StemUp: OCR A A level Chemistry M4 4.1 Basic concepts and hydrocarbons
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Define Homologous Series (1)
A series of organic compounds having the same functional group but with each successive member differing by CH2
Define Hydrocarbon (1)
A compound consisting of ONLY Hydrogen and Carbon
Define General Formula (1)
The algebraic formula for homologous series E.g Cn H2n
State the difference between displayed and skeletal formulae (2)
Displayed- Every bond is drawn
Skeletal - Carbon to Hydrogen bonds are not drawn
Define Functional group (1)
A group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a compound
Define Molecular formula (1)
The actual number of atoms of each element in the compound
What does the term structural formula mean? (2)
- It shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule without showing every bond
- E.g CH3CH2CH3 - Structural formula for propane
Define aliphatic (2)
A compound containing Carbon and Hydrogen joined together in straight chains, branched chains or non-aromatic rings
Define alicyclic (2)
An aliphatic compound arranged in non-aromatic rings with or without side chains
Define aromatic compounds (1)
A compound containing a benzene ring(s)
Functional group, prefix, and suffix of an alcohol (4)
- Functional group: OH
- Prefix: Hydroxy-
- Suffix: -ol
- Example: Ethanol
Functional group, prefix, and suffix of aldehydes (4)
- Functional group =
- Prefix: formyl-
- Suffix -al
- E.g Ethanal
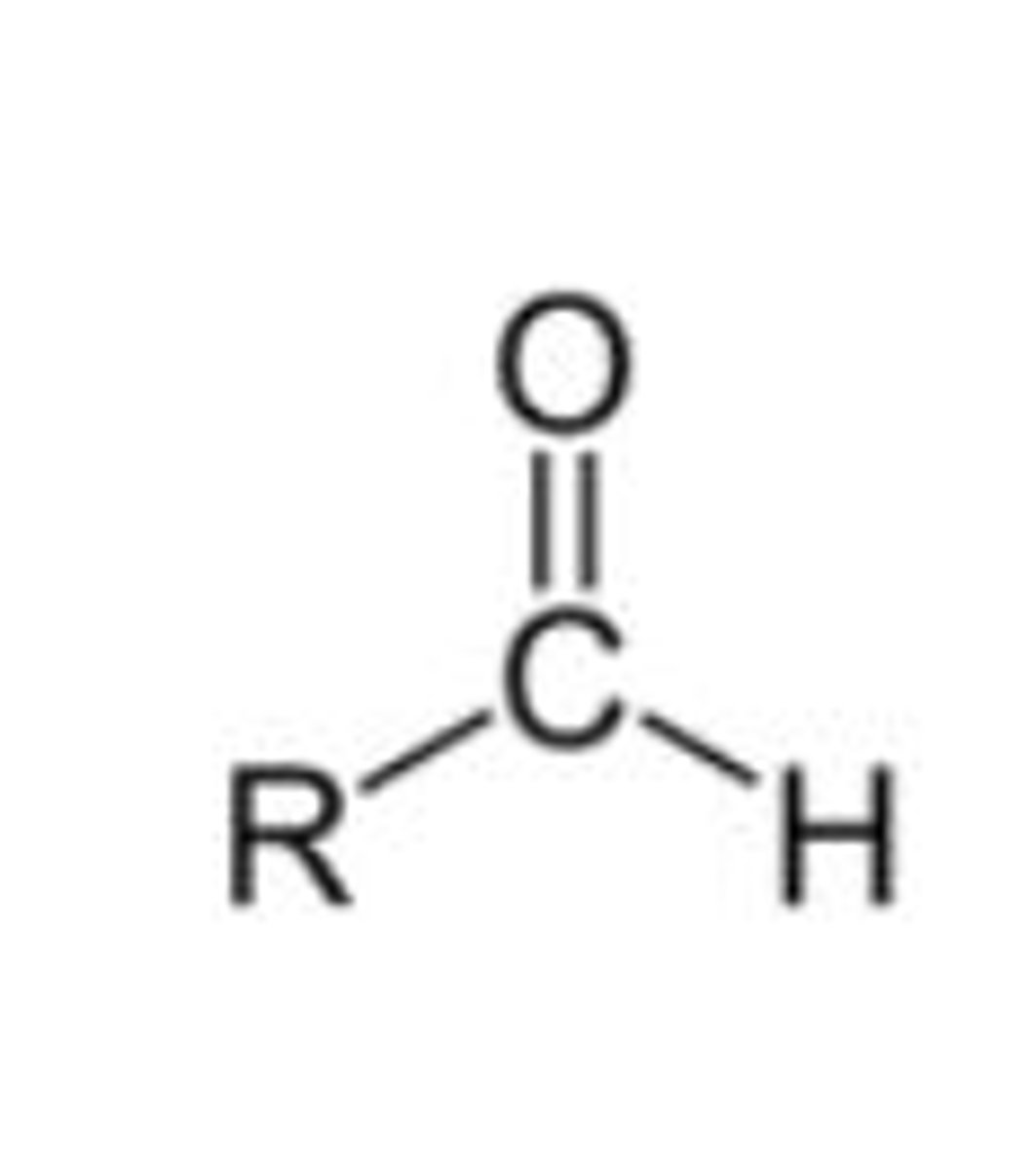
Functional group, prefix and suffix of ketones (5)
Functional group:
- Prefix: oxo-
- Suffix: -one
- E.g propone
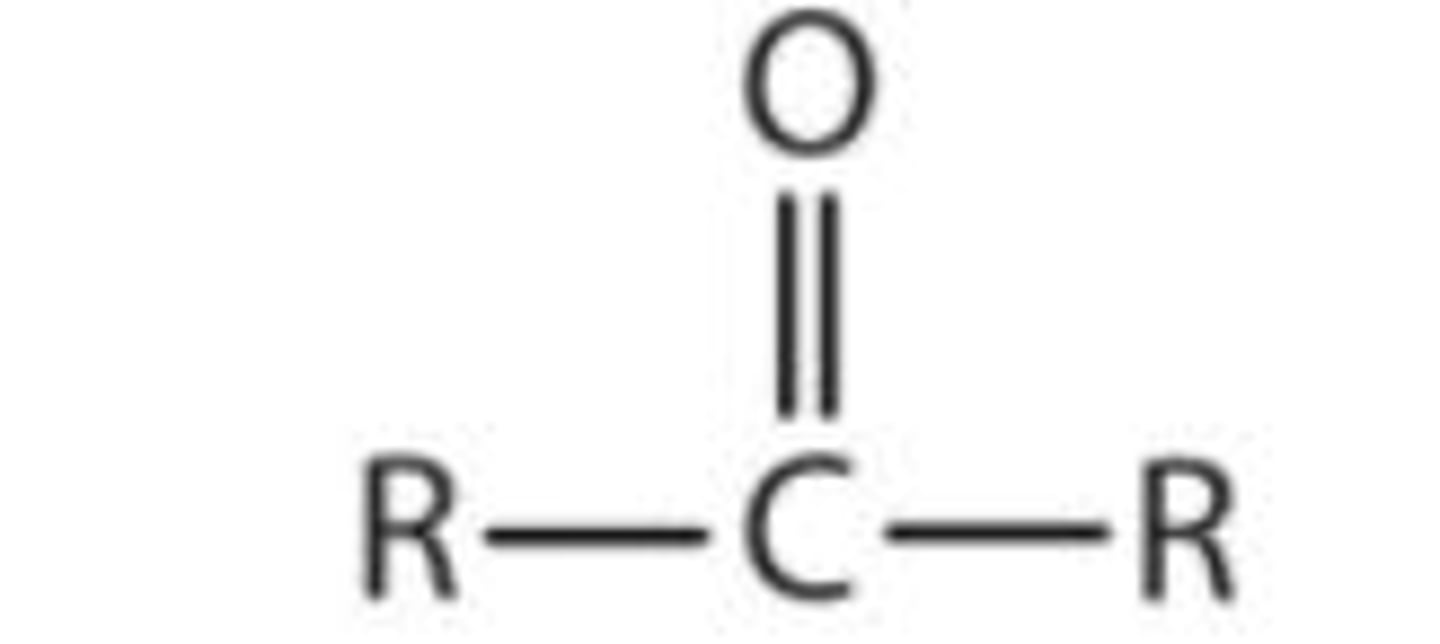
Functional group and suffix of carboxylic acids (3)
- Functional group:
- Suffix: -oic acid
- E.g Ethanoic acid
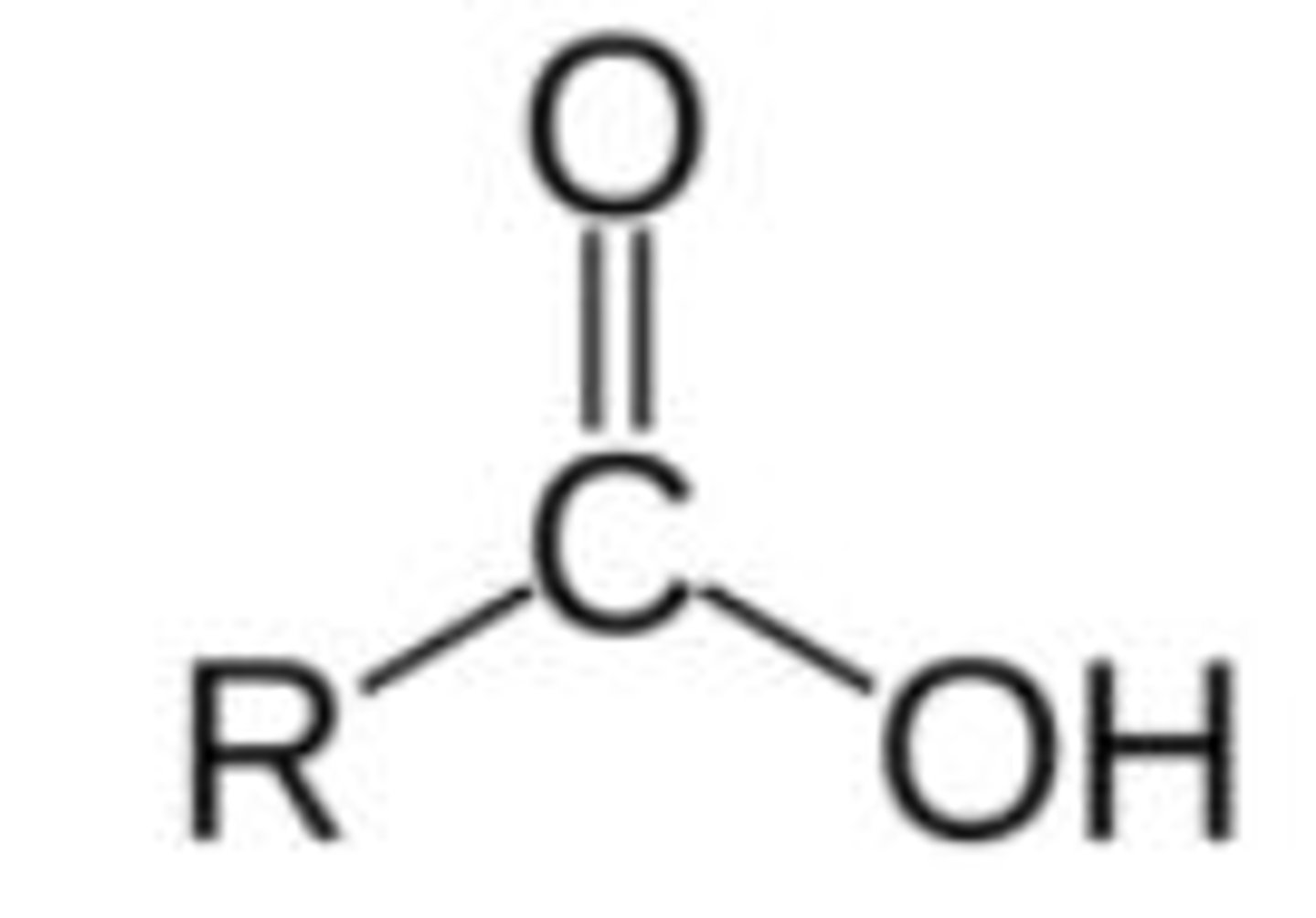
Functional group and suffix of esters (2)
- Functional group:
- Suffix: -yl oate
- E.g Methyl ethanoate
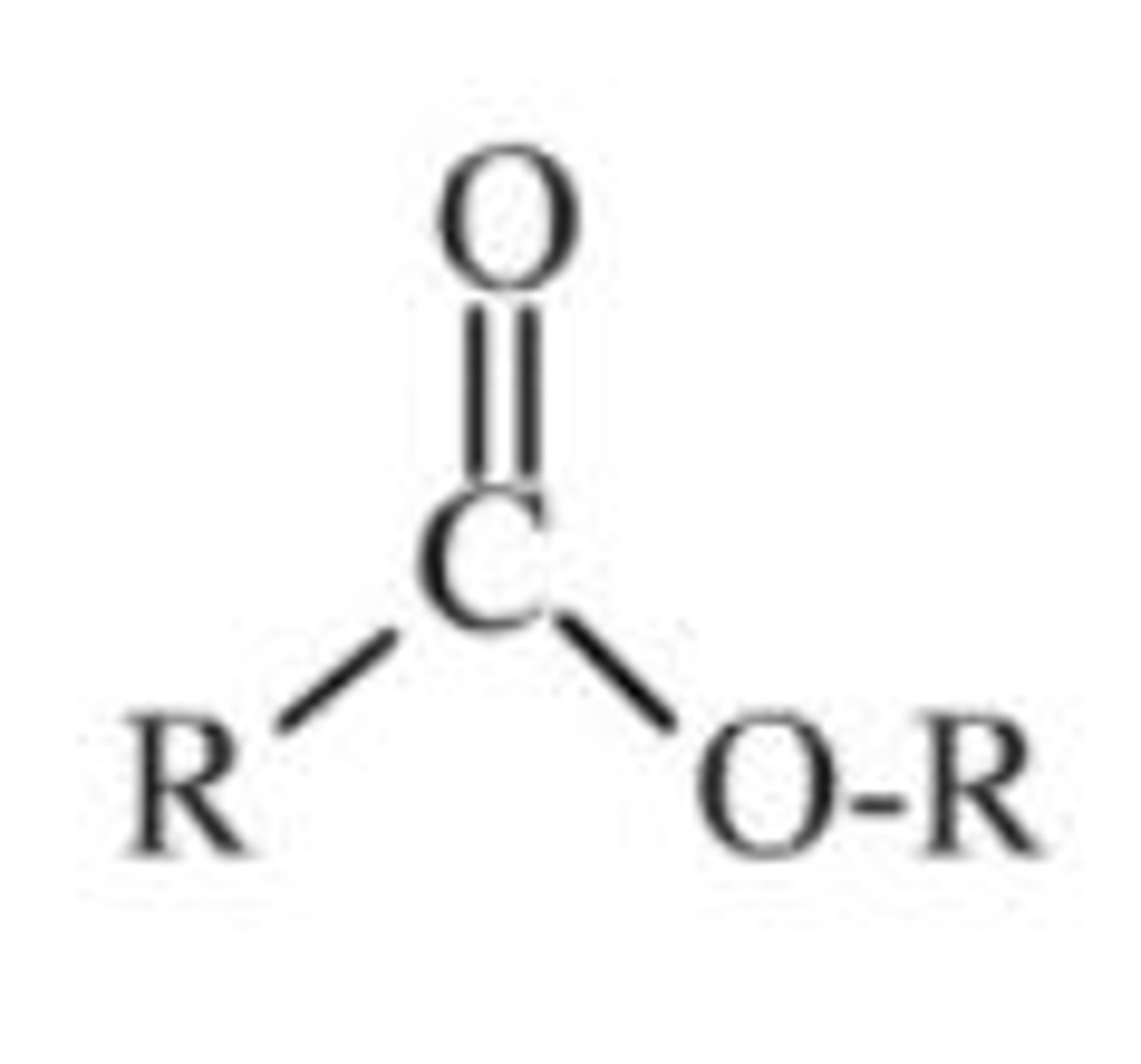
Functional group and prefixes of haloalkanes (6)
Functional group: C-X
- Prefix: fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, idodo-
- E.g Chloropropane
What does nomenclature mean? (1)
The system used for naming organic compounds
What does the displayed formula tell us? (1)
The relative positioning of atoms and the bonds between them
Define structural isomers (1)
