Chapter 31 clinical questions Disorders of Ventilation and Gas Exchange
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
As a consequence of a long-standing lung disease, a client is in a chronic state of hypoxia. Which of the following phenomena would the client's care team be most justified in anticipating? Select all that apply.
A) Metabolic alkalosis
B) Increased erythropoietin production
C) Pulmonary vasodilation
D) Hyperventilation
E) Personality changes
B) Increased erythropoietin production
D) Hyperventilation
E) Personality
Feedback: Increased production of erythropoietin, hyperventilation, and cognitive and personality changes are all associated with hypoxemia. Acidosis, not alkalosis, and vasoconstriction rather than vasodilation are likely to occur.
A patient who has been on a high-protein diet comes to the emergency department with respiratory symptoms. Upon analysis of arterial blood gases (ABGs), the patient is diagnosed with hypercapnia. The nurse will note the ABG results that confirm this diagnosis include: Select all that apply.
A) pH 7.31 (normal 7.35 to 7.45).
B) PO2 of 97%.
C) PCO2 of 58 mm Hg (normal 38 to 42).
D) Serum HCO3of –33 mEq/L (normal 22 to 28).
E) Serum K+ (potassium)of 3.6 mmol/L (normal 3.5 to 5.0).
A) pH 7.31 (normal 7.35 to 7.45).
C) PCO2 of 58 mm Hg (normal 38 to 42).
D) Serum HCO3of –33 mEq/L (normal 22 to 28).
Feedback: Hypercapnia affects a number of body functions, including acid–base balance and renal, neurological, and CV functions. Elevated levels of PCO2 (38 to 42) produce a decrease in pH (7.35 to 7.45) and respiratory acidosis. Compensatory mechanisms result in an increase in serum HCO3 (22 to 28). In this example, the PO2 level is within normal range. Serum K+ is not part of the ABG analysis.
A nurse is providing care for a patient who has been admitted with a newly diagnosed bilateral pleural effusion. Which of the following findings from the nurse's initial assessment of the patient is incongruent with the patient's diagnosis and would require further investigation?
A) The client complains of sharp pain exacerbated by deep inspiration.
B) The client's breath sounds are diminished on auscultation.
C) Pulse oximetry indicates that the client is hypoxemic.
D) The client complains of dyspnea and increased work of
breathing.
A) The client complains of sharp pain exacerbated by deep inspiration.
Feedback: Pleural effusion is not normally associated with pain, and intense pain that is worsened by deep breathing would necessitate further investigation. Diminished breath sounds, hypoxemia, and dyspnea are common findings associated with pleural effusion.

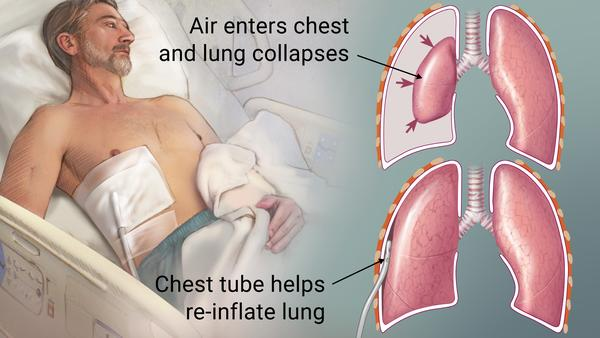
A patient arrives in the ED after an automobile accident. Which of the following clinical manifestations lead the nurse to suspect a pneumothorax? Select all that apply.
A) Respiratory rate 34
B) Asymmetrical chest movements, especially on inspiration
C) Diminished breath sounds over the painful chest area
D) Pulse oximetry 98%
E) ABG pH level of 7.38
A) Respiratory rate 34
B) Asymmetrical chest movements, especially on inspiration
C) Diminished breath sounds over the painful chest area
Feedback: Manifestations of pneumothorax include increase in respiratory rate, dyspnea, asymmetrical movements of the chest wall, especially during inspiration, hyperresonant sound on percussion, and decreased or absent breath sounds over the area of pneumothorax. The pulse oximetry reading is normal. ABG pH level of 7.38 is a normal finding.

A short, nonsmoking 44-year-old male presents to the emergency room with left-sided chest pain and a cough. He states that the pain started abruptly and worsens with deep breathing and coughing. He denies recent injury. Assessment includes shallow respirations with a rate of 36, normal breath sounds, and no cyanosis. Which condition is most likely causing his symptoms?
