CH12 - Innate Immune Response
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Nonspecific (natural/innate) immune response
Not specific to any organism, includes first line and second line of defense
First line of defense
Physical barriers, microbiota barrier, chemical barriers (surface protection)
Second line of defense
Phagocytosis, inflammation, fever, antimicrobial products (cellular and chemical)
Immunology
The study of all features of the body’s second and third lines of defense (response to infectious agents and allergies)
Antigens (markers)
White blood cells recognize these molecules on cell surfaces, allowing the immune system to identify whether a cell poses a threat and should be marked for destruction
What is a healthy immune system responsible for?
Surveillance of the body
Recognize foreign material
Destroy pathogens
Recognize macromolecules as self or nonself
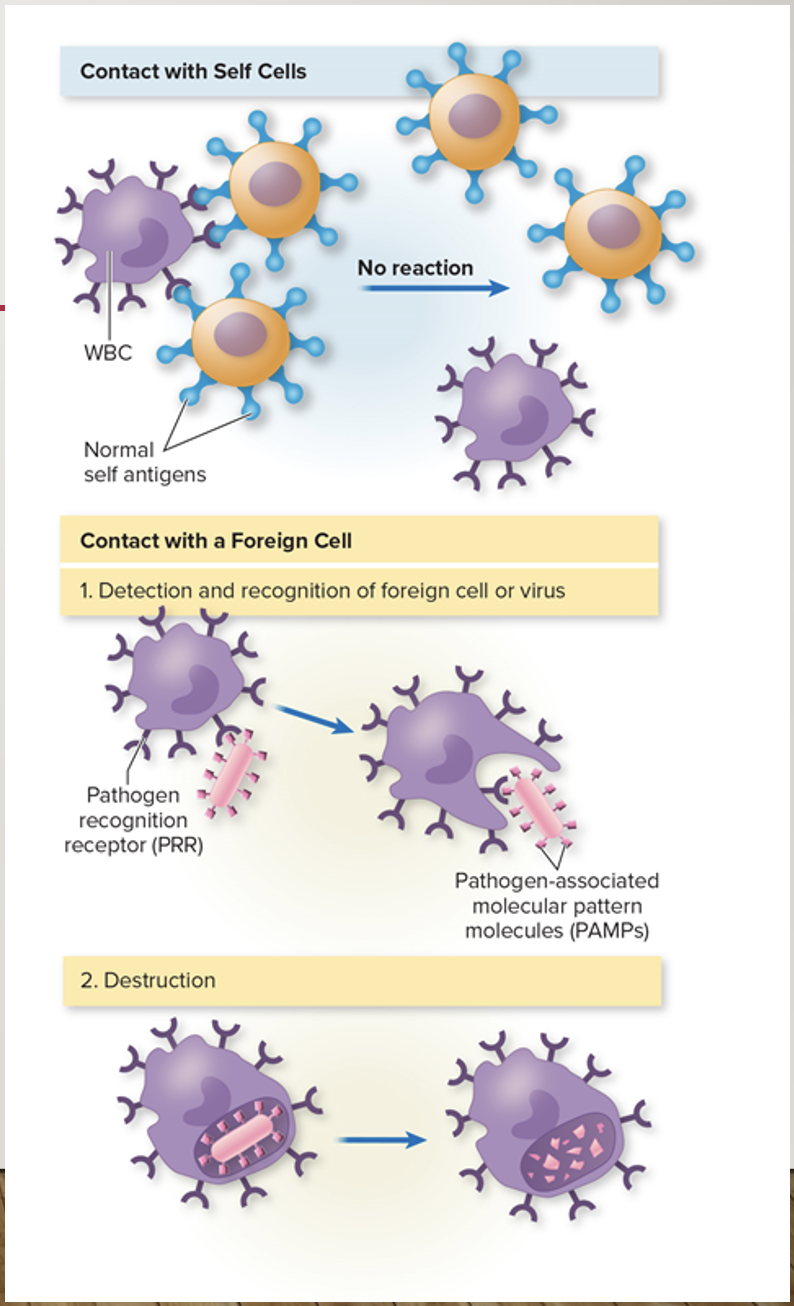
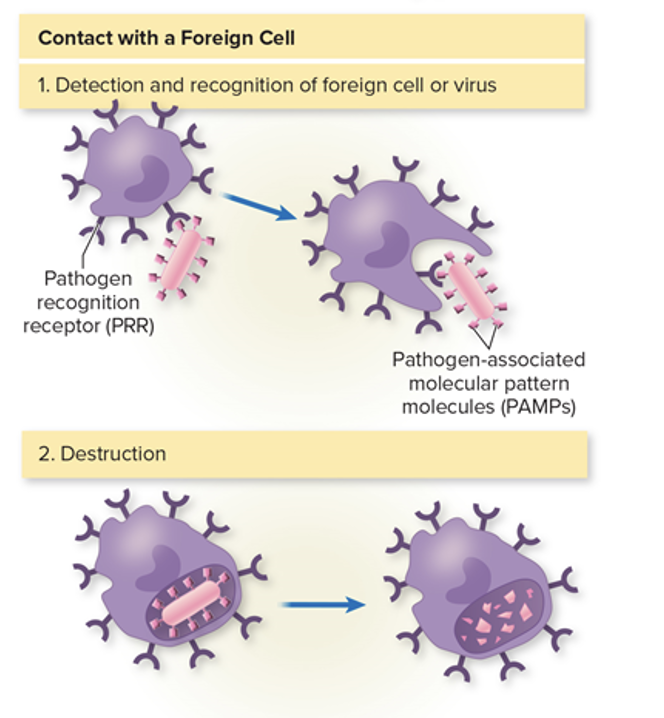
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
Innate immunity (second line)
Recognize pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules
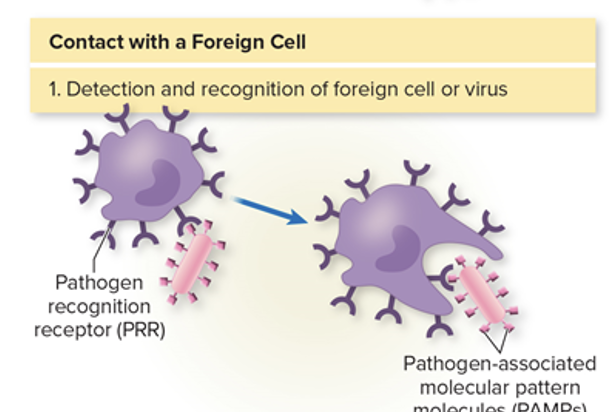
Pathogen associated molecular pattern molecules (PAMPs)
Markers that have different kinds of microbes in common
