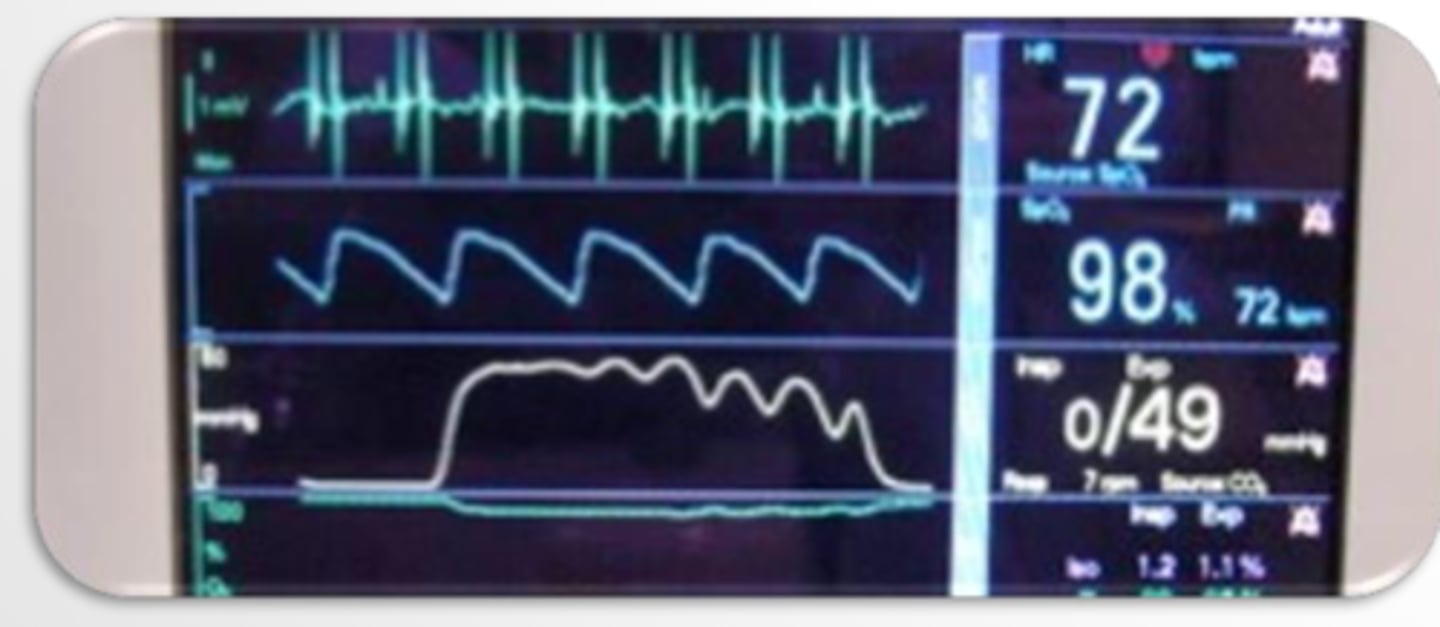
What does the star represent?
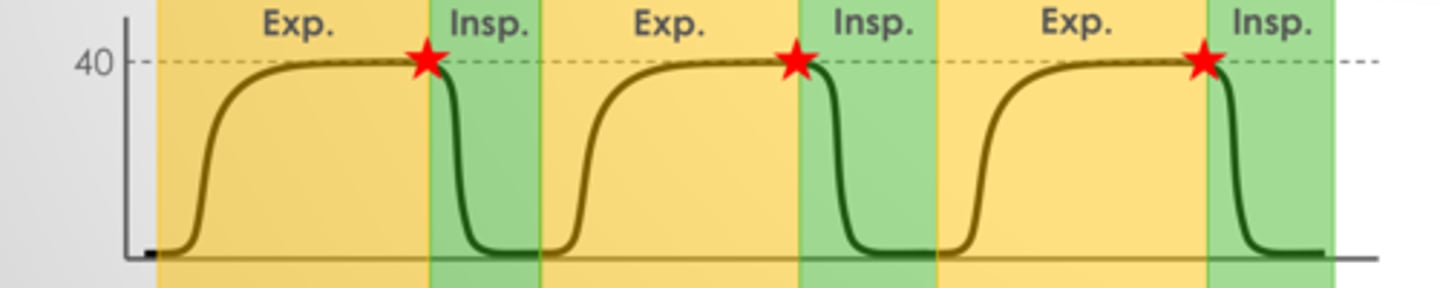
30-40 mmHg - can go up to 60mmHg in healthy pts
What should ETCO2 be in small animals?
20-30mmHg
What should ETCO2 be in large animals?
