Organizational Behavior Exam #4
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
decision making
entails identifying and choosing from among alternate solutions that lead to a desired state of affairs
What are the two systems or two ways of thinking?
System #1: Rely on intuition, involves mental shortcuts
System #2: Utilize analytical and conscious thought
System #1: Rely on intuition, involves mental shortcuts
can be quick, requires little cognitive effort
can also be thought of as a nonrational decision making
System #2: Utilize analytical and conscious thought
slow, logical, and requires cognitive effort
can also be thought of as rational decision-making
rational model of decision making
explains how managers should make decisions
assumes managers are completely objective and possess complete information
allows for optimizing, meaning solving problems by producing the best possible solution based on a set of highly desirable conditions
however, we are rarely rational when making decisions in complex situations
the conditions for optimization are hard to meet, given cost, time, and resource constraints
rational model of decision making stages
stage 1: identify the problem or opportunity
stage 2: generate alternative solutions
stage 3: evaluate alternatives and select a solution
stage 4: implement and evaluate the solution chosen
What are the three benefits of trying the rational decision making approach?
the quality of the decision is likely to be enhanced
greater transparency surrounds the process
greater responsibility accompanies this approach
nonrational models of decision making
explain how managers actually make decisions
Normative vs. Intuition Models
the normative model
guided by bounded rationality
manageable amounts of information sought, rather than complete or optimal amounts
results in sacrificing or choosing a solution that meets some minimum qualifications, and this is “good enough”
bounded rationality
means our ability to make decisions is restricted or bounded by a series of constraints
ex. resources and personal attributes
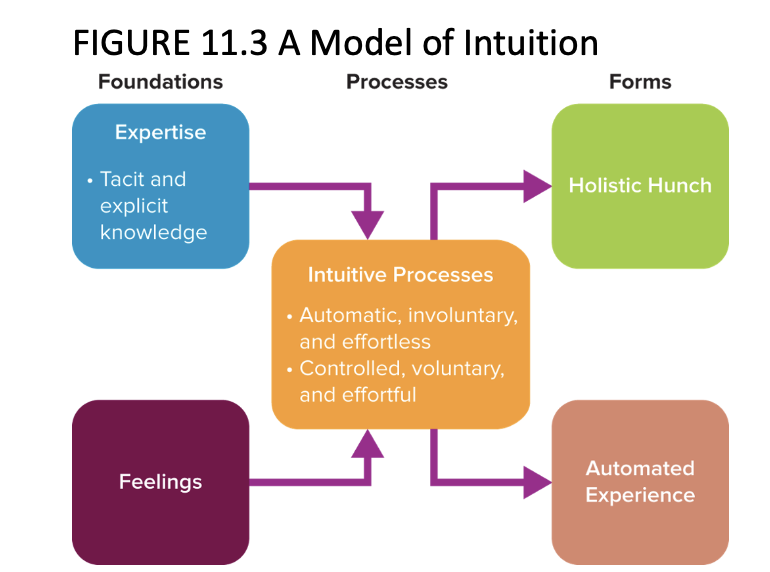
intuition model
based on intuition
useful when a quick decision is required or when resources are limited or difficult or costly to acquire
can be suspectible to bias and it may be difficult to gain acceptance
intuition
judgements, insights, or decisions that “come to mind on their own, without explicit awareness of the evoking cues and of course without explicit evaluation of the validity of these cues”
What are the two forms of intuition?
holistic hunch
automated experience
holistic hunch
a judgement based on the subconscious integration of information stored in memory
automated experience
represents a choice based on a familiar situation and a partially subconscious application of learned information related to it
judgmental heuristics
cognitive shortcuts or biases that are used to simplify the process of making decisions
can help managers make decisions but can lead to bad decisions
What are the eight types of biases?
confirmation bias
overconfidence bias
availability bias
representativeness bias
anchoring bias
hindsight bias
framing bias
escalation of commitment bias
confirmation bias
pertains to how we selectively gather information that supports our decision
overconfidence bias
results in overestimating our skills relative to those of others and overestimating the accuracy of our predictions
availability bias
a decision maker’s tendency to base decisions on information readily available in memory
representativeness bias
leads us to look for information that supports previosuly formed stereotypes
anchoring bias
occurs when decision makers are influenced by the first information they receive about a decision, even if it is irrelevant
hindsight bias
occurs when knowledge of an outcome influences our belief about the probability that we could have predicted the outcome earlier
framing bias
relates to the manner in which a question is posed or framed. It leads us to change the way we interpret alternatives.