Signal phagocytes and other defensive cells
Immune system
Complex network of cells and fluids
Lymphatic system
Red bone marrow
Circulatory system
Mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS)
Phagocytic cells enmeshed on the reticulum
Located in:
Thymus
Tonsils
Spleen
Lymphoid tissues
Mucosa of gut/resp tract
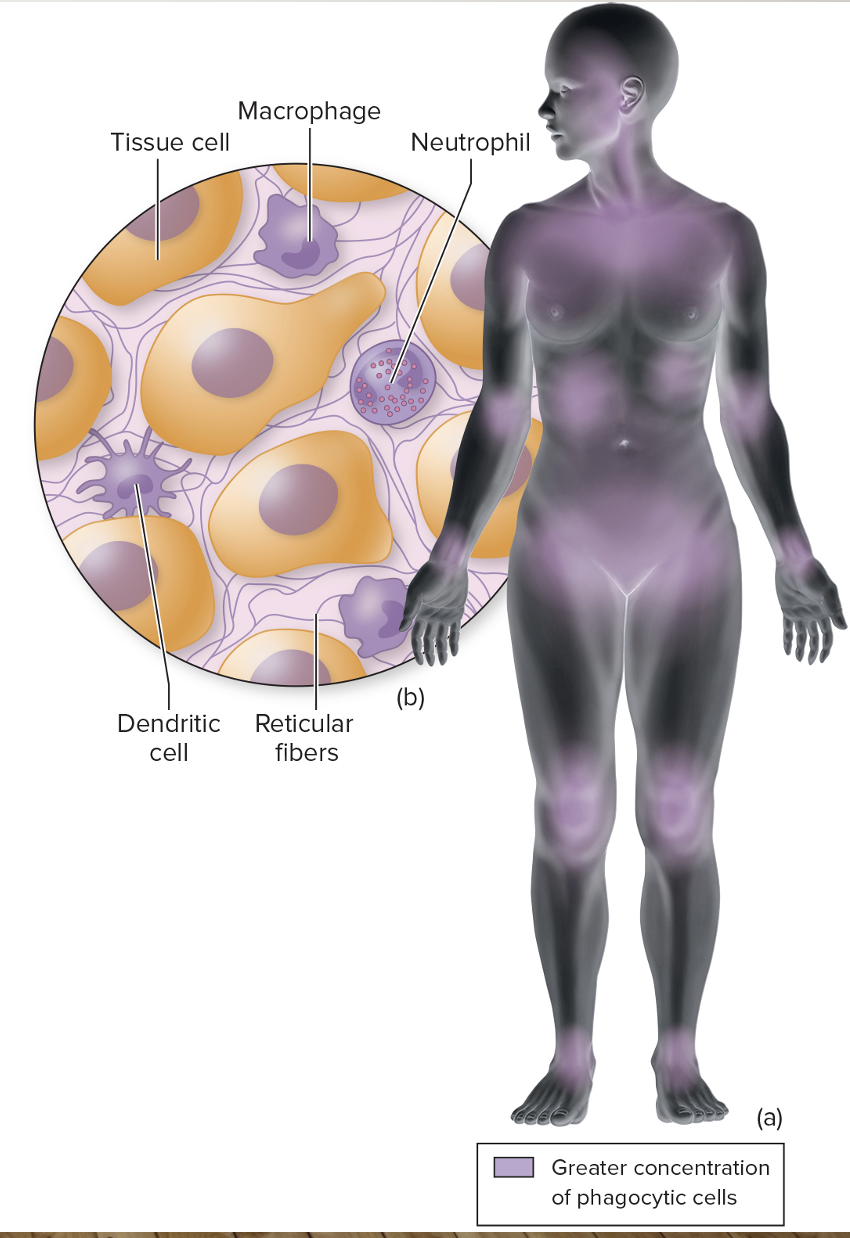
Reticulum
Connective tissues fibers that permeate tissues of the body
Interconnects cells and connective tissue that surround the organs
Lymphatic fluid
Plasma-like liquid that transports WBCs, fat, debris, and infectious agents
Primary lymphatic organs (birth, maturation)
Red bone marrow
Thymus
Secondary lymphatic organs (activation, residence, functioning)
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Associated lymphoid tissues
Red bone marrow
In flat bones and the end of long bones
Produce RBCs
B cells complete maturation here (then migrate to secondary organs)
Thymus
Site of T cell maturation (settle in lymph nodes and spleen)
Spleen
Secondary lymph organ
Filter for blood, removes worn-out blood cells
Filters pathogens from blood
Whole blood consists of:
Blood cells
Plasma
Serum
Hematopoesis
Production of blood cells
Stem cells