No plateau (tachypnea or dead space)
Extra peaks
When is a ETCO2 not reliable?
Give deep breath to get a plateau
If you are not seeing a plateau what can you do to evaluate ETCO2?
Mixture of inspired and expired gas that doesn't participate in gas exchange
What is dead space?
Too large ET tube
Too many adaptors
Pulmonary embolism
What can cause increased dead space?
1 - the highest value most reliable w/ extra peaks
Which value is most reliable?
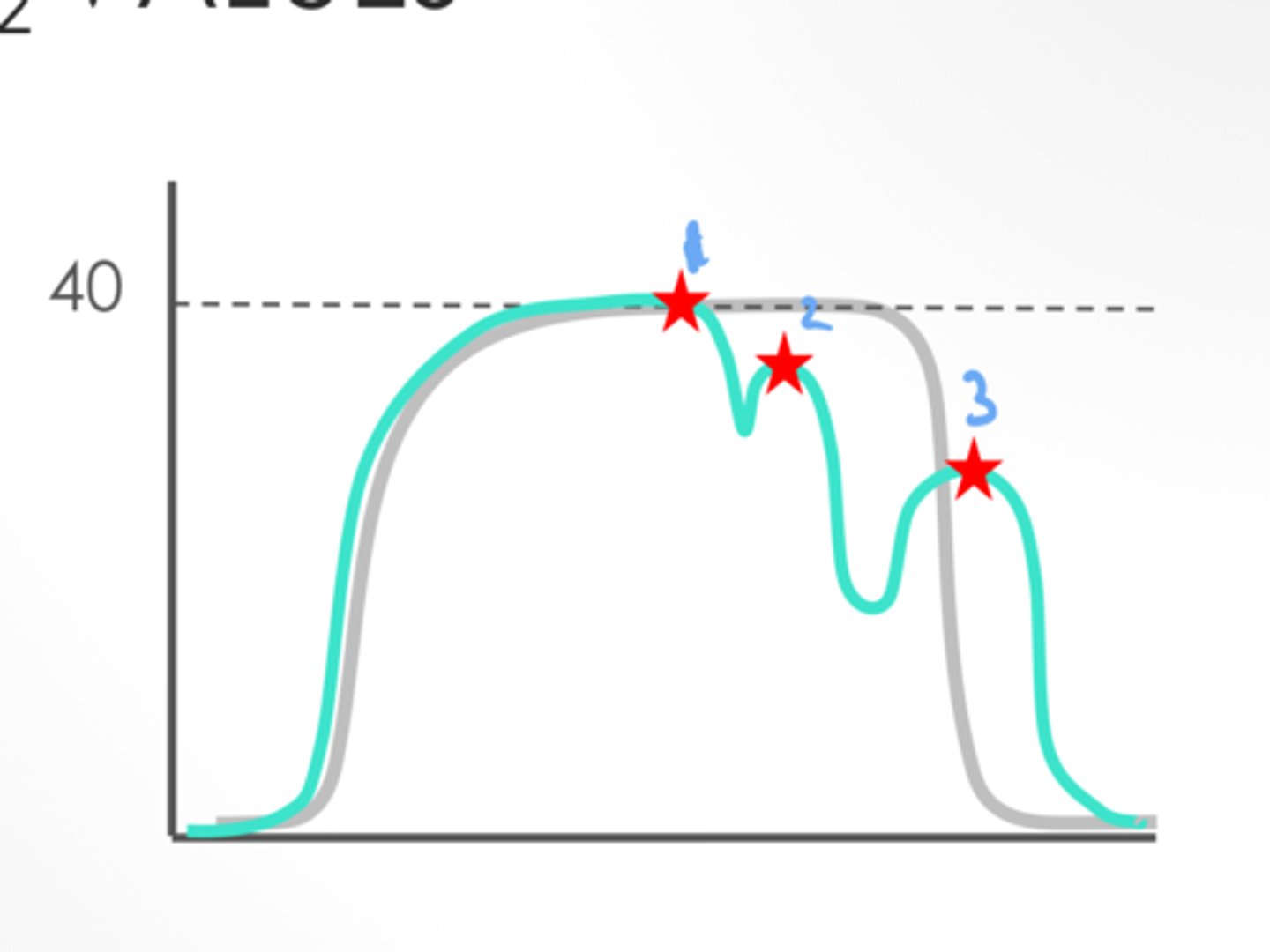
Hypercapnia/ hypercarbia
What does hypoventilation lead to?
False - just tells resp rate
T or F: Tachypnea will tell ventilation status
MV = TV x RR
How is minute ventilation calculated?
TV first
If an animal is shallow breathing what should you increase to counter the hypoventilation?
