Theory
1/324
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
325 Terms
What are the factors of production? name them all.
Four categories of resources that are required to produce any good or service. Land, labour, capital and enterprise.
Explain the interaction of the circular flow of income
households provides resources to businesses
firms provide income to household
firms uses the resources to produce goods and services for households.
households provide expenditure to business
\
The cycle repeats.
What are the assumptions in the circular flow of income
- There are only two sectors
- There is no saving
- There is no inventory (assets)
Assumptions of the Production Possibilities Curve
there is a fixed amount of resources
only two goods are being produced
technology and production techniques are fixed
all resources are used efficiently meaning no one is unemployed/ no good s are wasted.
What is the PPC (Production possibilities curve)
a model which illustrates the different combinations of two goods or services that an economy or firm can produce.
(good A and Good Bin the axis)
what does a point on the PPC mean?
All resources are employed and are used efficiently
What does a point within the PPC mean?
some resources are unemployed or used inefficiently
What does a point outside of the PPC mean?
not possible with the current level of resources
When does a linear PPC occur?
due to the marginal rate of transformation being constant throughout the curve
A linear PPC represents constant opportunity costs.
This is when for each additional unit produced, the same level of sacrifice is needed. The opportunity cost doesn't change as an economy shifts resources from one good to the other.
This occurs because all factors of production are equally useful for alternative production decisions, and resources can be easily reallocated between the two goods without increasing trade-offs.
When does a concave PPC occur?
A concave PPC represents increasing oppurtunity costs.
This is when for each additional unit produce, an increasingly larger sacrifice is needed.
This exists because not all factors of production are equally useful for alternative production decisions.
When can an economy’s PPC shift outwards?
An increase in the quantity of resources
An improvement in the quality of resources
an improvement in technology
what does an outward shift in the PPC indicate?
economic growth. occurs when there is an increase in the productive potential of an economy.
what does an inward shift in the PPC indicate?
Economic decline. Occurs when there is any impact on any economy that reduces quantity or quality.
What does positive economics use?
"Lions Roar, Howling Monkeys, They Explore Caves’’
Logic: Lions
Reasoning: Roar
Hypothesis: Howling
Models: Monkeys
Theories: They
Empirical Evidence: Explore
Ceteris Paribus Assumption: Caves
What does poverty address?
The distribution of income:
How money earned through work or investments is shared among people
The distribution of wealth:
How properties, stocks and savings are distributed
Because addressing poverty often involves both increasing equality (by redistributing resources) and promoting equity (by meeting the specific needs of disadvantaged individuals).
What factors affects economic inequality
Education and skill levels
Tax policies and social welfare programs
Economic structure and employment opportunities
Consequences of income inequality
Social: Increased crime rates, reduced social cohesion, and political instability.
Economic: Reduced economic growth, as lower-income individuals have less purchasing power.
Health: Worse health outcomes for those in lower economic strata.
What are the trends in economic inequality?
Technological advancement: Benefits highly skilled workers more, increasing inequality.
Globalization: Outsourcing and offshoring can reduce wages for low-skilled workers in developed countries.
Pandemic effects: COVID-19 disproportionately affected low-income individuals.
How to interpret a Lorenz curve?
The further the Lorenz Curve is from the line of equality, the greater the inequality.
Policymakers use this visual tool to assess economic inequality.
Why is wealth inequality usually higher than income inequality?
Higher income people are able to save more of their income and accumulate wealth.
The slow growth in wages hinders the accumulation of wealth by the poor.
What is a composite indicator of poverty
The MPI includes three main dimensions, each with specific indicators:
Health: Child mortality, nutrition
Education: Years of schooling, school attendance
Living Standards: Access to clean water, electricity, sanitation, housing, and assets
Struggles of emasuring poverty?
Data availability and reliability
Cultural differences in defining basic needs
Changing economic conditions and inflation
What are the 3 types of sustainability?
Economic Sustainability: Ensuring that economic activities can continue over the long term without exhausting resources
Environmental Sustainability: Preserving natural ecosystems and resources for future generations
Social Sustainability: Promoting social equity, justice, and well-being for all members of society
What strategies can promote sustainable development ?