precursor of all new blood cells, become RBCs, platelets, and WBCs
Monocytes
Blood phagocytes that rapid leave the circulation, mature into macrophages and dendritic cells
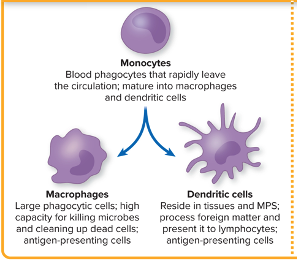
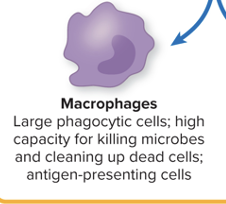
Macrophages
Large phagocytic cells,
High capacity for killing microbes and cleaning up dead cells
Antigen presenting cells
Agranulocyte
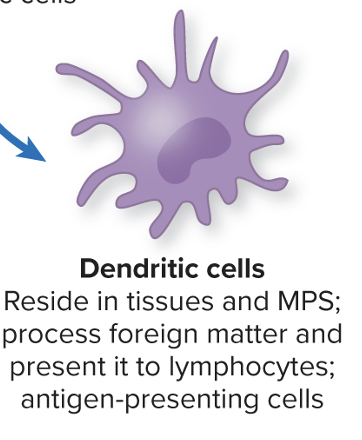
Dendritic cells
Reside in tissues and MPS, process foreign material and present to lymphocytes (antigen-presenting)
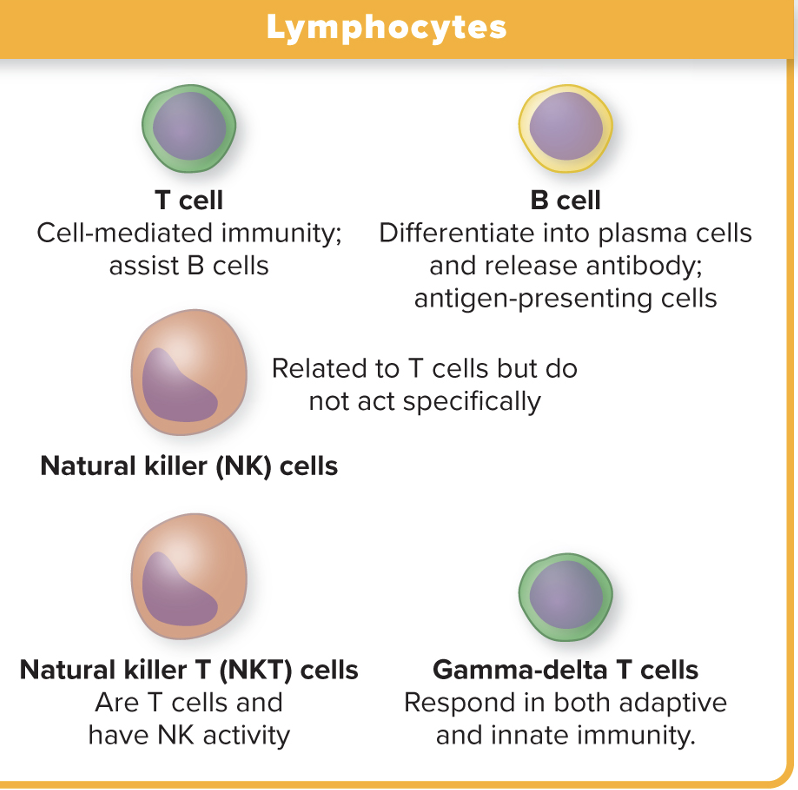
Lymphocytes
T cell
B cell
Natural killer cells
NKT cells
Gamma-delta T cells
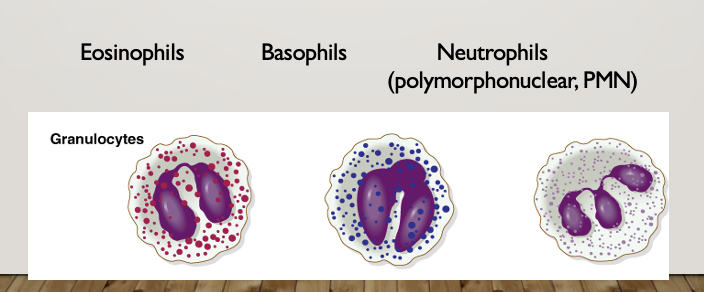
Neutrophils
Short-live phagocytes in blood, engulf and kill bacteria. Primary component of pus, high neutrophil count = bacterial infection

Basophils
Function in inflammatory events

Eosinophils
active in protozoal, helminth, and inflammatory reactions
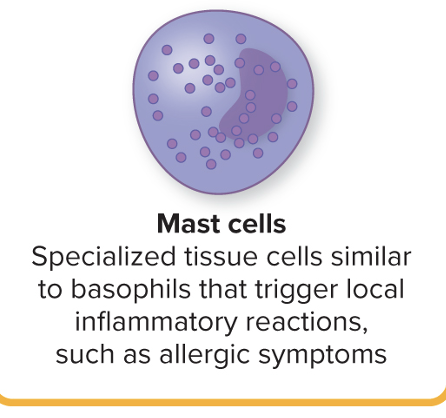
Mast cells
Specialized tissue cells similar to basophils that triger local inflammatory reactions, such as allergic symptoms
Cytokines
Regulate, stimulate and suppress cell development, inflammation, and immunity