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
What are the 3 ways in which structural isomers can be formed? (3)
- Alkyl groups can be in different places
- Functional groups can be bonded to different parts
- There can be different functional groups
Define chain isomers (1)
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangement of Carbon atoms
Define positional isomers (2)
- Compounds with the same molecular formula but different position of functional group
- e.g propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol
Define functional group isomers (1)
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different functional group
Define saturated (2)
Saturated means only single C-C bond
Define unsaturated (2)
Multiple carbon-carbon bonds e.g C=C and C≡C
What 3 factors affect the boiling points of a homologous series? (3)
1. Length of the main chain
2. Surface area of contact
3. Branching
Give 2 reasons why alkanes are mostly unreactive (2)
- C-C and C-H have high bond enthalpies
- Very low bond polarity (essentially non polar) as there is a very small difference in electronegativites between C and H in C-H
What is the general formula for a cycloalkane? (1)
CnH2n
Define Radical (1)
A reactive species with an unpaired electron
What is homolytic fission and what does it form? (2)
- Covalent bond breaks
- With each bonded atom getting an electron forming radicals ( the electrons are equally split, one of the bonded electrons goes to each atom)
What is heterolytic fission? (1)
- When a covalent bond breaks
- With one bonded atom getting both of the shared pair of electrons ( unequal splitting of electrons)
What type of bond fission is Radical Substitution? (1)
Homolytic fission
State the 3 steps of radical substitution (4)
- Initiation
- Propagation
- Termination
Give 2 limitations with radical substitution (2)
- Further substitution of termination products
- Lots of termination steps lead to impurities
Describe the condition needed for initiation to occur in radical substitution e.g reacting methane with chlorine (2)
- UV light
- UV light supplies enough energy to break the Cl-Cl bonds by homolytic fission
Describe what happens in the termination step in Radical substitution (1)
All radicals meet other radicals
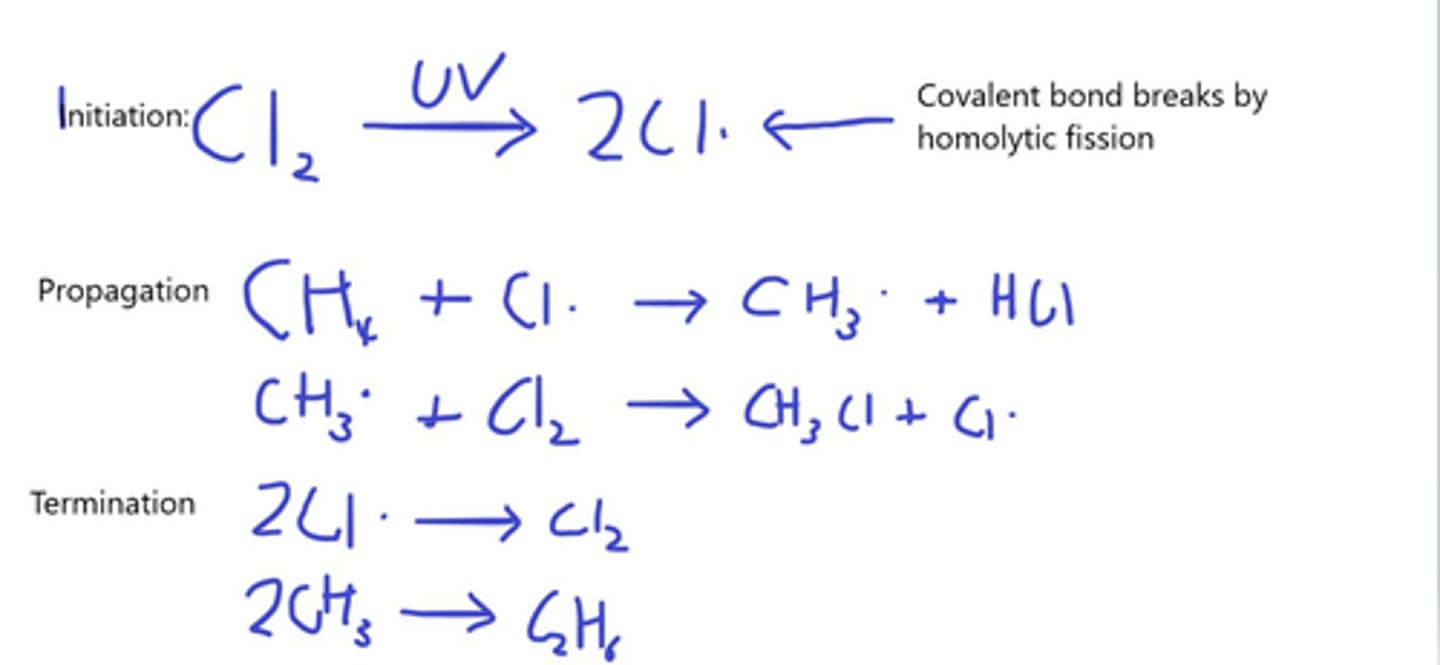