Renewable Energy: Investing in solar, wind, and other renewable sources
Education and Awareness: Teaching communities about sustainable practices
Technological Innovation: Developing technologies that reduce resource consumption
Policy and Regulation: Implementing laws that protect the environment
What are the challenges to sustainable development?
Political and economic interests
Lack of awareness and education
Technological and financial barriers
Conflicting interests between stakeholders
What are the challenges of implementing the SDGs
Financing: Mobilising the estimated trillions of dollars needed annually to achieve the goals.
Data and Monitoring: Collecting reliable data to track progress and hold governments accountable.
Policy Coherence: Ensuring that policies in different sectors support rather than undermine sustainable development objectives.
What is social progress and what are the different types of social progress
Social progress enhances human capital, which in turn supports economic growth and development.
Education
Increases productivity
Empowers individuals
Promotes innovation
Health
Extends life expectancy
Reduces disease burden
Improves quality of life
Equality
Gender equality
Social inclusion
Equal opportunities
What is political progress and what are the different aspects of it?
providing the institutional framework necessary for progress. Good governance ensures that resources are used effectively and equitably
Democracy
Promotes accountability
Protects human rights
Encourages citizen participation
Rule of Law
Ensures justice and fairness
Protects property rights
Reduces corruption
Governance
Effective institutions
Transparent decision-making
Responsive policies
What is environmental progress and what are the different aspects of it?
ensures that natural resources are preserved for future generations. Without sustainable practices, short-term gains can lead to long-term losses.
Sustainable Development
Balancing economic growth with environmental protection
Integrating environmental considerations into decision-making
Resource Management
Renewable energy
Conservation of biodiversity
Sustainable agriculture
Climate Change
Mitigation strategies
Adaptation measures
International cooperation
Difference between economic growth and development
Economic growth increase in GDP.
Economic development increase in welfare. This includes wealth but also quality of life.
Economic growth refers to quantitative increases in output (usually measured by GDP), while economic development encompasses qualitative improvements in living standards, including social, political, and environmental progress.
Economic Growth: An increase in a country's output of goods and services, usually measured by GDP.
Quantitative
Short-term focus
Can occur without improving people's lives
Economic Development: A broader process that includes economic growth but also improvements in quality of life.
Qualitative
Long-term focus
Emphasizes human well-being
Limitations for GDP per capita
measures average income but doesn't show how income is distributed.
doesn't account for non-monetary aspects of well-being, like health or education.
can be misleading in countries with high income inequality.
Limitations and advtanges of single indicators
Limited Scope
Single indicators capture only one aspect of economic development, missing other important factors.
For example, GDP per capita doesn't reflect income inequality or environmental sustainability.
Lack of Context
Single indicators can be misleading without additional information.
High school enrollment rates don't reveal the quality of education.
Data Reliability Issues
In many developing countries, data may be incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated.
This can lead to misleading conclusions.
Simplicity and Clarity
Single indicators are easy to understand and interpret because they focus on one specific measure.
Examples include GDP per capita, literacy rate, and life expectancy.
Comparability
Single indicators allow for straightforward comparisons between countries and over time.
They provide objective, quantifiable data that can be easily tracked.
Focused Analysis
Policymakers can target specific issues by analyzing single indicators.
For example, a low literacy rate can highlight the need for educational reforms.
Limitations of HDI
It does not account for income inequality
It ignores environmental sustainability
It excludes important aspects like political freedom and security
Advantages and disadvantages of composite indicators
Composite indicators offer several advantages:
Multidimensional Perspective
providing a broader view of development.
Better Policy Guidance
help identify patterns and correlations between different aspects of development.
They can highlight areas where progress in one area lags behind others.
Standardized Measurement
allow for rankings and benchmarks, facilitating international comparisons.
However, they also have drawbacks:
Complexity
Composite indicators can be difficult to interpret due to their multidimensional nature.
Understanding what drives changes in the overall index requires analyzing individual components.
Weighting and Subjectivity
Different components must be weighted, introducing subjectivity.
Deciding which aspects are more important can vary between experts and organizations.
Data Limitations
Composite indicators rely on the quality of underlying data.
Missing or inaccurate data in one component can affect the overall index.
How can economic development occur without growth?
By reallocating resources towards merit goods (like education and healthcare) within the existing production possibilities, improving quality of life without increasing total output.