Produced by monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, fibroblasts, mast cells, platelets, and endothelial cells
First line of defense
Physical, microbiota, and chemical barriers that impede the entry of microbes and foreign agents, whether living or not (inborn, nonspecific)
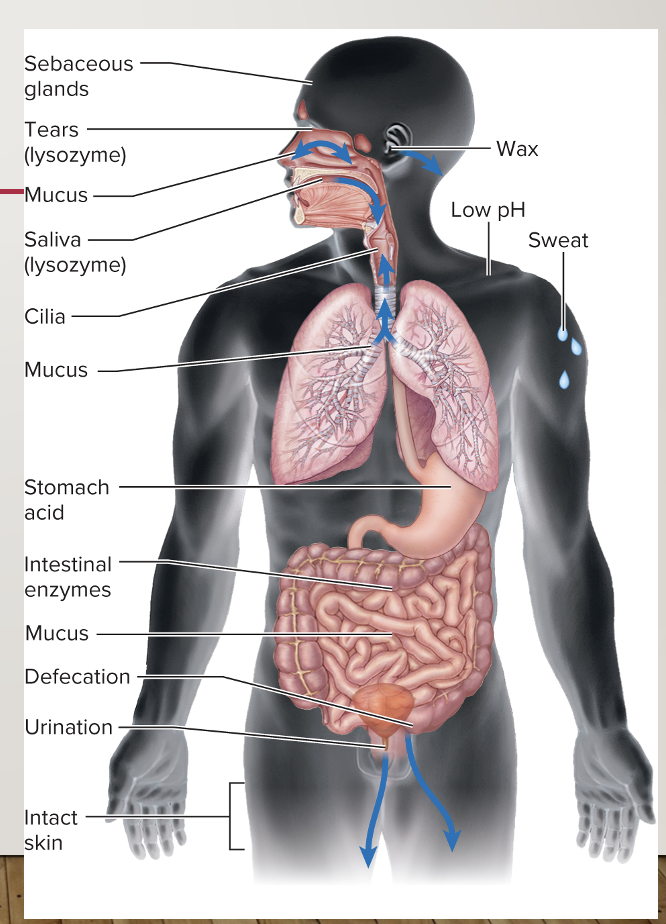
Mucous membranes
digestive, urinary, and respiratory tracts and of the eye
Defensins
antimicrobial peptides secreted from the skin, found in various body secretions
Lysozyme
Found in tears, sweat, and saliva, lyses gram positive bacteria
Iron binding proteins
Lactoferrin & transferrin
Second line of defense
Phagocytosis, inflammation, fever, antimicrobial proteins
Leukocytes
white blood cells, in two categories, granulocytes and mononuclear cells
Granulocytes
have a granular cytoplasm that contains digestive enzymes and other microbial chemicals
Eosinophils
Basophils
Neutrophils
Mononuclear leukocytes (agranulocytes)
Monocytes
Lymphocytes

5 types of leukocytes
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Eosinophils
Basophils
3 Phagocytes
Neutrophils
Monocytes
Macrophages
Histocytes
Alveolar macrophages
Kupffer cells (liver)
Dendritic cells (skin)
Macrophages (systemic)
Pathogen associated molecular. patterns (PAMPs)
