science test
1/118
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Inertia is...
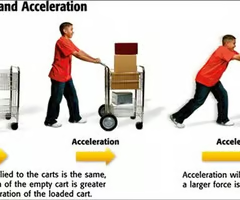
Newtons 2nd Law of Motion says…
acceleration is based on an objects mass and force applied to it






Animal Cell
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
Found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes and produces proteins
Electron Cloud
In order to have a current flowing, a circuit must:
be closed
An electrical current in a metal wire is a flow of:
electrons
The higher the voltage supplied to a circuit:
the bigger the "push" received by electrons
When a charged battery is connected to a closed circuit, electrons flow from the ____________ terminal to the ____________ terminal.
positive; negative
Most electric heaters work by passing an electrical current through a component with very high resistance.
Resistance arises from the collisions between flowing electrons and atoms; when electrons slow down their energy is converted into heat
Recall which units are used to measure resistance.
Ohms
Adding resistance to a circuit will:
decrease the current
Identify what current (I) is equal to, according to Ohm's law.
voltage divided by resistance (I = V/R)
A student is investigating a circuit with a fixed total resistance. When the student doubles the voltage by adding another battery, the current will:
stop
The circuit in a particular toy car has a total resistance of 400 Ω and the battery is supplying 4 V. Calculate how much current, in amps (A), is flowing.
1600 A
An electrician measures the current flowing through a 1000 Ω resistor as 0.02 A. Calculate what the voltage supplied to this resistor must be.
50,000 V
A student constructs the circuit shown on the right and measures the current through the ammeter (A) to be 0.4 A. Assuming that the loudspeaker and wires have zero resistance, determine the value of the resistor.
30 Ω
A student varies the voltage across a resistor of unknown value and measures the current. The data is graphed on the left. Determine the value of the unknown resistor.
400 Ω
What is the unit of measurement for electrical current?
Amperes
When resistance in a circuit increases, what happens to the current?
It decreases
What happens to the current in a circuit if you increase the voltage while keeping the resistance constant?
The current increases
In a series circuit, how do the resistance values add up?
They add up