-Increase in SNS tone
-Don't need PPV as much and therefore less neg circulatory effects
-Stimulates breathing center
What are advantages of having permissive hypercapnia?
CO
ETCO2 is proportional to what?
Circulatory collapse/ arrest
If there is a sudden decrease in ETCO2 what could be happening to the CV system?
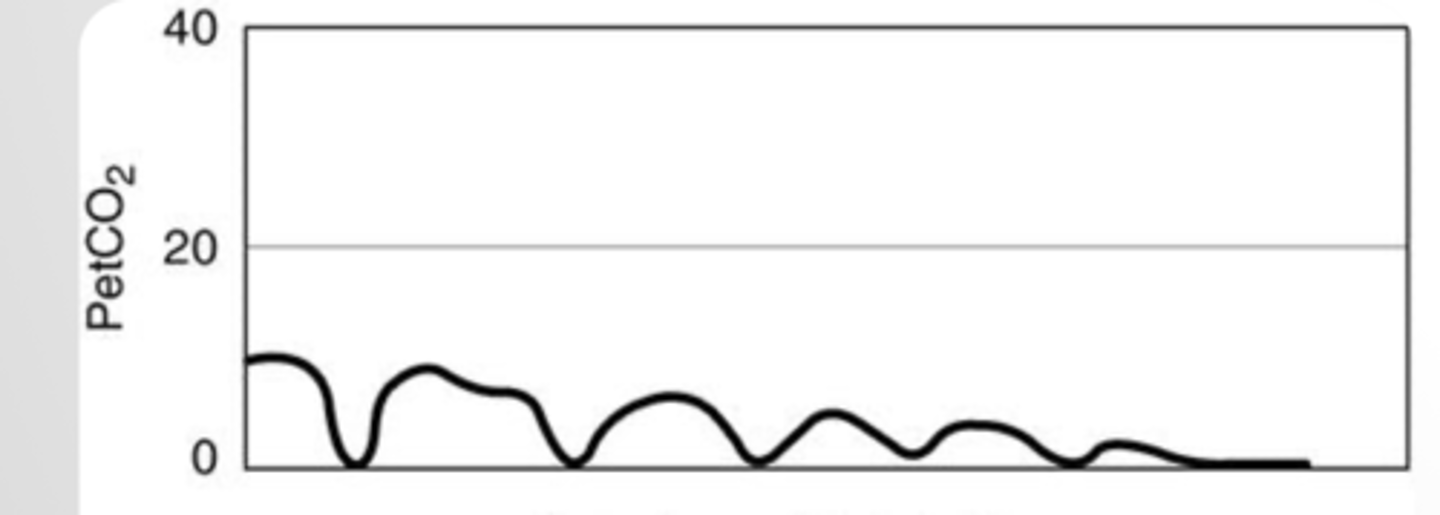
Esophageal intubation
What could explain this capnograph?
Inadequate fresh gas flow rate
Why might we see a capnograph not going to 0 in a non-rebreathing circuit?
Desiccated CO2 absorbent
Stuck open expiratory valve
Why might we see a capnograph not going to 0 in a rebreathing circuit?
Decrease dead space