What factors contribute to the poverty cycle?
Economic factors: Lack of access to credit, high unemployment rates
Social factors: Discrimination, lack of social networks
Geographical factors: Living in remote or resource-poor areas
Political factors: Corruption, lack of government support
Role of human capital in Poverty traps
Human capital refers to the skills, knowledge, and health of individuals.
In poverty traps, human capital is often underdeveloped due to lack of education and healthcare.
Improving human capital is one of the most effective ways to break poverty traps.
Role of physical capital in Poverty traps
Physical capital includes tools, machinery, infrastructure, and technology.
In poverty-stricken areas, physical capital is often outdated or nonexistent.
Without physical capital, productivity remains low, perpetuating poverty.
The Role of Social Capital in Poverty Traps
Social capital refers to the networks, relationships, and social structures that facilitate cooperation and support.
In poverty traps, social capital is often weak or fragmented.
Strong social capital can provide access to job opportunities, financial support, and information.
3 ways the poverty cycle can be broken
Education
increases human capital, leading to better job opportunities and higher income.
has positive spillover effects, such as improved health and reduced crime rates.
Healthcare
Poor health reduces productivity, increases medical expenses, and limits educational opportunities.
Preventive healthcare and nutrition programs can have significant long-term benefits.
Access to credit/financial services allows individuals and businesses to invest in education, healthcare, and physical capital.
What are all the economic barriers to growth and development?
Rising economic inequality
Lack of access to infrastructure and appropriate technology
Low levels of human capital—lack of access to
healthcare and education
Dependence on primary sector production
Lack of access to international markets
Informal economy
Capital flight
Indebtedness
Geography including landlocked countries
Tropical climates and endemic diseases
Why is an rising economic inequality economic barrier?
- limits opportunities for low-income households as they lack resources for education or starting businesses
Why is Lack of access to infrastructure and appropriate technology economic barrier?
Poor roads and ports increase transportation costs
Limited internet access restricts participation in the digital economy
Outdated machinery lowers productivity and product quality
Why is Low levels of human capital economic barrier?
Inadequate education leads to a less skilled workforce
Poor healthcare reduces worker productivity
Mismatch of skills and job requirements leads to high unemployment
Why is Dependence on primary sector production economic barrier?
Price volatility of raw materials creates economic instability
Selling raw materials instead of finished goods limits value-added profits
Focus on resource extraction hinders economic diversification
Why is Limited access to international markets an economic barrier?
High tariffs and trade restrictions make exports uncompetitive
Complex international standards can be too costly for local businesses to meet
Reduced export opportunities limit economic growth
Why is Informal economy an economic barrier?
Workers without formal contracts lack job security and social benefits
Businesses avoiding taxes deprive governments of revenue
Informal businesses struggle to access credit
Why is capital flight an economic barrier?
Reduced domestic investment
Decreased funds for business growth
Brain drain as skilled workers leave for better opportunities abroad
Why is Indebtedness an economic barrier?
Debt repayments consume government budgets, reducing funds for essential services
Currency depreciation makes foreign debt more expensive
Developing countries often face high interest rates on loans
What are all the components of a weak institutional framework?
Legal System
Provides the rules and enforcement mechanisms for contracts and property rights.
Taxation Structure
Determines how government revenue is collected and distributed.
Banking System
Facilitates financial transactions, savings, and investments.
Property Rights
Define ownership and usage rights for land and assets.
Eocnomic consequences of gender inequality
Economic Consequences of Gender Inequality
Education
Limited access to education for girls reduces human capital development.
Employment
Women often face barriers to entering the workforce or are confined to low-paying jobs.
Property Rights
Legal and cultural restrictions often prevent women from owning or inheriting property.
Decision-Making
Lack of women in leadership positions leads to policies that overlook female needs.
How does corruption hinder development?
Bribery
Acts as an extra tax on businesses, increasing costs and reducing competitiveness.
misallocation of Public Funds
Government resources are diverted into private accounts, reducing funds for essential services.
Inefficient Infrastructure investments
Projects are approved based on kickbacks rather than actual need, leading to inefficient investments.
Business Environment
Companies focus on building political connections rather than improving efficiency.
How does unequal power and status negative development?
Tax Policies favouring the wealthy
Wealthy groups influence tax laws to protect their assets, while the poor bear a heavier burden.