A) Myocardial infarction
B) Spontaneous pneumothorax
C) Pleuritis related to infection
D) Obstructive atelectasis
C) Pleuritis related to infection
Feedback: Pleuritis, which frequently accompanies infections that cause cough, is unilateral, starts abruptly, and is worsened by coughing or deep breathing. The client's shallow, rapid breathing may be due to anxiety but also is a way of maintaining adequate air intake while avoiding deep breathing, which exacerbates the pain of pleuritis. His cough may be an indication of infection, especially as he is not a smoker. The pain of myocardial infarction is not worsened by deep breathing or coughing. Spontaneous pneumothorax would be very unlikely in a short, nonsmoking middle-aged man. Tachypnea might indicate obstructive atelectasis, but normal breath sounds and lack of cyanosis argue against it.
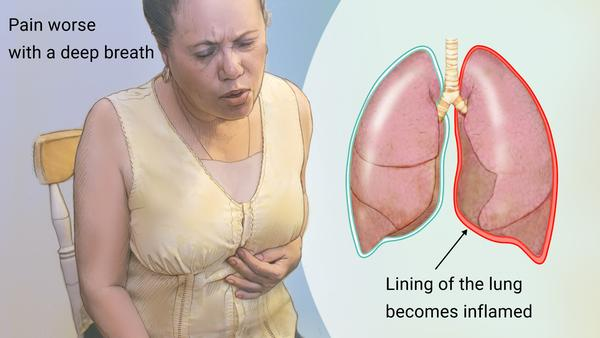
A 51-year-old female client who is 2 days postoperative in a surgical unit of a hospital is at risk of developing atelectasis as a result of being largely immobile. Which of the
following teaching points by her nurse is most appropriate?
A) “Being in bed increases the risk of fluid accumulating between your lungs
and their lining, so it's important for you to change positions often.”
B) “You should breathe deeply and cough to help your lungs expand as much as
possible while you're in bed.”
C) “Make sure that you stay hydrated and walk as soon as possible to avoid us
having to insert a chest tube.”
D) “I'll proscribe bronchodilator medications that will help open up your airways and
allow more oxygen in.”
Ans: B
Feedback:
Atelectasis is characterized by incomplete lung expansion and can often be prevented by
deep breathing and coughing. Pleural effusion, not atelectasis, is associated with fluid
accumulation between the lungs and their lining, and neither chest tube insertion nor
bronchodilators are common treatments for atelectasis.
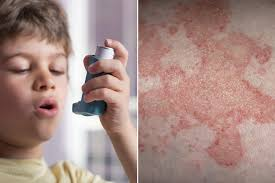
Which of the following statements best captures the etiology of the acute response phase of extrinsic (atopic) asthma?
A) IgG production is heightened as a consequence of exposure to an allergen.
B) Airway remodeling results in airflow limitations.
C) Epithelial injury and edema occur along with changes in mucociliary function.
D) Chemical mediators are released from presensitized mast cells.
D) Chemical mediators are released from presensitized mast cells
Feedback: The acute response phase of extrinsic asthma is characterized by the release of chemical mediators from mast cells that have been sensitized. Epithelial injury and edema, as well as airway remodeling, are not associated with the acute phase, and IgE, not IgG, is primarily involved in asthma.

The mother of a 7-year-old boy who has recently been diagnosed with childhood asthma has come to the education center to learn more about her son's condition. Which of the following teaching points is most justifiable?
A) “Research has shown that viruses may actually be a factor in many children's asthma.”
B) “The most reliable indicator that your child is having an asthma attack is audible wheezing.”
C) “Steroids that your child can inhale will likely be the first line of defense.”
D) “Your son will likely need to limit or avoid exercise and sports.”