Methane reacts with Chlorine by radical substitution Describe fully, with equations, the mechanism for this reaction (6)
What is a σ bond (1)
The direct overlap of orbitals between the bonding atoms
What is a π bond (with a diagram)
The sideways overlap of adjacent p orbitals to form a π bond above and below the plane of the molecule
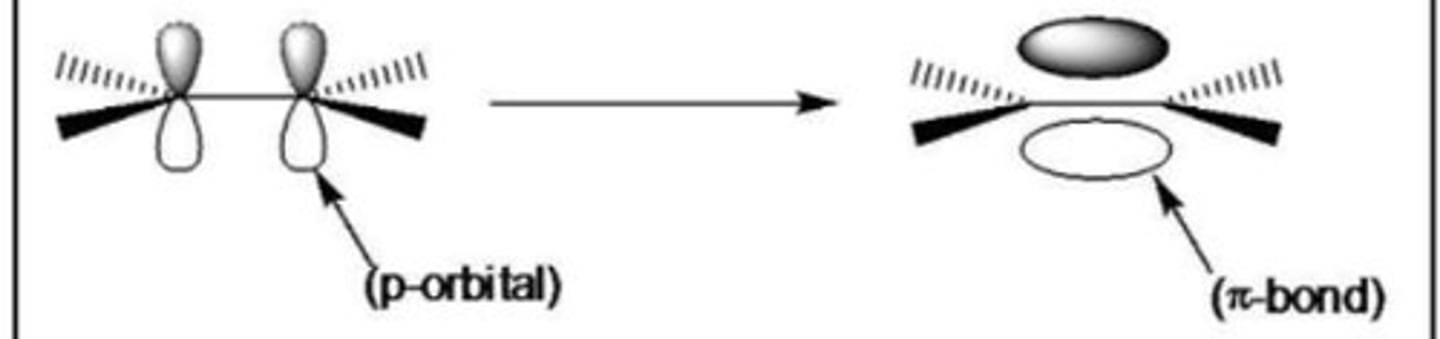
Give 2 differences between a π bond and a σ bond (3)
- π bond has a lower bond enthalpy than a σ bond
- σ bond has electron density between bonding atoms AND π bond has electron density above and below bonding atoms
- σ bond has direct overlap of orbitals but π bond has sideways overlap
What is a stereoisomer? (1)
Compounds with the same structural formula but with a different spatial arrangement of atoms
What 2 things are required for E-Z stereoisomerism to arise? (2)
1. A double C=C bond - which provides limited rotation
2. Two different groups on each Carbon atom around the double bond
Describe what occurs during propagation in radical substitution of Methane with Chlorine (3)
- Chlorine radicals remove H atoms from the Methane to form methane radicals
- These react with Cl2 molecules to form Chloromethane and Cl•