Signal molecules found on microbial surfaces recognized by phagocytes and other defensive cells (peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide)
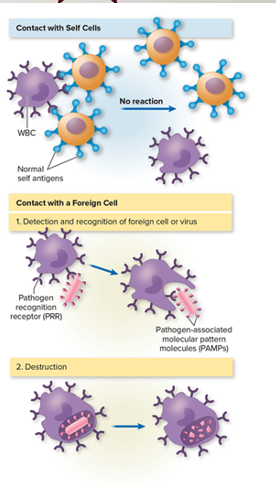
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
found on phagocytes, dendritic cells, endothelial cells, and lymphocytes, recognize and bind PAMPS
Signs of inflammation
Redness
Warmth
Swelling
Pain
Loss of function
Extravasation
how cells leave the blood vessels
Chemotaxis
migration of cells from other sites
Margination
accumulation of WBC along blood vessel wall
Diapedesis
The migration of WBCs out of blood vessels into tissues
Selectins
molecules produced by endothelial cells that attract WBCs
Integrins
on surface of WBC to help adhere to endothelial cell
Fever purposes
Inhibits rapid microbial growth
Inactivates toxins
Encourages rapid tissue repair
Heightens phagocytosis
Interferon
Small proteins produced naturally by certain white blood and tissue cells, released by infected cell to warn surrounding cell to block replication of viruses
Interferons alpha and beta
produced by lymphocytes, fibroblasts, and macrophages
Interferon gamma
produced by T cells
Complement system
consists of over 30 blood proteins, destroy bacteria and certain viruses, parasits and nearby cells