A) “Research has shown that viruses may actually be a factor in many children's
Feedback: Viruses have been implicated as a contributing factor in childhood asthma. Wheezing may or may not be present in children, and inhaled corticosteroids are not common as an initial therapy. Current treatment guidelines do not advise the categorical avoidance of exercise

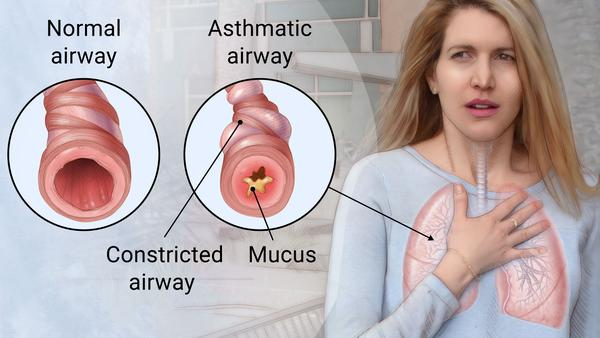
In the early morning, an African American woman brings her 5-year-old son to the emergency room. The boy is wheezing, is short of breath, and has a dry cough. The mother states that he has always been very healthy. He went to bed with only a slight cold and a runny nose but woke her with his coughing shortly after 4 AM. His symptoms worsened so dramatically that she brought him to the hospital. The care team would most likely suspect that he has
A) respiratory syncytial virus.
B) influenza.
C) asthma.
D) pneumonia
C) asthma.
Feedback: Although the child may have an infectious disease, his symptoms and the timing of them (both in terms of his age and the time of symptom onset) are classic for asthma. They are not as closely associated with RSV, influenza, or pneumonia.
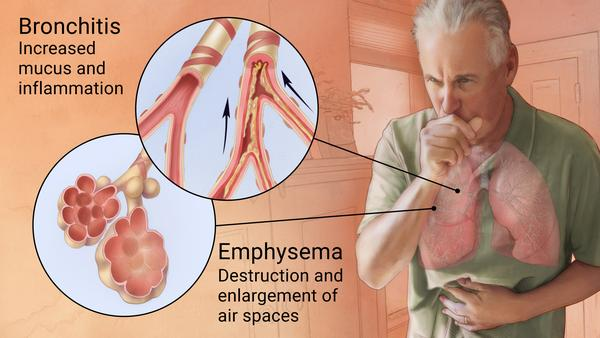
Which of the following residents of a long-term care facility is most likely to be exhibiting the signs and symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
A) A 79-year-old lifetime smoker who is complaining of shortness of breath and pain
on deep inspiration
B) An 81-year-old smoker who has increased exercise intolerance, a fever, and
increased white blood cells
C) An 81-year-old male who has a productive cough and recurrent respiratory infections
D) An 88-year-old female who experiences acute shortness of breath and airway
constriction when exposed to tobacco smoke
C) An 81-year-old male who has a productive cough and recurrent respiratory infections
Feedback: Productive cough and recurrent respiratory infections are associated with COPD, while pain, fever, and increased white cells are not common signs and symptoms of COPD. Acute shortness of breath and bronchoconstriction are associated with asthma.

A COPD patient asks the nurse what medications are prescribed to help his breathing. The nurse, looking at the list of medications, will educate the patient about which of the following medications to help his COPD in the long term? Select all that apply.
A) Salmeterol (Serevent), a bronchodilator
B) Tiotropium (Spiriva), anticholinergic
C) Alprazolam (Xanax), a benzodiazepine
D) Sildenafil (Viagra), a vasodilator
E) Ketorolac (Toradol), an NSAID
A) Salmeterol (Serevent), a bronchodilator
B) Tiotropium (Spiriva), anticholinergic
Feedback: Pharmacologic treatment of COPD includes the use of bronchodilators (Serevent) and anticholinergic drugs (Tiotropium). Benzodiazepines are used for anxiety, and sildenafil is a vasodilator commonly prescribed not only for erectile dysfunction but also for patients with pulmonary hypertension. Toradol (ketorolac) is an NSAID for pain and inflammation.
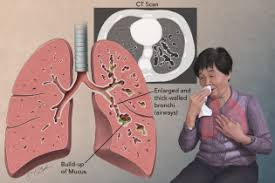
A nurse is providing care for a client who has been admitted to a medical unit with a diagnosis of bronchiectasis. Which of the following signs and symptoms should the nurse expect to find during physical assessment of the client and the review of the client's history? Select all that apply.
A) Recurrent chest infections
B) Production of purulent sputum
C) A barrel chest
D) Low hemoglobin levels
E) Recent surgery
A, B, D
Feedback: Chest infections, copious production of purulent sputum, and anemia are all associated with bronchiectasis. A barrel chest is more commonly evident with emphysema, and recent surgery is not a noted factor.