Example
Lower corporate taxes and higher indirect taxes increase inequality.
Development Priorities favouring elite areas
Government spending is concentrated in areas where influential people live.
Business success tied to political connections
than economic merit.
Example
Entrepreneurs without political ties face barriers to entry.
concentration of Public Services in privileged areas
Essential services are concentrated in privileged areas, neglecting marginalized communities.
Example
Healthcare facilities are often better equipped in wealthy areas.
What are all the compartment of strategies which can promote economic growth?
Trade strategies
diversification
social enterprise
market-based policies
interventionist policies
provision of merit goods
inward foreign direct investment
foreign aid
multilateral development assistance institutional change
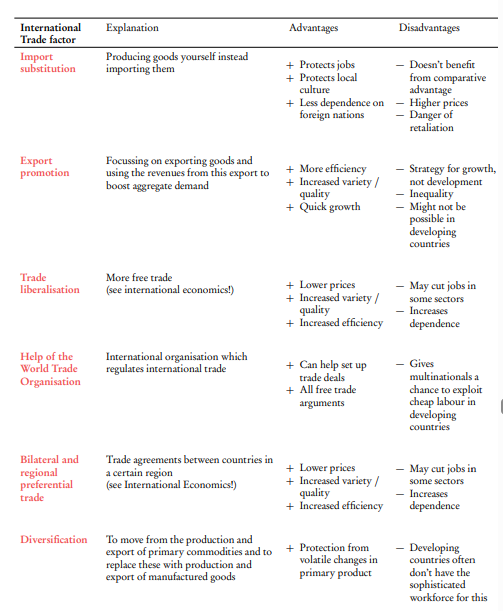
What are the different trade strategies which can help promote economic development? along with strengths and weaknesses
Import Substitution
Focuses on producing goods domestically that were previously imported
Uses trade barriers like tariffs to protect local industries
Aims to reduce dependency on foreign goods
+protects and develops infant domestic industries
+Creates local jobs and industrial capacity
+Reduces dependency on foreign imports
+Helps conserve foreign exchange reserves
-often leads to inefficient production
-higher prices for domestic consumers
-reduced access to foreign technology
Export Promotion
Emphasizes producing goods for international markets
Supports industries with export potential
Aims to integrate into the global economy
Strengths of Export Promotion
Generates foreign exchange earnings
Creates competitive industries
Achieves economies of scale
Attracts foreign investment
Limitations of Export Promotion
Vulnerable to global market fluctuations
May lead to over-dependence on exports
Requires significant initial investment
Faces tough international competition
How does social enterprise promote eocnomic growth?
Prioritizing social impact over profit maximization
Reinvesting profits into social missions
Operating in various sectors like education, healthcare, and agriculture
Strengths of Social Welfare Programs
Reduces income inequality
Provides social protection
Helps vulnerable groups
Maintains social stability
Limitations of Social Welfare Programs
High fiscal costs
May reduce work incentives
Administrative challenges
Possible market distortions
What market based policies help promote economic growth? along with their strengths and weaknesses
Trade Liberalization
Reducing tariffs and trade barriers
Opening markets to international competition
Strengths of Trade Liberalisation
Increases competition and efficiency
Provides access to new technologies
Lower prices for consumers
Wider product choice
Limitations of Trade Liberalisation
May destroy local industries
Can increase unemployment
May worsen income inequality
Initial economic disruption
Privatization
Selling state-owned enterprises to private investors
Aiming to improve efficiency through competition
Strengths of Privatisation
Improves operational efficiency
Reduces government spending
Attracts private investment
Better service quality
Limitations of Privatisation
May lead to job losses
Can create private monopolies
May increase prices
Possible foreign ownership concerns
Deregulation
Reducing government control over markets
Allowing market forces to determine prices and allocation

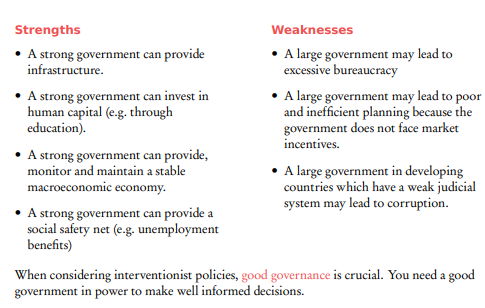
How do interventionist policies promote economic growth? along with strengths and weaknesses
Redistribution
Progressive taxation to reduce income inequality
Transfer payments like social security and unemployment benefits
Provision of Merit Goods
Government provision of essential services with positive externalities
Education, healthcare, and infrastructure
MINIMUM WAGES
FDI benefits and challenges
Advantages of FDI
• Provide employment and education.
