cell fractionation + ultracentrifugation
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
what is cell fractionation?
process in which different parts and organelles of a cell are separated so they can be studied in detail
name the 3 main stages of cell fractionation
homogenisation
filtration
ultracentrifugation
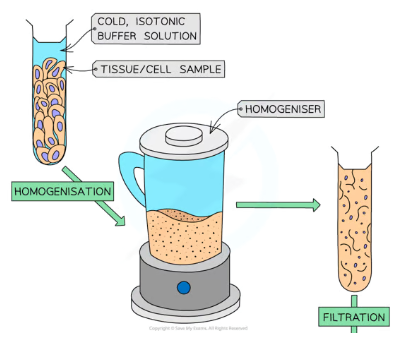
what happens in homogenisation?
cells broken up using a homogeniser (blender)
breaks plasma membrane of cells + releases organelles into the homogenate (a solution)
carried out in a cold, isotonic, buffered solution
cold: slows enzyme activity
isotonic: prevents osmotic damage to organelles
buffered: maintains pH to avoid protein/enzyme denaturation
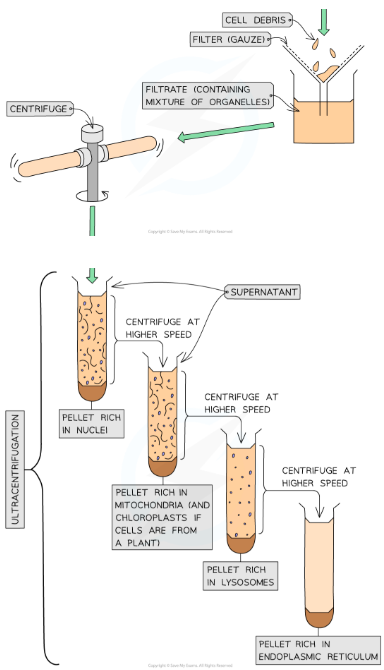
what happens in filtration?
homogenate is filtered through a gauze to remove large debris
organelles remain in the filtrate (filtered solution)
what happens in ultracentrifugation?
filtrate placed into a tube → tube placed in a centrifuge (machine which separates materials by spinning)
filtrate spun in centrifuge at increasing speeds
heaviest organelles form a pellet at the bottom while the rest stay suspended in the solution above the pellet } solution is called ‘supernatant’
supernatant is re-spun at higher speeds to isolate lighter organelles
process repeated at increasing speeds until all different types of organelle present are separated out
order the weight of organelles from heaviest to lightest
nucleus
chloroplasts
mitochondria
lysosomes
endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes