ap exam4
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
What are the functions of the muscular system?
Movement, posture, joint stabilization, and heat production.
Origin
The fixed, stationary attachment of the muscle
Belly
The thick, middle part of the muscle
Insertion
The movable attachment where the muscle exerts force
Which part of the muscle is typically still?
Origin is still
Which part moves the bone?
Insertion moves the bone
Tendon
A fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone
Aponeurosis
A flat, sheet-like tendon that muscles
Agonist
The primary mover in an action (e.g., biceps in elbow flexion)
Antagonist
The muscle that opposes the agonist (e.g., triceps in elbow flexion)
What can a muscle’s name tell you?
It can indicate action, location, attachment points, shape/size, number of origins, and fiber direction
How can you remember muscle actions if you forget?
Think about what happens when the muscle shortens or where it is located
Mastication
The process of chewing; involves muscles that move the mandible
What do the pterygoid muscles do that the masseter and temporalis can’t?
They allow side-to-side grinding movements of the jaw
What does the transversus abdominis do?
Stabilizes the core and compresses the abdomen
When the diaphragm contracts, does it move up or down? Do you inhale or exhale?
Moves down → Inhale
What is the role of scapular muscles in shoulder movement?
They stabilize and move the scapula to allow full arm movement
What are the rotator cuff muscles? What bone do they insert on?
SITS Muscles (Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor, Subscapularis); insert on the humerus
Which muscle is more developed in boxers?
Boxers: Serratus Anterior (punching motion)
Which muscle is more developed in swimmers?
Swimmers: Latissimus Dorsi (pulling motion)
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal (voluntary), Cardiac (heart, involuntary), Smooth (organs, involuntary)
Why are skeletal muscle fibers multinucleated?
They form by the fusion of multiple cells during development
Describe the organization of muscle tissue from smallest to largest.
Myofilaments → Myofibrils → Muscle Fiber → Fascicle → Whole Muscle
What makes up thick filaments?
Myosin
What makes up thin filaments
Actin, troponin, tropomyosin
What covers the binding sites on actin?
Tropomyosin covers
What moves the binding sites on actin?
Troponin moves it when calcium binds
What are the key parts of the neuromuscular junction?
Synaptic knob, Synaptic cleft, Motor end plate
Synaptic Knob
End of neuron, releases neurotransmitter
Synaptic cleft
Gap between neuron and muscle
Motor end plate
Part of the muscle that recieves the signal
What ion enters the synaptic knob to trigger neurotransmitter release?
Calcium (Ca²⁺)
What is the neurotransmitter for skeletal muscle contraction?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
What organelle stores calcium in muscle cells?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
What molecule is needed for myosin to perform a power stroke?
ATP
Motor unit
A motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls
What are the three ways muscles generate ATP?
Creatine phosphate system, Anaerobic glycolysis, Aerobic respiration
Creatine phospahte system
Immediate, short-lasting
Anaerobic glycolysis
Uses glucose, no oxygen, short duration)
Aerobic respiration
Uses oxygen, long-lasting
What are the three types of skeletal muscle fibers?
Slow oxidative, Fast glycolytic, Fast oxidative
low oxidative
Endurance, fatigue-resistant
Fast glycolytic
Powerful, fatigues quickly
Fast oxidative
Intermediate power and endurance
What are the two main types of contractions?
Isotonic and Isometric
Isotonic
Muscle changes length
Concentric
Muscle shortens
Eccentric
Muscle lengthens
Isometric
Muscle doesn’t change length
Orbicularis Oculi
Closes eyelid
Orbicularis Oris
Closes and puckers lips
Temporalis
Elevates mandible (chewing)
Sternocleidomastoid
Turns and flexes head
Rectus Abdominis
Flexes spine
Internal/External Obliques
Rotate and flex torso
Transverse Abdominis
Compresses abdomen
Trapezius
Elevates/depresses scapula
Pectoralis Major
Flexes and adducts shoulder
Latissimus Dorsi
Extends and adducts shoulder
Deltoid
Abducts arm
Biceps Brachii
Flexes elbow
Triceps Brachii
Extends elbow
Rectus Femoris
Extends knee, flexes hip
Gastrocnemius
Plantarflexes ankle
Masseter Muscle Origins & Insertions (Examples)
Origin: Zygomatic arch → Insertion: Mandible
Deltoid Muscle Origins & Insertions (Examples)
Origin: Clavicle/scapula → Insertion: Humerus
What determines muscle contraction strength?
Size and number of motor units recruited.
What are the three ways muscles generate ATP?
Creatine phosphate, glycolysis, aerobic respiration.
Which ATP pathway is most immediate but short-lasting?
Creatine phosphate.
Which pathway uses glucose but not oxygen?
Glycolysis.
Which ATP pathway lasts the longest?
Aerobic respiration (needs oxygen).
What brings an electrical impulse deep into the muscle cell?
T-tubules.
What stores calcium in muscle cells?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Which sarcomere structures get smaller when a muscle contracts?
I band and H zone.
Describe muscle tissue organization from myofilaments to whole muscle.
Myofilaments → Myofibrils → Muscle Fibers → Fascicles → Whole Muscle.
What is the sarcolemma?
The plasma membrane of a muscle cell.
What is the sarcoplasm?
The cytoplasm of a muscle cell.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth.
What causes skeletal muscle fibers to be multinucleated?
Fusion of myoblasts during development.
How long are muscle fibers?
Can be several centimeters long.
What do the endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium form when merged?
A tendon.
What do the pterygoid muscles do that the masseter/temporalis can't?
Side-to-side jaw movement.
What does the transversus abdominis do?
Compresses the abdomen, not movement.
When the diaphragm contracts, does it move up or down?
Downward.
Do you inhale or exhale when the diaphragm contracts?
Inhale.
What is the role of scapular muscles in shoulder movement?
Stabilize and assist movement.
What are the rotator cuff muscles?
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis.
What bone do all rotator cuff muscles insert on?
Humerus.
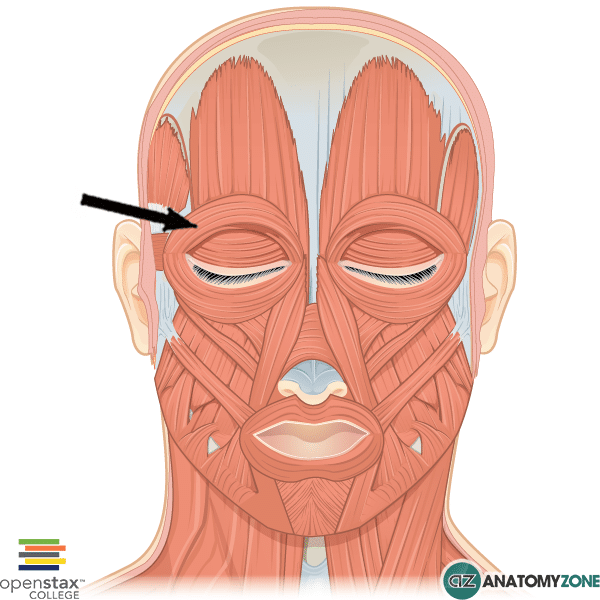
Orbicularis Oculi
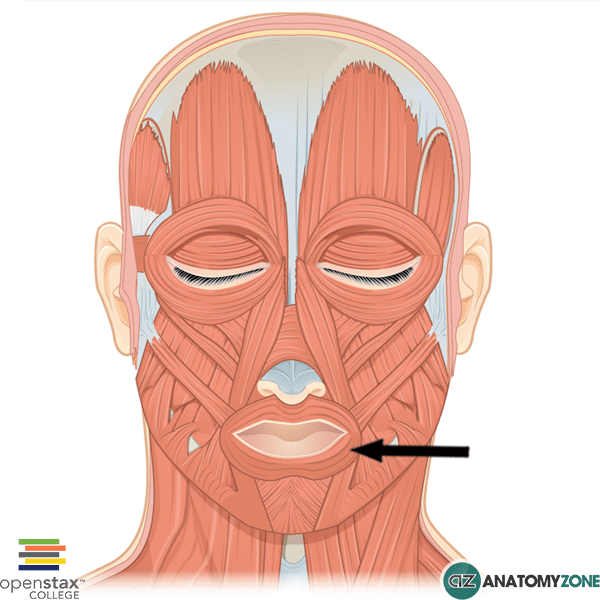
Orbicularis Oris
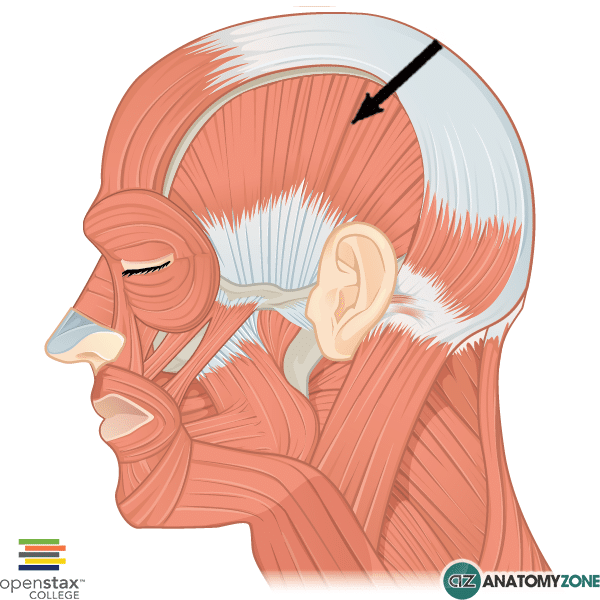
Temporalis
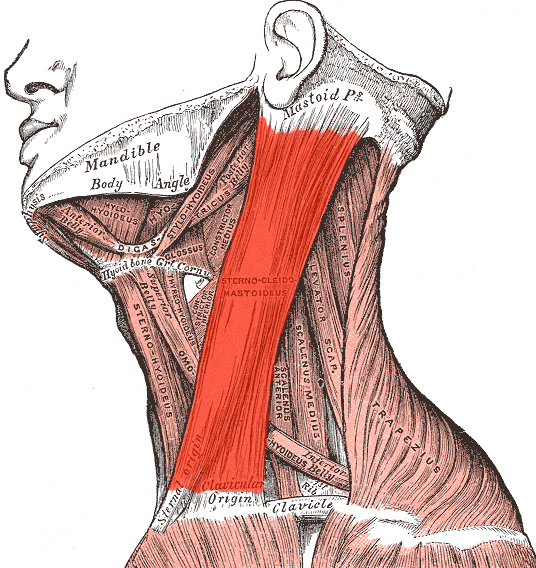
Sternocleidomastoid
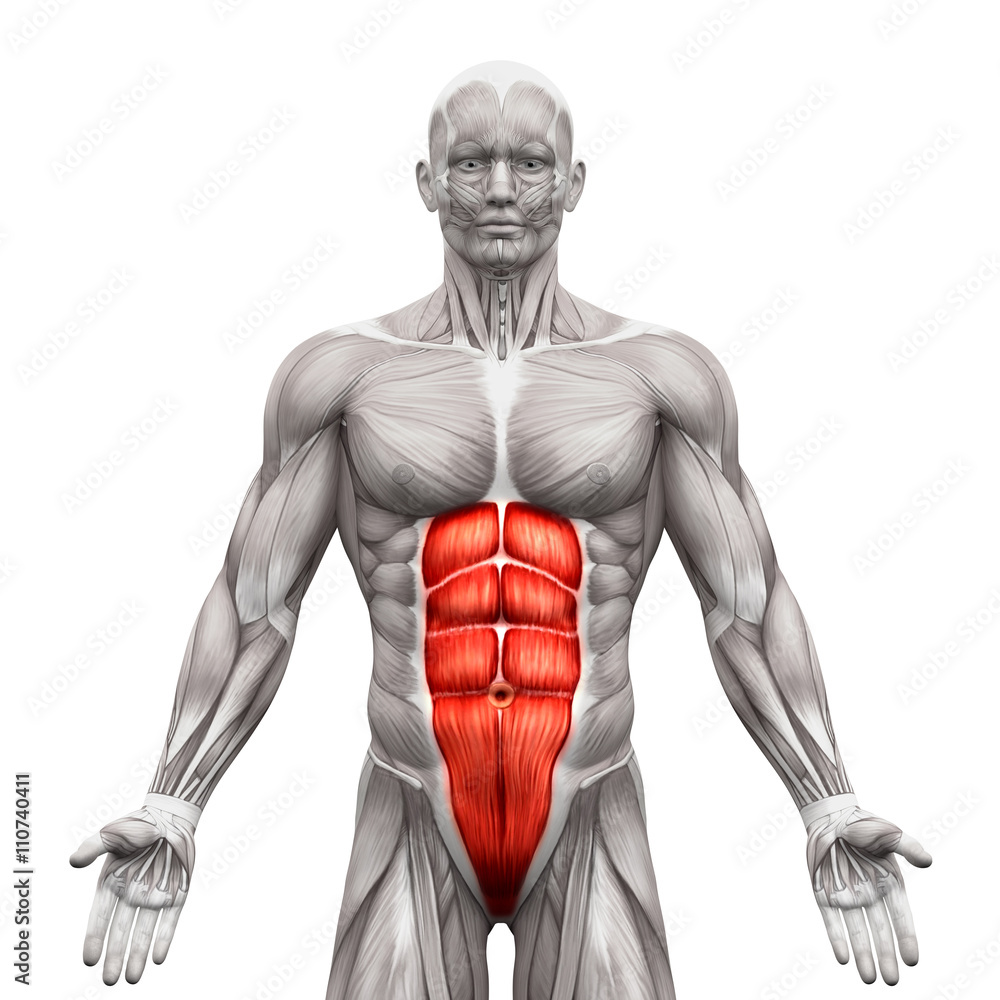
Rectus Abdominis
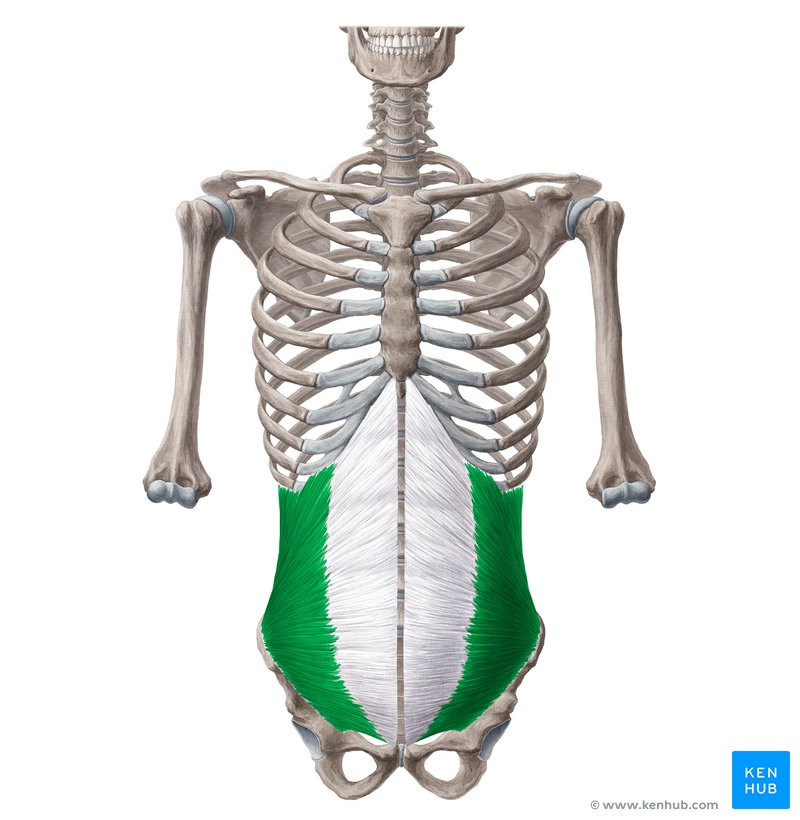
Internal Oblique
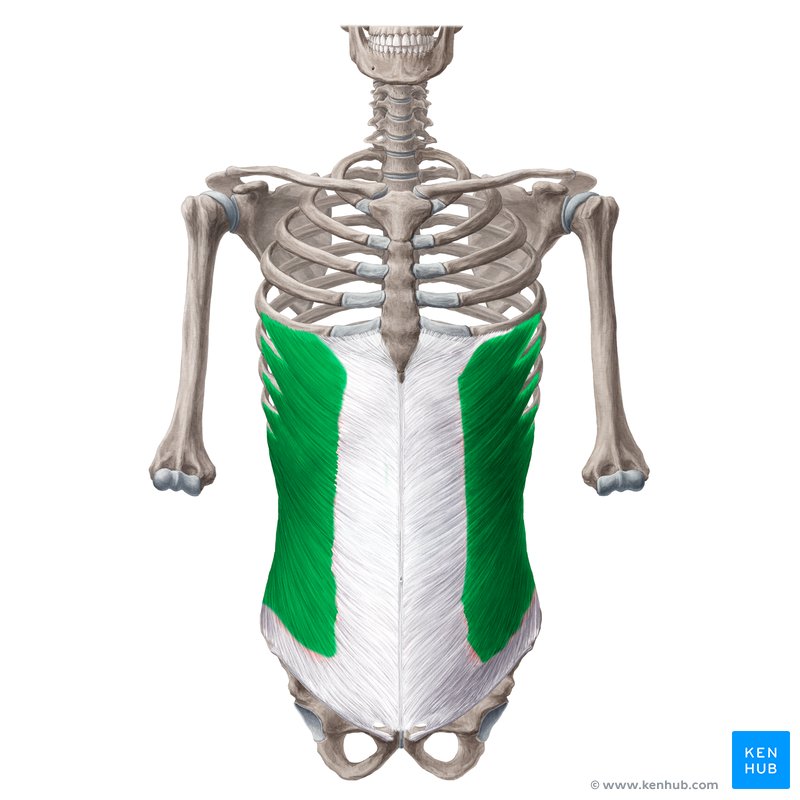
External Oblique
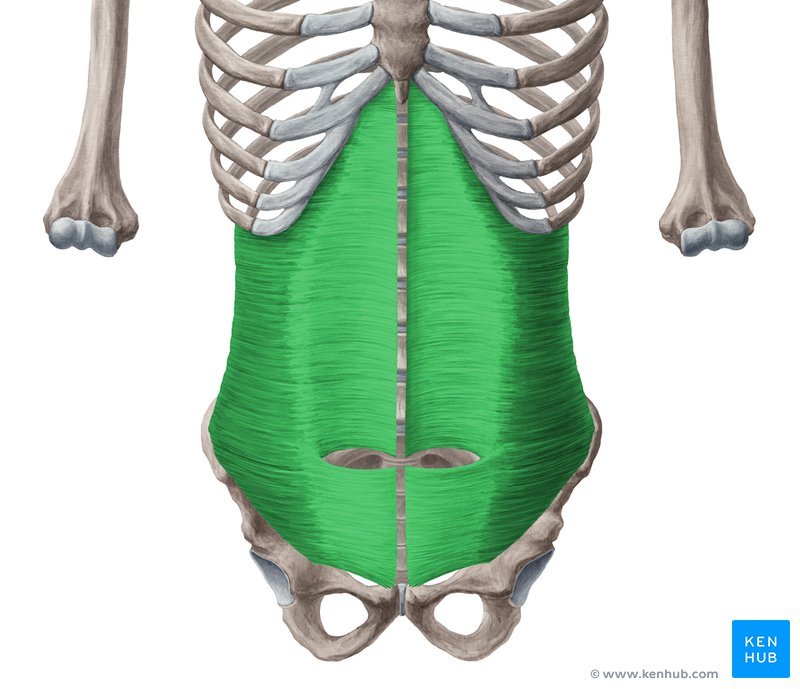
Transverse Abdominis
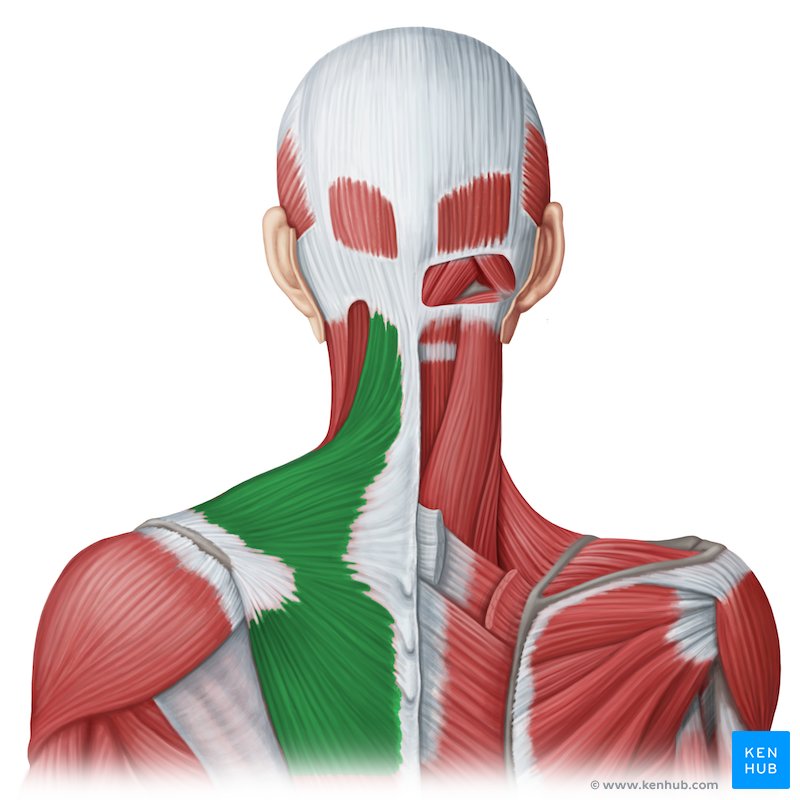
Trapezius
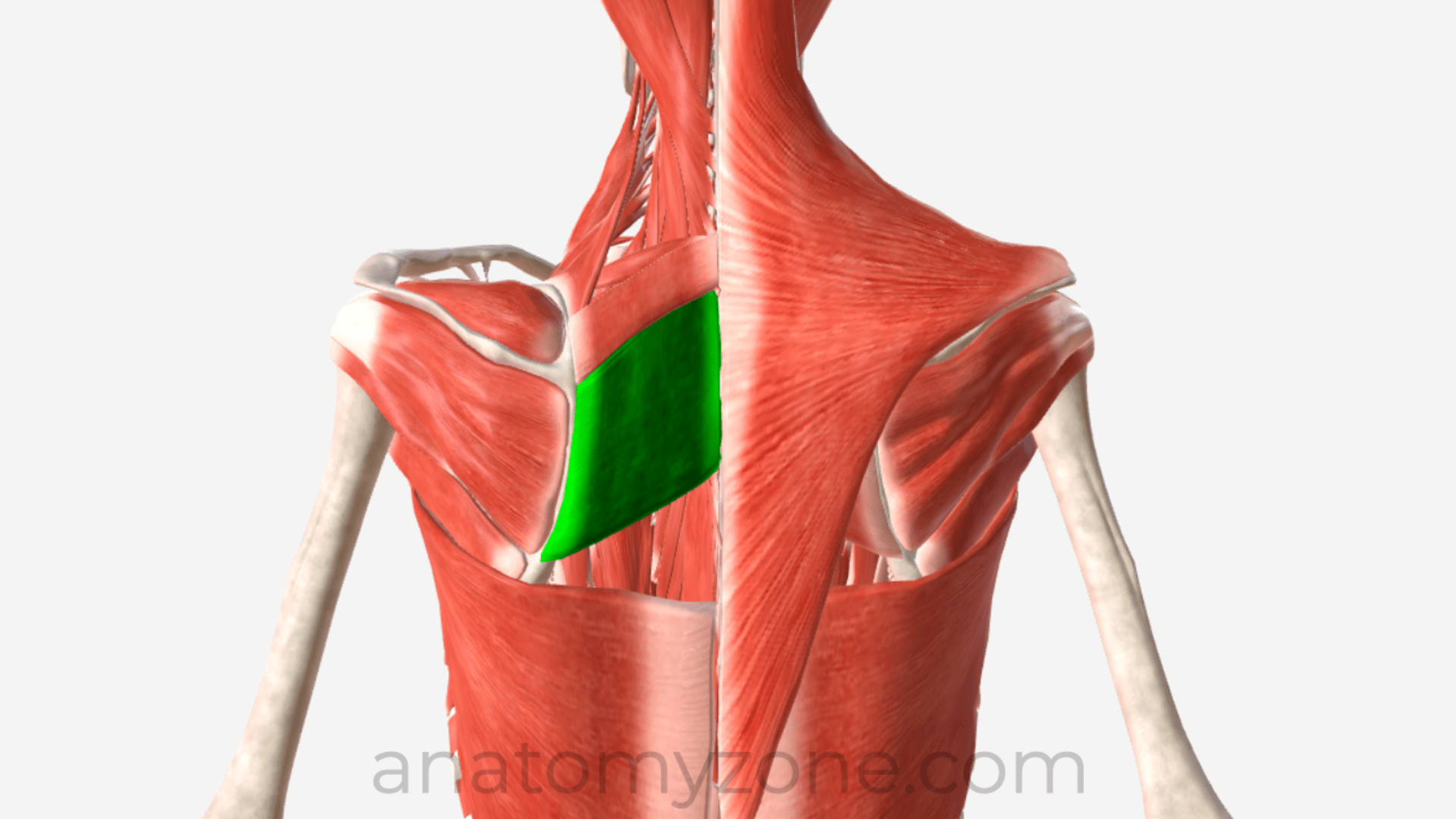
Rhomboid Major
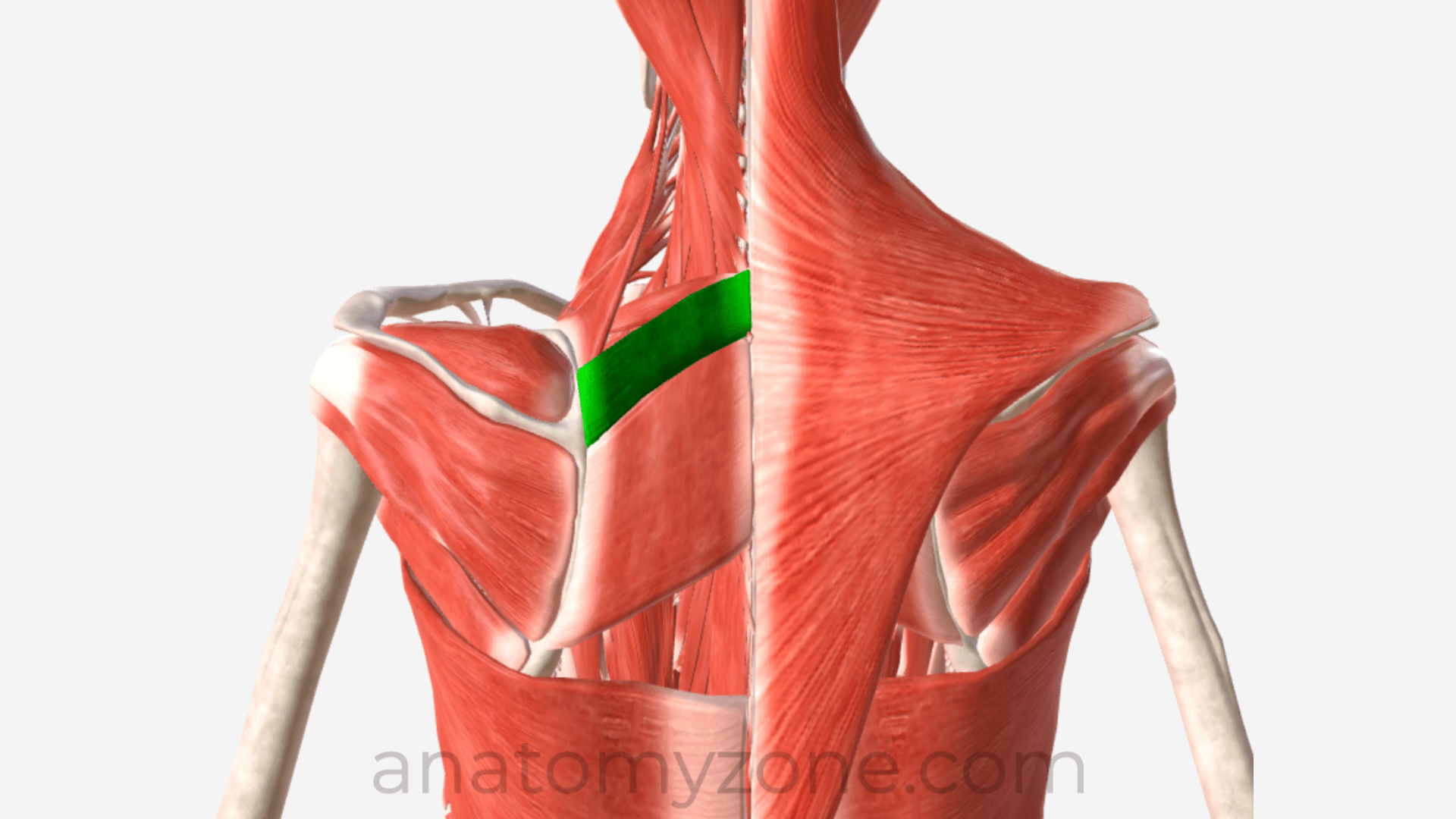
Rhomboid Minor
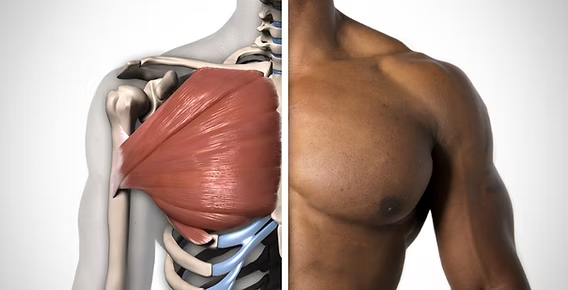
Pectoralis Major