escalation of commitment bias
the tendency to hold to an ineffective course of action even when it is unlikely the bad situation can be reversed
evidence-based decision making
the process of conscientiously using the best available data and evidence
an approach used when making, informing, or supporting a decision
big data
reflects the vast quantity of data available for decision-making
artificial intelligence (AI)
a form of computing that allows machines to perform cognitive functions
decision-making style
the way an individual perceives and comprehends stimuli and the general manner in which he or she chooses to respond to such information
What are the two dimensions of decision-making styles?
value orientation
tolerance for ambiguity
value orientation
the extent to which an individual focuses on either task and technical concerns or people and social concerns when making decisions
tolerance for ambiguity
indicates the extent to which a person needs structure or control in his or her life
What are the four decision-making styles?
analytical
directive
conceptual
behavioral
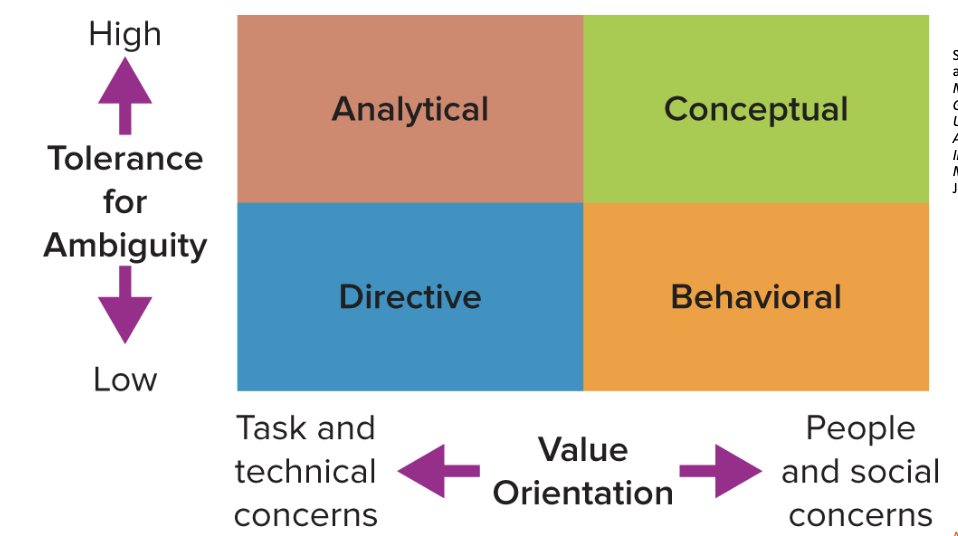
directive style
action-oriented decision makers who focus on facts
analytical style
careful and slow decision makers who like lots of information
conceptual style
intuitive decision makers who involve others in long-term thinking
behavioral style
highly people-oriented decision makers
What are the advantages of group decision making?
large knowledge pool
diversity in approaches
commitment to decision
better understanding of decision rationale
visible role modeling
What are the disadvantages of group decision-making?
social pressures
potential for few participants to be dominant
goal displacement
groupthink
groupthink
occurs when members become deeply involved in a cohesive in-group and striving for unanimity overrides motivation to realistically appraise alternative courses of action
What are the eight symptoms of groupthink?
invulnerability
inherent morality
rationalization
stereotyped views of opposition
self-censorship
illusion of unanimity
peer pressure
mind guards
invulnerability
an illusion that the group cannot make a mistake breeds excessive optimism and risk taking
inherent morality
assuming the group is highly moral encourages members to ignore ethical implications
rationalization
members protect their personal or “pet” ideas and assumptions
stereotyped views of opposition
the group may underestimate opponents
self-censorship
keeping ideas and questions to yourself stifles critical debate
illusion of unanimity
members’ silence can be interpreted to mean consent
peer pressure
be careful when the loyalty of dissenters is questioned
mindguards
self-appointed protectors can shut out adverse information
What are some techniques for preventing groupthink?
each member of the group gets assigned the role of critical evaluator or dissenter role
top-level executives should not use policy committees to rubber-stamp decisions that have already been made
different groups with different leaders should explore the same policy questions
managers should encourage subgroup debates and bring in outside experts to introduce fresh perspectives
someone should be given the role of devil’s advocate when discussing major alternatives
once a consensus has been reached, everyone should be encouraged to rethink their position to check for flaws
brainstorming
a technique that helps groups generate multiple ideas and alternatives for solving problems
What are the rules for brainstorming?
