orgo chapter 13 - ethers
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
oh my
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
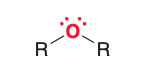
Name the type of molecule.
Ether
An ether consists of an oxygen atom bonded to ___ _____ ______
2 R groups

Give the common name for the molecule
tert-butylmethylether
If the two substituents coming off an oxygen molecule are different in an ether, it is called ____
unsymmetrical
An ether in which the oxygen contains an ethyl group on either side is called ____ _____.
Diethyl ether
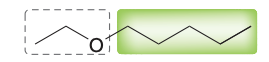
Name the molecule.
1-ethoxypentane
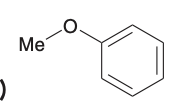
Give the common name for this molecule
methylphenyl ether
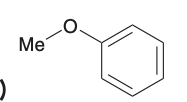
Give the systematic name for this molecule
methoxybenzene
Ethers tend to have (higher/lower) boiling points compared to their isomeric alcohols due to the (presence/lack) of hydrogen bonding ability.
lower, lack
Ethers tend to have (higher/lower) boiling points compared to their isomeric alkanes due to the presence of ___ ___ interactions.
dipole-dipole
Ethers with larger alkyl substituents tend to have (higher/lower) boiling points due to the presence of ____ ____ forces.
higher, London dispersion
A molecule containing multiple ether groups is called a _____
polyether
A cyclic polyether is also known as a _____ ______
crown ether
Because the oxygen atoms all tuck into the inside of a crown ether, the outer structure resembles that of a
hydrocarbon
Crown ethers can be readily dissolved in (organic/polar) solvents.
organic
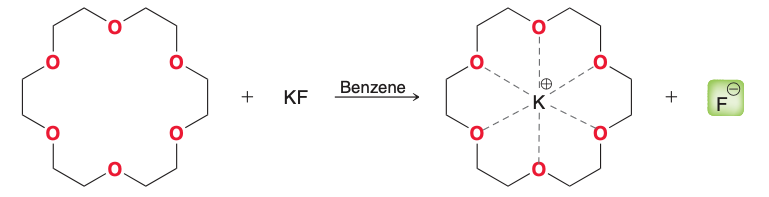
What is the solvent for this reaction? (i typed this card so i would look at it)
Benzene
Industrial synthesis of diethyl ether typically uses what reaction process?
Acid-catalyzed dehydration
The proton transfer involved in the first step of Williamson synthesis is caused by a
hydride ion
The first step of Williamson ether synthesis results in the formation of an ____ ion
alkoxide
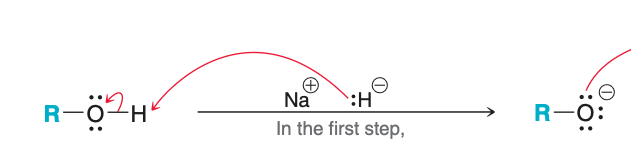
The image depicts step (1/2) of Williamson synthesis
1
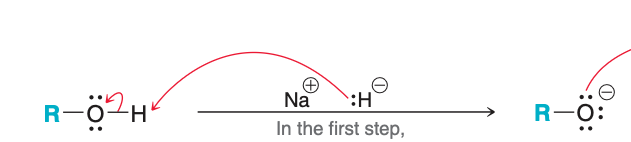
Name the type of reaction occurring in the image
Proton transfer
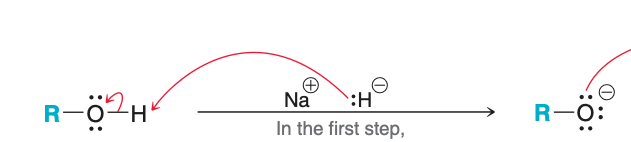
What acts as the base in the pictured reaction?
hydride ion
The second step of Williamson synthesis is an (SN1/SN2) reaction.
SN2
What type of reaction occurs in the second step of Williamson synthesis?