• Provide greater access to Research & Development, technology and expertise.
• Improves infrastructure of the country.
capital inflow and export growth
• Drop in consumer prices and more diversity in goods
. • More efficient allocation of world resources.
Disadvantages of FDI
• MNCs may only use low-wage/unskilled workers of the country.
• MNCs may exploit the favourable tax rules leading to less revenue for the country’s government.
• MNCs may exploit the weak legislation on pollution of the country, which may lead to unsustainable and polluting production
Types of foreign aid
Humanitarian Aid: Emergency assistance during crises (food/medical/emergency relief)
Development Aid: Long-term support for economic and social progress
• sums of money given to invest in development.
• Concessional (= with favourable conditions) long-term loans.
• Project aid (e.g. support for schools and hospitals)
• Programme aid (e.g. support for sectors such as education and financial sector)
• Relief: Reduction or cancellation of debt obligations
Which two organisations provide multi developmental assistance?
the World Bank focuses on long-term development, while the IMF addresses short-term financial stability.

What are all the components of balance of payments?
Current account
Balance of trade in goods
Balance of trade in services
Income
Current transfers
Capital Account
Capital transfers
Transaction in non-produced, non-financial assets
Financial account
Foreign direct investment (FDI)
Portfolio investment
Reserve assets
Official borrowin
What are the 4 sub components of the current account?
Inflows of trade and income (credit) against outflows (debit)
• Balance of trade in goods: exports of goods minus import of goods.
• Balance of trade in services: exports of services minus import of services.
ex: tourism, transportation
• Income: earnings from investment leaving (−) and entering (+) the country.
ex: wages, intrest, rent, profits
• Current transfers: net payments to governments without retribution (e.g. gifts, aid etc.)
surplus: country has more inflows than outflows
What is the financial account and what are the different categories of it?
The inflows from investments from abroad (credit) against investment to abroad (debit).
: • Direct investment: purchase of long-term assets (such as buildings or factories).
• Portfolio investment: purchases of stocks and bonds.
• Reserve assets: purchases of reserves of gold and foreign currencies.
and
OFFICIAL BORROWING: inflow (borrowing): credit and outflow (lending): debit
What are the 2 sub components of the capital account?
Miscellaneous income (credit) or expenses (debit) that can’t be placed in any other category
Capital Transfers are funds exchanged when an asset changes ownership:
Examples include debt forgiveness, investment grants, and sale of fixed assets
Transactions in Non-Produced, Non-Financial Assets include:
Land
Mineral rights
Airspace
Electromagnetic spectrum
What can happen due to a consistent account deficit?
Downward pressure on the domestic currency exchange rate: more imports than exports lead to relatively more supply than demand for the domestic currency.
Increase in indebtedness: to finance the net outflow of money the country must borrow money, resulting in more indebtedness and higher interest rates. this can result in declining international credit ratings.
More foreign ownership of domestic assets: a current account deficit can be financed with a financial account surplus, meaning the net ownership of foreign countries of domestic country’s assets will increase.
What are the supply and demand for currency?
Demand for a currency comes from people who want to buy it
supply of a currency comes from people who want to sell it.
What factors causes an increase in demand for a currency?
I FIRE PIES
I:Imports for domestic demand
F: Foreign direct investment
I: Inflation
R: Remittance
E: Export demand for foreign consumers
P: Portfolio Investment
I: Intrest rates
E: Expectations (speculation)
S: Stabilization (Central bank intervention)
How does domestic demand for imports affect the supply and demand of currencies?
↑Domestic demand for imports= ↑Demand foreign currencies to pay for imports = ↑supply of domestic currency in foreign exchange market
↓ Imports → ↓ Demand for foreign currency →↓ Supply of domestic currency.
How does Foreign direct investments affect the supply and demand of currencies?
Inward FDI (↑ FDI into the country):
↑ FDI into the country →→↑ Demand for domestic currency (to invest)= (Foreign companies need to convert their currency into the domestic currency to build factories, buy equipment, and pay local workers) = ↑ Supply of foreign currency = (Foreign companies are selling their currency to buy the domestic currency, increasing the supply of foreign currency in the foreign exchange market).
Outward FDI (↑↑ FDI going out of the country):
↑ FDI going out of the country → ↑ Demand for foreign currency (to invest abroad) = (Domestic companies need to convert their currency into foreign currency to build factories, buy equipment, and pay workers in the foreign country) ↑ Supply of domestic currency = (Domestic companies are selling their domestic currency to buy the foreign currency, increasing the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market).
How does Inflation affect the supply and demand of currencies?
↑ Inflation → ↓ Demand for domestic currency (exports become more expensive) → ↑ Supply of domestic currency (people want to hold foreign currency).
↓ Inflation → ↑ Demand for domestic currency (exports become cheaper) → ↓ Supply of domestic currency.
How does Remittance affect the supply and demand of currencies?
↑ Remittances sent into the country:
↑ Demand for domestic currency (to receive remittances) → = People receiving remittances in foreign currency will want to exchange it for the domestic currency to use for local expenses.
↑ Supply of foreign currency → = To obtain the domestic currency, recipients sell the foreign currency they received, thus increasing the supply of foreign currency in the foreign exchange market.
↑ Remittances sent out of the country:
↑ Demand for foreign currency (to send remittances) → = People sending remittances need to exchange their domestic currency for the foreign currency that they will send to recipients abroad.
↑ Supply of domestic currency → = To obtain the foreign currency, remitters sell their domestic currency, thus increasing the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
How does foreign demands for exports affect the supply and demand of currencies?
↑ Exports:
↑ Demand for domestic currency (foreigners need domestic currency to buy exports) → = Foreigners need to buy the domestic currency to pay for the country's exports.
↓ Supply of domestic currency → = To buy the domestic currency, foreigners sell their foreign currency, more foreigners are holding the domestic currency instead of selling it.
↓ Exports:
↓ Demand for domestic currency → = Foreigners need less of the domestic currency because they are buying fewer exports.
↑ Supply of domestic currency → = With less demand for the domestic currency, foreigners sell it off,
How does portfolio investment affect the supply and demand of currencies?
Inward Portfolio Investment (↑ investment in domestic stocks/bonds):
↑ Investment in domestic stocks/bonds → ↑ Demand for domestic currency (to buy assets) → = Foreign investors need to convert their currency into the domestic currency to purchase stocks and bonds in the domestic market.
↑ Supply of foreign currency → Foreign investors are selling their currency to buy the domestic currency,
Outward Portfolio Investment (↑ investment in foreign stocks/bonds):
↑ Investment in foreign stocks/bonds → ↑ Demand for foreign currency (to buy assets) → Domestic investors need to convert their currency into foreign currency to purchase stocks and bonds in the foreign market.
↑ Supply of domestic currency → =Domestic investors are selling their domestic currency to buy the foreign currency,
How does affect the supply and demand of currencies?
How does Intrest rates affect the supply and demand of currencies?
↑ Interest Rates → ↑ Demand for domestic currency (foreign investors want to earn higher returns) = Higher interest rates in a country attract foreign investors seeking better returns on their investments. To invest, they need to buy the domestic currency
→ ↓ Supply of domestic currency = As foreign investors buy the domestic currency, they are taking it out of circulation in the foreign exchange market
↓ Interest Rates → ↓ Demand for domestic currency = Lower interest rates make a country less attractive to foreign investors, as returns are lower.
→ ↑ Supply of domestic currency = As foreign investors sell off the domestic currency to invest elsewhere,
How does expectations speculations affect the supply and demand of currencies?
Expectation of currency appreciation → ↑ Demand for domestic currency (speculators buy currency hoping to profit)
→ ↓ Supply of domestic currency → = As speculators buy up the currency, they are taking it out of circulation
Expectation of currency depreciation → ↓ Demand for domestic currency (speculators sell currency to avoid losses)
→ ↑ Supply of domestic currency → = As speculators sell off the currency, its supply in the foreign exchange market increases.