defer judgment
build on the ideas of others
encourage wild ideas
go for quantity or quality
be visual
stay focused on the topic
one conservation at a time
delphi technique
a group process that anonymously generates ideas or judgments from physically dispersed experts
decision support systems
computer-based interactive systems that help decision makers use data and models to solve unstructured problems
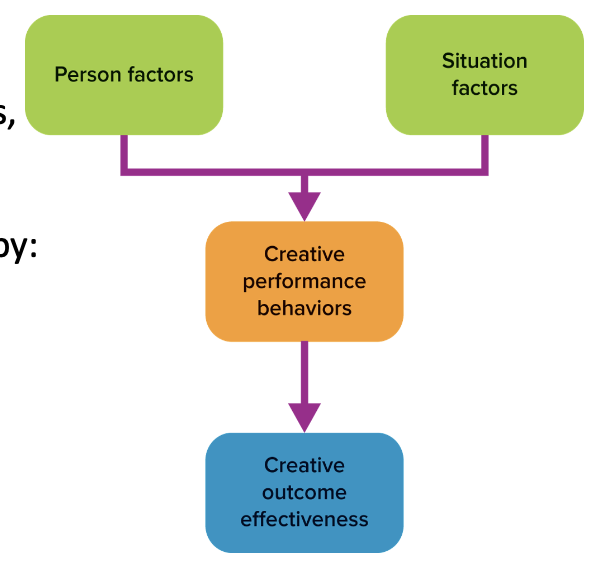
creativity
defined as the process of producing “new and useful ideas concerning products, services, processes, and procedures”
accomplished by: changing your commute, listen to noise, move your lunch, etc.
What are some drivers of creative performance behaviors?
problem formation and definition
preparation and information gathering
idea generation
idea evaluation and validation
What are some drivers of creative outcome effectiveness?
person factors: motivation, personality, self-efficacy, and national culture
situation characteristics: high commitment work practices & organizational culture and climate
power
the discretion and the means to enforce your will over others
highly related to influence
5 different types
legitimate power
used by managers who obtain compliance primarily by using their formal authority to make decisions
reward power
used when an individual obtains compliance by promising or granting rewards valued by the other party
coercive power
used when an individual makes threats of punishment and they have the authority to deliver actual punishment
expert power
when an individual has valued knowledge or information
referent power
derived from personal characteristics and social relationships that effectively gain others’ compliance
position power
derived from a particular job or position within an organization
personal power
something you possess independent of your position or job
What are the three primary responses to power?
resistance
compliance
commitment
resistance
people can simply be indifferent, be passive-aggressive or actively resist. They can also purposefully undermine or even sabotage your efforts.
compliance
those who comply do only what is expected, nothing more
commitment
those who are committed believe in the cause and often go above and beyond to ensure its success
empowerment
efforts to enhance employee performance, well-being, and positive attitudes by:
giving employees greater influence
use of centralized management practices
structural empowerment
job redesign to transfer of power to employees
psychological empowerment
enhancing self-efficacy and intrinsic motivation
authoritarian power
manager/leader imposes decisions
influence sharing
manager/leader consults followers when making decisions
power sharing
manager/leader and followers jointly make decisions
power distribution
followers granted authority to make decisions
meaning
belief that your work values and goals align with those of your manager, team, or employer
competence
personal evaluation of your ability to do the job
self-determination
sense that you have control over your work and its outcomes
impact at work
feeling your efforts make a difference and affect the organization
influence tactics
conscious efforts to affect and change behaviors in others
What are the five soft influence tactics?
rational persuasion
inspirational appeals
consultation
ingratiation
personal appeals
What are the four hard influence tactics?
exchange
coalition tactics
pressure
legitimating tactics
rational persuasion
trying to convince someone with reason, logic, or facts
inspirational appeals
trying to build enthusiasm by appealing to others’ emotions, ideals, or values
consultation
getting others to provide insights, experience or information you canuse in planning and making decisions
ingratiation
getting someone in a good mood prior to making a request. Being friendly and helpful and using praise, flattery, or humor. A particular form of ingratiation is brownnosing.
personal appeals
referring to friendship and loyalty when making a request
exchange
making explicit or implied promises and trading favors
coalition tactics
getting others to support your efforts to persuade someone
pressure
demanding compliance or using intimidation or threats
legitimating tactics
basing a request on authority or right, organizational rules or policies, or explicit/implied support from superiors
Involving influence, what are some examples of match tactics to desired outcomes?
be believable and trustworthy
consult rather than legitimate
expect little from schmoozing
be subtle
learn to influence
organizational politics
intentional acts of influence to enhance or protect the self-interest of individuals or groups that are not endorsed by or aligned with those of the organization
What are some key causes of political behavior?
organizational injustice
lack of trust in co-workers
negative affect
uncertainty
What are the nine political tactics?
building a network of useful contacts
using “key players” to support initiatives
making friends with power brokers
bending the rules to fit the situation
using self-promotion
creating a favorable image
praising others
attacking or blaming others
using information as a political tool
building a network of useful contacts
cultivating a support network both inside and outside of the organization
using “key players” to support initatives
getting prior support for a decision or issue; building others’ commitment via participation
making friends with power brokers
teaming up with powerful people who can get results
bending the rules to fit the situation
interpreting or enforcing rules to serve your own interests