Nucleophilic attack
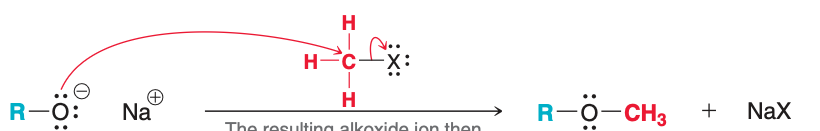
Name the nucleophile in the image
alkoxide ion
The image depicts the (first/second) step of Williamson synthesis
second
Because of the SN2 nature of the process, the second step of Williamson synthesis requires a ___ or ____ alkyl halide.
primary, secondary
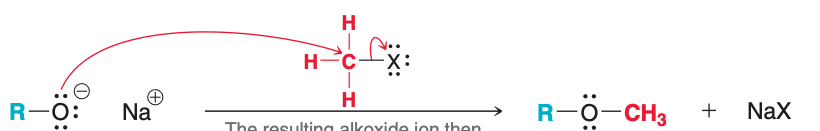
The process of adding ROH via Markovnikov addition is called
alkoxymercuration-demercuration
Alkoxymercuration-demercuration (follows/does not follow) Markovnikov addition.
follows
What reactants are added for the first step of alkoxymercuration-demercuration?
Hg(OAc)₂, ROH
What reactants are added for the second step of alkoxymercuration-demercuration?
NaBH₄
Alkoxymercuration-demercuration is used to prepare ethers from ____.
Alkenes
When an ether is heated in the presence of a very strong acid, it will undergo ____ _____.
acidic cleavage
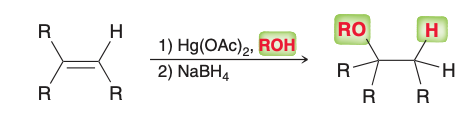
Name the reaction.
alkoxymercuration-demercuration
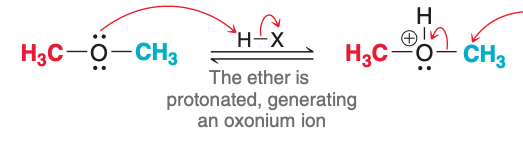
The image depicts the ___ step of acidic cleavage.
first
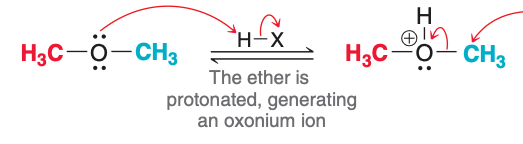
The first step of acidic cleavage, as pictured, involves what type of reaction?
Proton transfer
The first two steps of acidic cleavage result in the formation of
ROH and RX
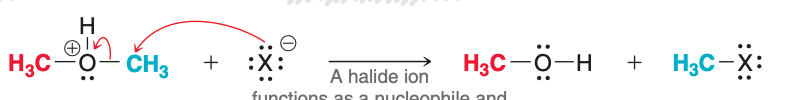
The image depicts the ____ step of acidic cleavage.
second
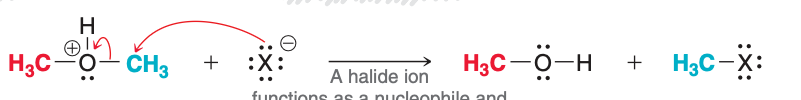
The second step of acidic cleavage, as pictured, involves what type of transfer?
SN2

The image depicts the ___ step of acidic cleavage.
third
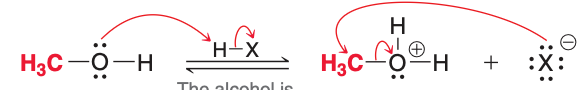
The third step of acidic cleavage, as pictured, involves what type of reaction?
Proton transfer
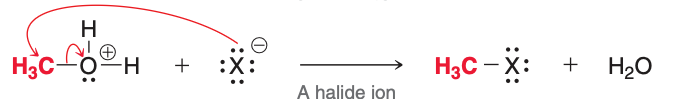
The image depicts the ___ step of acidic cleavage.
fourth
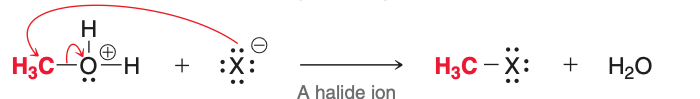
The third and fourth (pictured) steps of acidic cleavage result in the formation of
H₂O and RX
In acidic cleavage, if either R group is tertiary, its portion of the reaction will proceed through an ___ process to form alkyl halides.
SN1
In acidic cleavage, if either R group is primary, its portion of the reaction will proceed through an ____ process to form alkyl halides.
SN2
The two halogen acids that readily participate in acidic cleavage of ethers are
HBr, HI