How does stabilization (CENTRAL BANK INTERVENTION) affect the supply and demand of currencies?
Central Bank buys domestic currency → ↑ Demand for domestic currency = directly increasing the demand for it in the foreign exchange market.
↑ Demand for domestic currency → ↓ Supply of domestic currency → = By buying up the currency, the central bank is taking it out of circulation
Central Bank sells domestic currency → ↑ Supply of domestic currency → = When a central bank sells its own currency, it is directly increasing the supply of it in the foreign exchange market.
↑ Supply of domestic currency → ↓ Demand for domestic currency → = By flooding the market with its currency, the central bank is decreasing its value and thus the demand for it.
How does economic growth rates affect the demand and supply for a currency?
strong eocnomic growtth attracts forgein investmes and increases demands for exports leading to an increased demand for the countrys currency leading to appriciation of it
How does exchange rate affect the current account balance?
When a currency appreciates:
Exports become more expensive for foreign buyers.
Imports become cheaper for domestic consumers.
When a currency depreciates:
Exports become cheaper for foreign buyers.
Imports become more expensive for domestic consumers.
How does demand pull inflation occur?
Increase in AD
demand exceeds supply causing prices to rise
Currency depreciation can lead to demand-pull inflation through higher Net Exports.
This increase in the general price level is demand-pull inflation.
How does costpush inflation occur?
Occurs when rising production costs push up prices.
Currency depreciation can lead to cost-push inflation through higher import prices for raw materials.
What are the possible consequences of changes in the exchange rate on economic indicators?
I Got U Covered, Love
Inflation rate Growth (economic) Unemployment Current account balance Living standards
the inflation rate
economic growth
unemployment
the current account balance
living standards
How does changes in Exchange rate affect inflation?
Demand-Pull Inflation
Occurs when increased demand for goods and services pushes up prices.
Currency depreciation can lead to demand-pull inflation through higher Net Exports.
Cost-Push Inflation
Occurs when rising production costs push up prices.
Currency depreciation can lead to cost-push inflation through higher import prices for raw materials.
Hudders changes in the exchange rate cause and effect on economic growth?
Short-Term Effects
Increased Net Exports:
When a currency depreciates, the country's goods and services become cheaper for foreign buyers.
At the same time, foreign goods and services become more expensive for domestic buyers.
This leads to an increase in exports and a decrease in imports, boosting net exports (Exports - Imports).
Boost to Aggregate Demand (AD):
Net exports are a component of Aggregate Demand
Long-Term Effects
High Inflation:
While depreciation can initially boost exports, it also makes imports more expensive.
If a country relies heavily on imported raw materials or goods, these higher import costs can lead to cost-push inflation.
Uncertainty:
Persistent currency depreciation can create uncertainty in the economy.
Businesses may delay investments due to concerns about future exchange rate fluctuations and their impact on costs and revenues.
How does changes in the exchange rate affect unemployment?
Currency Depreciation reduces Unemployment
Higher Demand for Exports:
When a country's currency depreciates, its goods and services become cheaper for foreign buyers.
This leads to an increase in the demand for exports.
Increased Production and Job Creation:
To meet the higher demand for exports, domestic firms need to increase their production.
requires hiring more workers, leading to job creation and reduced unemployment.
Currency Appreciation increases Unemployment
Lower Demand for Exports:
When a country's currency appreciates, its goods and services become more expensive for foreign buyers. leading to a decrease in the demand for exports.
.
Reduced Production and Job Losses:
With lower demand for exports, domestic firms may need to reduce their production.
lead to layoffs and job losses, increasing unemployment.
Why does a country choose fixed exchange rate?
To provide stability and predictability for international trade
To control inflation by tying the currency to a stable foreign currency
To attract foreign investment by reducing exchange rate risk
How is a foreign exchange market maintained?
Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market:
How it Works: The central bank buys or sells its own currency in the foreign exchange market to influence its supply and demand.
Example:
If there is downward pressure (depreciation), the central bank buys its own currency using its foreign exchange reserves (e.g., U.S. dollars, euros). This increases demand for the domestic currency, counteracting the depreciation.
Conversely, if there is upward pressure(appreciation), the central bank sells its own currency and buys foreign currency. This increases the supply of the domestic currency, counteracting the appreciation.
