Electronic Principles DC Current and AC Current (2b)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are power sources, and what are the main types?
provide electrical energy to circuits, machines, and devices.
DC Power Sources: supply constant voltage or current.
AC Power Sources: supply alternating voltage or current.
Essential for driving current in all electrical circuits.
What are the key characteristics of mains electricity (grid supply)?
Standard in households and industries
Frequency: 50 Hz (Europe) or 60 Hz (USA)
Voltage: 110–240 V depending on the country
What do AC generators (alternators) do, and where are they used?
Convert mechanical energy (from turbines or engines) into AC electricity.
Used in power plants: hydro, thermal, nuclear, and wind.
What is the purpose of an inverter?
convert DC electricity (from batteries or solar panels) into AC electricity for use in appliances.
What are AC power supplies (variable sources) used for?
are laboratory or industrial devices that provide adjustable AC voltage and frequency.
What types of waveforms are commonly used in electronics?
Sine wave (most common)
Square wave
Triangular wave
How do batteries provide power?
are stand-alone power sources that generate electrical energy through a chemical reaction, powering devices without relying on wall outlets.
Range from small cells (watches, phones) to large units (cars).
What are primary batteries?
are designed to produce energy until their chemical reaction is depleted.
Cannot be recharged once the charge is used up
What are secondary batteries?
can be recharged by applying a reverse voltage to the cells, restoring their chemical energy for repeated use.
What happens when batteries are connected in parallel?
Voltage does not increase.
Resistance is reduced, which increases the overall current available from the batteries.
How does a power supply convert AC mains to usable DC for appliances?
Transformer: Steps down high-voltage AC to low-voltage AC.
Rectifier: Converts AC to DC.
Smoothing: Flattens the DC wave toward a straight line.
Regulator: Maintains a constant voltage.
What is a variable DC power supply, and why is it useful?
A variable DC power supply connects to a wall outlet and lets you adjust the output DC voltage.
Some also allow variable current (AC or DC) for testing different devices.
More control = higher cost, but it’s useful for electronics projects and experiments.
What is an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and how does it work?
A UPS draws power from AC and a battery to provide continuous power.
If AC power is interrupted, the battery takes over instantly.
Commonly used with computers to allow safe shutdown, preventing data loss or system damage.
What is a switched-mode power supply (SMPS) and why is it used in computers?
SMPS converts AC mains power into multiple DC voltages needed by computer circuits.
Uses rapid on/off switching to regulate voltage instead of constant linear delivery.
More efficient and complex than linear power supplies.
Can provide high current for CPUs and handle a wide range of input/output voltages.
Draws less power when off, saving energy.
What is a transformer?
Is a static electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits using electromagnetic induction.
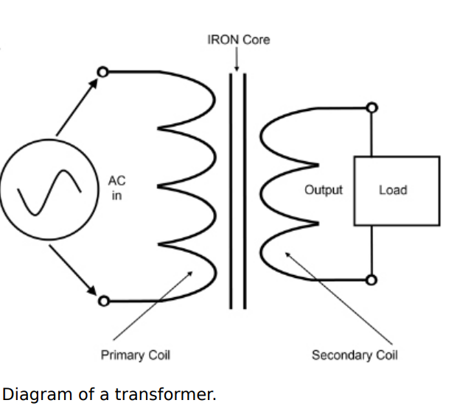
What does a transformer do, and what type of current does it work with?
Changes voltage and current levels without altering frequency.
Works only with AC, not DC.
What is induction in electricity?
Induction is the production of voltage when a conductor moves through a magnetic field.
It can change voltage and current levels without altering frequency.
How does the number of coil turns affect a transformer?
The voltage induced in each coil depends on the ratio of turns between the primary and secondary coils.
What is the formula relating voltage and coil turns in a transformer?
Vs/Vp=Ns/Np
Where:
VPV_PVP = primary voltage
NPN_PNP = primary turns
VSV_SVS = secondary voltage
NSN_SNS = secondary turn
What induces current in a loop and how is it calculated?
A change in magnetic flux through a loop induces a current.
Formula:
Where:
ε = induced voltage
NN = number of loops
ΔΦ\Delta \PhiΔΦ = change in magnetic flux
Δt\Delta tΔt = change in time
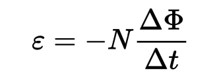
What is the basic principle of a transformer?
An alternating current in the primary coil creates a changing magnetic flux in the core.
This changing flux induces an EMF (electromotive force) in the secondary coil.
What is a step-up transformer and why is it used?
Secondary voltage > Primary voltage
Used in power transmission to reduce current, which minimises energy loss.
What is a step-down transformer and where is it used?
Back:
Secondary voltage < Primary voltage
Used in power distribution, such as converting mains power for home appliances.
What are the two main types of transformer construction?
Core type: Windings around two limbs of the core.
Shell type: Windings around central limb, offers better shielding.
What material is used for a transformer core and why?
Core material: Soft iron or laminated steel
Provides a low reluctance path for magnetic flux, improving efficiency.
What is the function of the secondary winding in a transformer?
The secondary winding delivers the transformed output voltage to the load.
What is the purpose of insulation in a transformer?
Insulation prevents short circuits between the turns of the winding.
What is the purpose of the oil and cooling system in large transformers?
The oil and cooling system prevents overheating, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
What defines an ideal transformer?
No losses, 100% efficiency
Power in = Power out
VPIP=VSISV_P I_P = V_S I_SVPIP=VSIS
Where VP,IPV_P, I_PVP,IP are primary voltage and current, and VS,ISV_S, I_SVS,IS are secondary voltage and current.
What defines a real (practical) transformer and its efficiency?
Has losses:
Copper loss: I²R in windings
Iron loss: Eddy currents and hysteresis in core
Leakage flux loss
Efficiency: Typically 95–99% for large transformers
Magnetic Fields
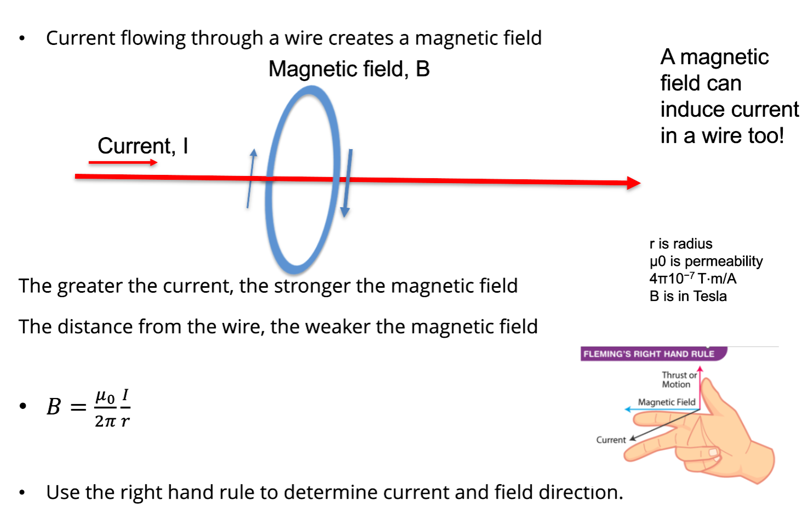
What is an inductor and how does it behave in a circuit?
Inductors temporarily store energy as a magnetic field.
Coiling a wire increases the magnetic field.
Opposes changes in current:
When current is applied: resists increase
When current is removed: tries to maintain current