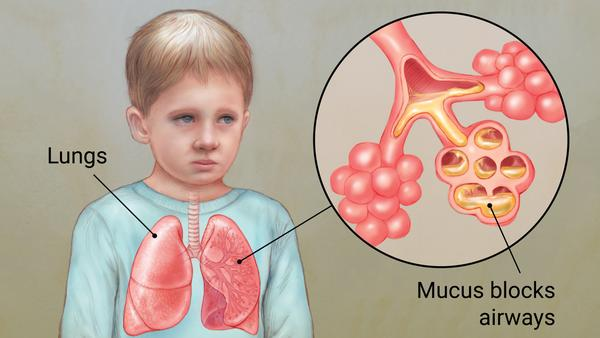
A physician is providing care for a child who has a diagnosis of cystic fibrosis (CF). Place the following events in the etiology of CF in ascending chronological order. Use all the options.
A) Airway obstruction
B) Recurrent pulmonary infections
C) Impaired Cl– transport
D) Decreased water content of mucociliary blanket
E) Increased Na+ absorption
C, E, D, A, B
Feedback: CF is associated with impaired Cl– transport and a consequent increase in Na+ absorption. These result in a lowered water content of the mucociliary blanket making it more viscid. These changes to the mucociliary blanket cause airway obstruction and, ultimately, pulmonary infections.
Which of the following clinical findings would be most closely associated with a client who has interstitial lung disease in comparison to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
A) Audible wheezing on expiration
B) Reduced expiratory flow rates
C) Decreased tidal volume
D) Normal forced expiratory volume
C) Decreased tidal volume
Feedback: Because it takes less work to move air through the airways at an increased rate than it does to stretch a stiff lung to accommodate a larger tidal volume, interstitial lung disease is commonly associated with an increased respiratory rate but decreased tidal volume. Wheezing and decreased expiratory flow rate are more closely associated with COPD.
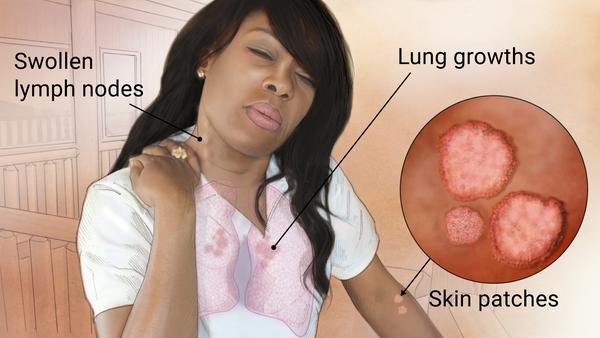
A patient is admitted for a relapse for sarcoidosis. Knowing this is usually caused by an inflammatory process, the nurse can anticipate administering
A) a bronchodilator.
B) a corticosteroid.
C) aspirin.
D) an albuterol inhaler.
B) a corticosteroid.
Feedback: Treatment is directed at interrupting the granulomatous inflammatory process that is characteristic of the disease and managing the associated complications. When treatment is indicated, corticosteroid drugs are used. Bronchodilators may be used if there is wheezing, but this is not a normal medication for this disease. Aspirin is a blood thinner. Albuterol is a short-term bronchodilator for acute asthma
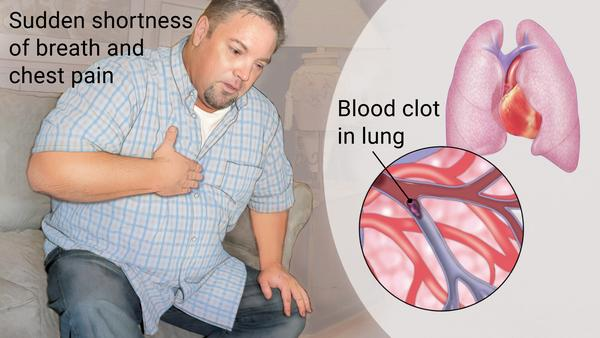
Which of the following clients are displaying known risk factors for the development of pulmonary emboli? Select all that apply. A client who is:
A) immobilized following orthopedic surgery.
B) experiencing impaired Cl– and Na+ regulation.
C) taking amiodarone for the treatment of premature ventricular contractions.
