Biology Final 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
1
New cards
Biome
region characterized by distinct abiotic characteristics and dominant vegitation
2
New cards
Tropical Rainforest
at equator, hot, no seasons, lots of rainfall, constant growing season, lush vegetation
3
New cards
Tropical Savanna
on either side of equator, grasslands, always growing season, seasonal rainfall, wet and dry seasons, variation in temperature
4
New cards
Desert
30 N and 30 S, very dry, can be hot or cold, some have seasons, low precipitation, cacti
5
New cards
Temperate Grassland
true seasons, Kansas, specific growing season in spring and summer, seasonal rainfall, few trees, thick organic layer on soil, farmland
6
New cards
Temperate Forest
seasons, growing seasons, us, changes in temperature, steady rainfall throughout year, true growth
7
New cards
Boreal Forest
northern hemisphere, limited growing season, very cold most of the year, lots of seasonality, not a lot of rain, dry band, acidic soil, coniferous trees
8
New cards
Tundra
extremely short growing season, minimally seasonal, low precipitation, dry, windy, cold, sparse vegetation
9
New cards
Population
individuals of a certain species in a certain area that can interbreed
10
New cards
Ecology Order
ecosystem, community, population, organism
11
New cards
Community
all species in a particular region
12
New cards
Ecosystem
all abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) organisms in a particular region
13
New cards
Abiotic
non-living
14
New cards
Niche
the specific conditions a species can tolerate
15
New cards
Climate
long-term weather conditions
16
New cards
Weather
short-term atmospheric conditions
17
New cards
Rainshadow
land forced to become a desert because mountains block water from covering it
18
New cards
Neritic Zone
area between intertidal zone and continental shelf
19
New cards
Intertidal Zone
area below highest tide and above lowest tide
20
New cards
Benthic
on the bottom
21
New cards
Photic Zone
area of water that light can penetrate (photosynthesis)
22
New cards
Aphotic Zone
area light cannot penetrate
23
New cards
Resource Partitioning
way that species reduce competitive exclusion by allowing them to coexist, roots are different lengths
24
New cards
Competitive Exclusion
two species compete for the same resource, and one is driven to local extinction
25
New cards
Ways to Prevent Competitive Exclusion
resource partitioning, character displacement
26
New cards
Character Displacement
way to prevent competitive exclusion by shifting the range of variation for specific traits, birds with different beaks
27
New cards
Species Richness
number of species in a community
28
New cards
Species Eveness
relative abundance of species in an area
29
New cards
Biosphere
regions of the earth populated by certain organisms
30
New cards
Abundance
total number of a species in an area
31
New cards
Density
amount of each species in an area
32
New cards
Cohort
group of same-aged individuals
33
New cards
Cohort Life Table
estimates survivorship and fecundity of a cohort
34
New cards
Static Life Table
"screenshot" of the specific age at death of individuals in a species
35
New cards
Survivorship Curve
a summary of pattern of survival in a population, three types
36
New cards
Curve Type I
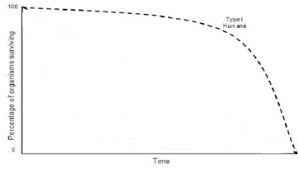
37
New cards
Curve Type II
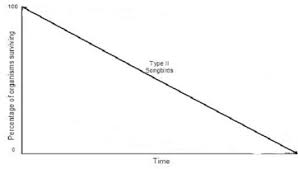
38
New cards
Curve Type III
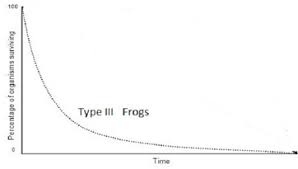
39
New cards
Fecundity
reproductive output
40
New cards
Ecological Efficiency
percent of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next
41
New cards
Primary Producer
bottom of food chain, plants
42
New cards
Primary Consumer
second to last in food chain, insects
43
New cards
Secondary Consumer
second from top in food chain, birds and fish
44
New cards
Tertiary Consumer
top of food chain, bears and wolves
45
New cards
Primary Succession
new growth on freshly exposed substrates (moss, liverworts)
46
New cards
Functional Response
increase in animal feeding rate
47
New cards
Numerical Response
change in density of a predator population
48
New cards
Commensalism
one species benefits while the other is unaffected
49
New cards
Mutualism
both species benefit
50
New cards
Competition
neither species benefit
51
New cards
Predation
one species benefits while the other suffers
52
New cards
Parasitism
one species benefits while the other struggles
53
New cards
Keystone Species
species that has a greater influence on an ecosystem than their abundance would predict, wolves
54
New cards
Deuterostome
anus develops first, largest and most morphologically complex
55
New cards
Biomass
mass or weight of living tissue