PPV
How can you compensate for deadspace ventilation?
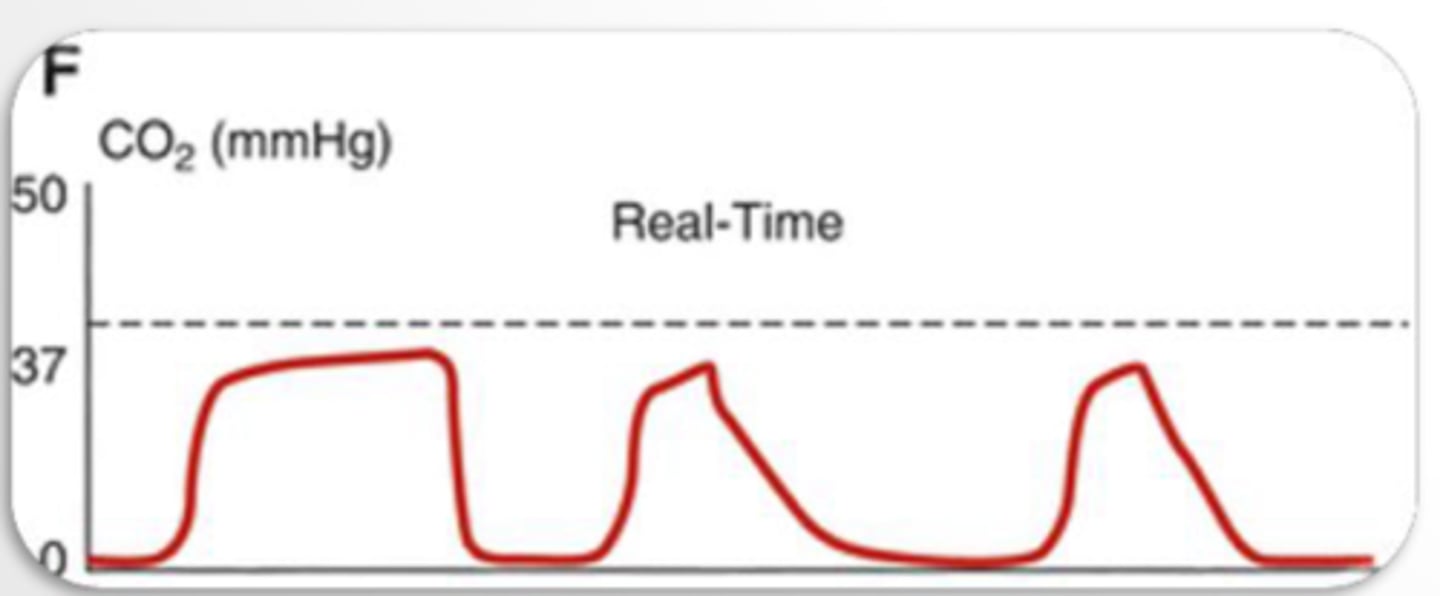
ET tube leak
What could explain the capnograph?
Mucus plug obstruction
What could explain the capnograph?
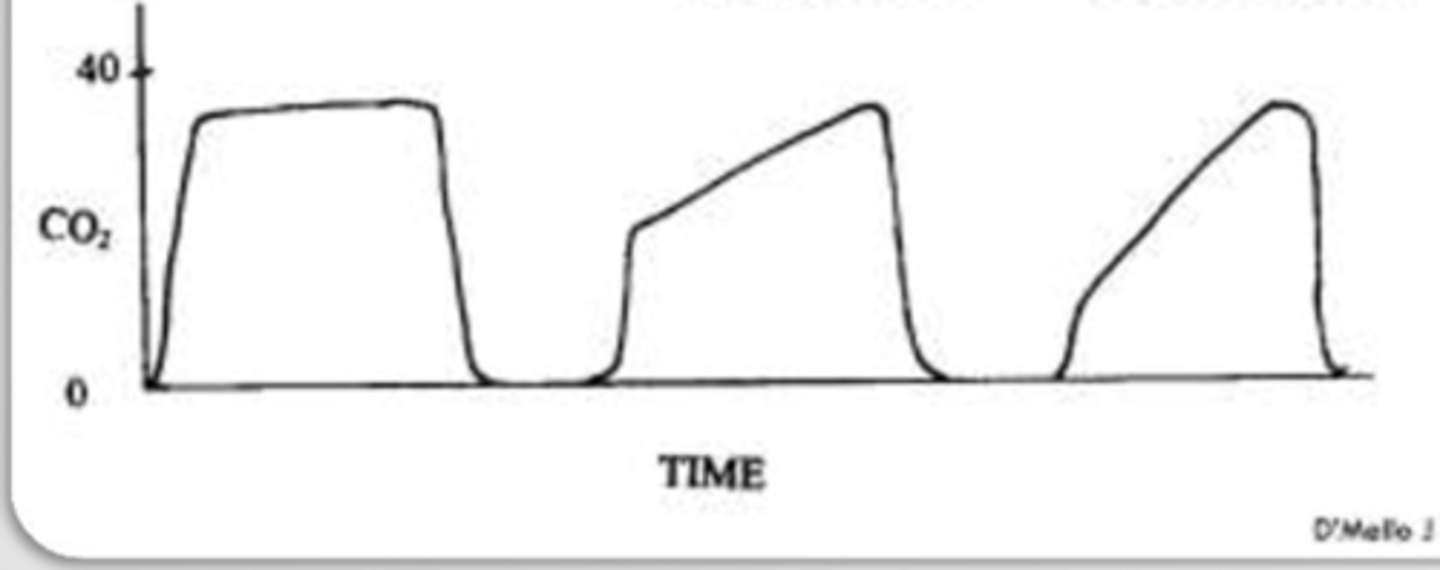

Give a breath - hopefully resp center will catch up and pet will start breathing
How to you tx apnea?
Heart beats push against lungs causing extra breaths - no need to tx
What could cause this capnograph?
3-12 BPM
What is normal resp rate in most species?
4-7BPM
What is normal resp rate in a horse?
Watch chest movements
Watch reservoir bag movements
Capnography
What are methods of monitoring RR under anesthesia?