Monetary Policy Adjustments:
How it Works: The central bank adjusts interest rates to influence capital flows.
Example:
If the domestic currency is facing downward, the central bank can raise interest rates. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency and supporting its value.
If the domestic currency is facing pressure to appreciate, the central bank can lower interest rates. Lower interest rates make the country less attractive to foreign investors, reducing demand for the domestic currency and easing upward pressure.
Capital Controls:
How it Works: These are restrictions on the flow of money in and out of the country.
Example:
Restrictions on how much domestic currency residents can invest abroad.
Limits on the amount of foreign currency that can be brought into the country.
Taxes on foreign exchange transactions.
Purpose: Capital controls can help limit the demand for foreign currency or the supply of domestic currency,
Challenges of fixed exchange rates
Loss of monetary policy independence
The need for large foreign currency reserves
Vulnerability to speculative attacks
What do central banks use to manage exchange rates in a managed exchange rate system?
Buying and selling domestic currency: When the currency is too strong, they buy foreign currency and sell domestic currency, increasing supply and lowering its value.
Using foreign reserves: Central banks hold reserves of foreign currencies to facilitate these transactions.
Changing interest rates: Raising interest rates can attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency and raising its value.
What’s the first stage of economic integration?
Preferential Trade Agreements (PTA):
Agreements give preferential access to certain products from certain countries.
achieved by ↓↓ tariffs or other trade restrictions
What’s the second stage of economic integration?
Free trade area
Countries trade freely among themselves.
Each country can trade with countries outside the FTA however they like.
Example: NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) between the US, Canada, and Mexico.
What's the third stage of economic integration?
Customs union:
Countries trade freely among themselves.
They adopt common external barriers against any country outside the union.
Example: MERCOSUR (Southern Common Market) between Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
What's the fourth stage of economic integration?
Common market:
A customs union + common policies on product regulation.
Free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor.
Example: The European Economic Community (EEC) before it became the EU.
What's the 5th stage of economic integration?
Monetary Union (MU):
A common market + common currency and common central bank.
Example: The Eurozone, where member countries use the Euro (€) as their currency and the European Central Bank sets monetary policy.
What's the 6th stage of economic integration?
Complete economic integration
Countries have no control of economic policy.
Full monetary union with complete harmonization of fiscal policy.
What are the 4 advantages of Economic integration?
greater access to markets offer potential for economies of scale
with freedom of labour, there are greater employment opportunities
membership in a trading bloc may allow for stronger bargaining power in multilateral negotiations
greater political stability and cooperation
What are the two main disadvantages of economic integration?
Loss of Sovereignty:
Countries give up some control over their economic policies.
Decision-making shifts to a supranational body (e.g., EU Commission, common central bank).
National laws and regulations must align with the integrated bloc's rules.
Loss of sovereignty → National governments have less autonomy in setting tariffs, taxes, regulations, and monetary policy.
Less autonomy → Reduced ability to respond to unique national circumstances or pursue independent economic goals.
Example:
Joining the Eurozone means a country can't devalue its currency to boost exports during a recession.
Challenge to Multilateral Trading Negotiations:
Economic integration can create trade blocs that discriminate against non-member countries.
Focus shifts inward, potentially undermining global trade liberalization efforts.
Challenge to multilateral trading negotiations →Trade blocs may prioritize internal trade deals over broader multilateral agreements (e.g., WTO negotiations).
Prioritizing internal deals → Reduced incentive to lower trade barriers with countries outside the bloc, hindering global free trade.
Example:
The EU's common external tariff can make it more difficult for non-EU countries to access the European market.
If the EU focuses on deepening integration among its members, it may be less willing to compromise in WTO negotiations to lower global trade barriers.
What are the objectives of WTO?
Non discrimination
Refrain from discriminating between the goods and services or nationals of their trading partners
more open as an economy
Reducing artificial trade barrierspredictable and transparent
Investors and governments become more confident in international trade a trade barriers should not be used arbitrarily or indiscriminately. creates jobs in the long term
more competitive
Enable consumers around the world to enjoy the benefit of greater choice and lower prices reducing living costs for allmore beneficial for economically less developed countries
protect the environment
Any restrictions or sanctions imposed on forgein businesses also apply to domestic firms.