56
New cards
Secondary Succession
growth following disturbance, fire
57
New cards
Pioneer Species
colonizing species present in early habitats
58
New cards
Climax Community
late community that remains stable until a disturbance
59
New cards
Pentaradial Symmetry
divisible into five equal parts, adult echinoderms
60
New cards
Vertebrae
chordate with a backbone, protects spinal chord and brain, central nervous system
61
New cards
Cranium
skull
62
New cards
Tetrapod
species with four legs
63
New cards
Tetrapod Adaptations
vertebrae column, fins for crawling, nostrils and lugs, modified sensory systems
64
New cards
Amniote
organism that lays shelled, amniotic eggs
65
New cards
Homonid
great apes, large body, long arms, short legs, no tail, distinct walking patters
66
New cards
Anthropoid
human-like primates
67
New cards
Ectotherm
require heat from outside the body
68
New cards
Endotherm
can heat themselves
69
New cards
Major Lineages of Deuterostomes
echinoderms, chordates, hemichordes, xenoturbella
70
New cards
Echinoderm Characteristics
1 bilaterally symmetrical larvae
2 edoskeleton
3 tube feet (ampulla inside and podium outside)
4 mass, suspension, and graze feeding
2 edoskeleton
3 tube feet (ampulla inside and podium outside)
4 mass, suspension, and graze feeding
71
New cards
Chordate Characteristics
1 notochord
2 pharyngeal gill slits
3 dorsal hollow nerve chord
4 post anal tail
2 pharyngeal gill slits
3 dorsal hollow nerve chord
4 post anal tail
72
New cards
Lineages of Chordates
1 Cepholochordates
2 Urochordates
3 Vertebrates
2 Urochordates
3 Vertebrates
73
New cards
Vertebrate Lineages
1 fish (gnathostomata)
2 amphibians
3 reptiles
4 mammals
5 birds
2 amphibians
3 reptiles
4 mammals
5 birds
74
New cards
Agnathans
jawless fish, hagfishes and lamprey, typically parasites
75
New cards
Gnathostomata
jawed fishes
76
New cards
Actinoptergyii
bony fish, ray-finned
77
New cards
Sarcopterygii
bony fish, deemed necessary to evolutionary tree
78
New cards
Amphibians
first tetrapod on land, adults on land, eggs in water, gas exchange on moist skin, lungs, metamorphosis, salamanders
79
New cards
Orders of Amphibians
1 Caudata (tail)
2 Anura (no tail)
3 Gymnophiona (legless, worm-like)
2 Anura (no tail)
3 Gymnophiona (legless, worm-like)
80
New cards
Reptile Lineages
1 Lizards and Snakes
2 Turtles
3 Crocodiles and Alligators
4 Birds
2 Turtles
3 Crocodiles and Alligators
4 Birds
81
New cards
Reptile Characteristics
water-tight skin, lungs, amniotes, ectotherms
82
New cards
Mammal Characteristics
lactation, endotherms, hair, grew during K-T boundary, first were small and nocturnal
83
New cards
Lineages of Mammals
1 Egg-laying Monotremes
2 Marsupials
3 Placental
2 Marsupials
3 Placental
84
New cards
Anthropoid Characteristics
1 hands and feet that can grasp
2 flattened nails
3 large brains
4 color vision
5 complex social behavior
6 parental care
7 forward-facing eyes
2 flattened nails
3 large brains
4 color vision
5 complex social behavior
6 parental care
7 forward-facing eyes
85
New cards
Amniotic Egg
a hard-shelled egg filled with fluid membranes and a yolk that will develop into an embryo
86
New cards
Humans to Primates
humans are a subset of anthropoidal primates
87
New cards
Cause of Climates
earth's tilt and rotation around the sun
88
New cards
Salinity
proportion of solutes dissolved in water
89
New cards
Water Depth
affects sunlight availability
90
New cards
Nutrient Avalability
coastal runoff, ocean upwelling, and lake turnover cause change in nutrients
91
New cards
Lake Turnover
shift of hot and cold water in lakes, winter stratification, spring turnovers, summer stratification, and fall turnovers
92
New cards
Exponential Population Growth
upward curve, continuous population growth in an unlimited environment
93
New cards
Logistic Population Growth
s-shaped, as resources are depleted, population growth rate slows and eventually stops
94
New cards
Carrying Capacity
the maximum amount of individuals an environment can support
95
New cards
Density-Dependent Factors
disease and resource competition
96
New cards
Density Independent Factors
natural disasters and weather
97
New cards
Arms Race
predator and prey are always in competition to out-do one another, the prey evolves to survive and the predators evolve to kill
98
New cards
Top-Down Controls
factors that influence consumers, and go on to have effects that trickle down the food web
99
New cards
Bottom-Up Controls
influences of physical and chemical factors on the primary producers of an ecosystem, usually cause a decrease in all above organisms
100
New cards
Ecological Succession
gradual change in plant and animal communities in an area following a disturbance