D) a smoker and who takes oral contraceptives.
E) undergoing radiation therapy for the treatment of breast
cancer.
A) immobilized following orthopedic surgery
D) a smoker and who takes oral contraceptives.
Feedback: Postsurgical immobility, smoking, and the use of oral contraceptives are all identified risk factors for the development of pulmonary emboli. Impaired Cl– and Na+ regulation are associated with cystic fibrosis, while amiodarone and radiation therapy are linked to interstitial lung diseases.
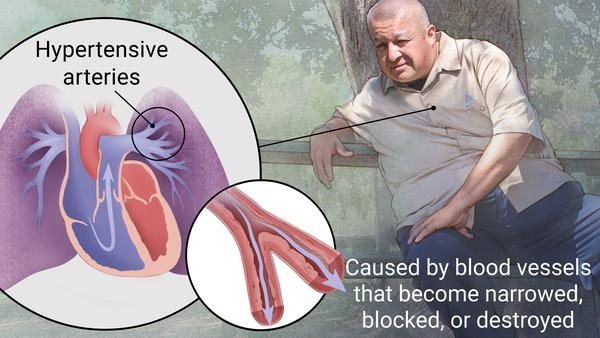
A patient with pulmonary hypertension may display which of the following clinical manifestations? Select all that apply.
A) Shortness of breath
B) Decreased exercise tolerance
C) Nasal flaring
D) Grunting on expiration
E) Swelling (edema) of the legs and feet
A) Shortness of breath
B) Decreased exercise tolerance
E) Swelling (edema) of the legs and
Feedback: Symptoms of PAH typically progress from shortness of breath and decreasing exercise tolerance to right heart failure, with marked peripheral edema and functional limitations. Other common symptoms include fatigue, angina, and syncope (fainting) or near-syncope. Nasal flaring and expiratory grunting are usually seen in infants experiencing respiratory distress.
Upon admission to the ICU, a patient with a history of cor pulmonale will likely be exhibiting which of the following clinical manifestations of right heart failure? Select all that apply.
A) Fine crackles throughout both lung fields
B) +4 pitting edema in lower extremities
C) Expectorating copious amounts of frothy, pink sputum
D) Jugular vein distension
E) Altered level of consciousness
B) +4 pitting edema in lower extremities
D) Jugular vein distension
E) Altered level of consciousness
Feedback: Signs of right-sided HF include venous congestion (jugular vein distension), peripheral edema (+4 pitting edema in feet), shortness of breath, and productive cough. Altered level of consciousness may occur as the result of carbon dioxide retention. Fine crackles in all lung fields and frothy, pink sputum are common in left-sided HF.
A 41-year-old male client has presented to the emergency department with an acute onset of increased respiratory rate and difficulty breathing. STAT chest x-ray indicates diffuse bilateral infiltrates of his lung tissue, and ECG displays no cardiac dysfunction. What is this client's most likely diagnosis?
A) Cor pulmonale
B) Acute lung injury
C) Pulmonary hypertension
D) Sarcoidosis
B) Acute lung injury
Feedback: Rapid onset of respiratory distress accompanied by diffuse bilateral infiltrates of lung tissue and an absence of cardiac changes are associated with acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. These particular signs and symptoms are not as closely associated with cor pulmonale, pulmonary hypertension, or sarcoidosis.

While rock climbing, a 22-year-old male has endured a severe head injury. Which of the following statements best captures expected clinical manifestations and treatments for his immediate condition?
A) Oxygen therapy is likely to decrease his respiratory drive and produce an
increase in PCO2.
B) Cheyne-Stokes breathing is likely but will respond to bronchodilators.
C) The client is unlikely to respond to supplementary oxygen therapy due to impaired
diffusion.
D) Hypoventilation may exist, resulting in increased PCO2 and hypoxemia that may require mechanical ventilation.
D) Hypoventilation may exist, resulting in increased PCO2 and hypoxemia that may require mechanical ventilation.
Feedback: Brain injuries and accompanying hypoventilation are often associated with increased PCO2 and by hypoxemia that responds to oxygen therapy. Persons with COPD are more vulnerable to diminished respiratory drive secondary to oxygen therapy, while Cheyne-Stokes breathing is not identified as a likely consequence of brain injury. Impaired alveolar diffusion is not an aspect of the client's injury.