- The new radical continues the chain reaction
What is E/Z isomerism? (3)
- An example of stereoisomerism where
- There is a C=C which provides restricted rotation
- There are 2 priority groups attached to each carbon of the C=C
What is cis-trans isomerism? (1)
A special case of E/Z isomerism ( stereoisomerism in general) where a substituent group on carbon of the C=C group is the same as the other carbon
How would you try reduce further substitution from happening in radical substitution? (1)
Use an excess of the alkane
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes? (2)
- The pi bond has a lower bond enthalpy than the σ bond
- Hence more energy is required to overcome the σ bond compared to the pi bond
Define electrophile (1)
A species that accepts a lone pair of electrons
What is the hydration of alkenes and its conditions? State the mechanism. (4)
- Mechanism: Electrophilic addition
- Forming alcohols from alkenes
- Conditions: Steam, H3PO4 catalyst, high temperature and high pressure
- Example: C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
What is the mechanism for hydration, hydrogenation and halogenation? (1)
Electrophilic Addition
What is the test for unsaturated compounds? (2)
1. Add bromine water
2. If the bromine water turns orange to colourless there is a C=C bond present
Draw and describe the electrophilic addition between bromine and ethene (3)
1. The Br2 molecules approaches the alkene
2. Electrons in the pi bond induce a temporary dipole in Br2 causing the Br+ to attack the electron dense pi bond whilst also the Br-Br bond breaks by heterolytic fission
3. The positive carbon on the primary carbocation intermediate attracts the Br- ion
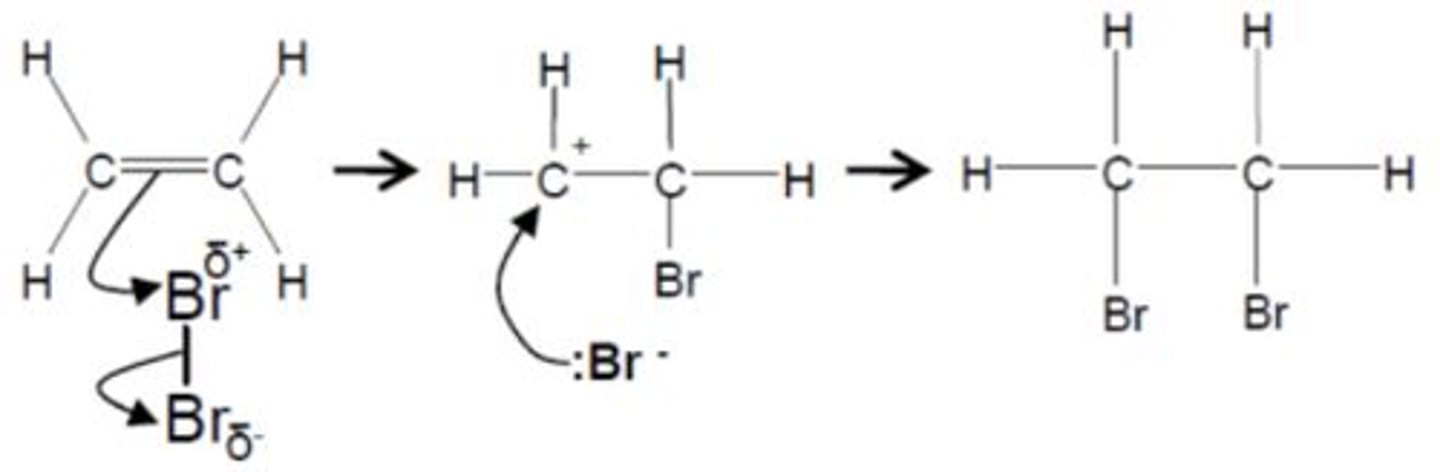
What is Markovnikovs rule used for? (1)
Used to determine the major and minor products of electrophilic addition between hydrogen halides and alkenes
What is a primary carbocation? (1)
The positive charge on a carbon atom is attached to 1 alkyl group
What is a secondary carbocation? (1)
The positive charge on a carbon atom is attached to 2 carbon chains (2 alkyl groups)
What is a tertiary carbocation? (1)
The positive charge on a carbon atom is attached to 3 alkyl groups
What type of bond fission occurs when C2H4 reacts with Br2 (2)
The Br-Br bond breaks by heterolytic fission
Draw the polymerisation of ethene into (poly)ethene
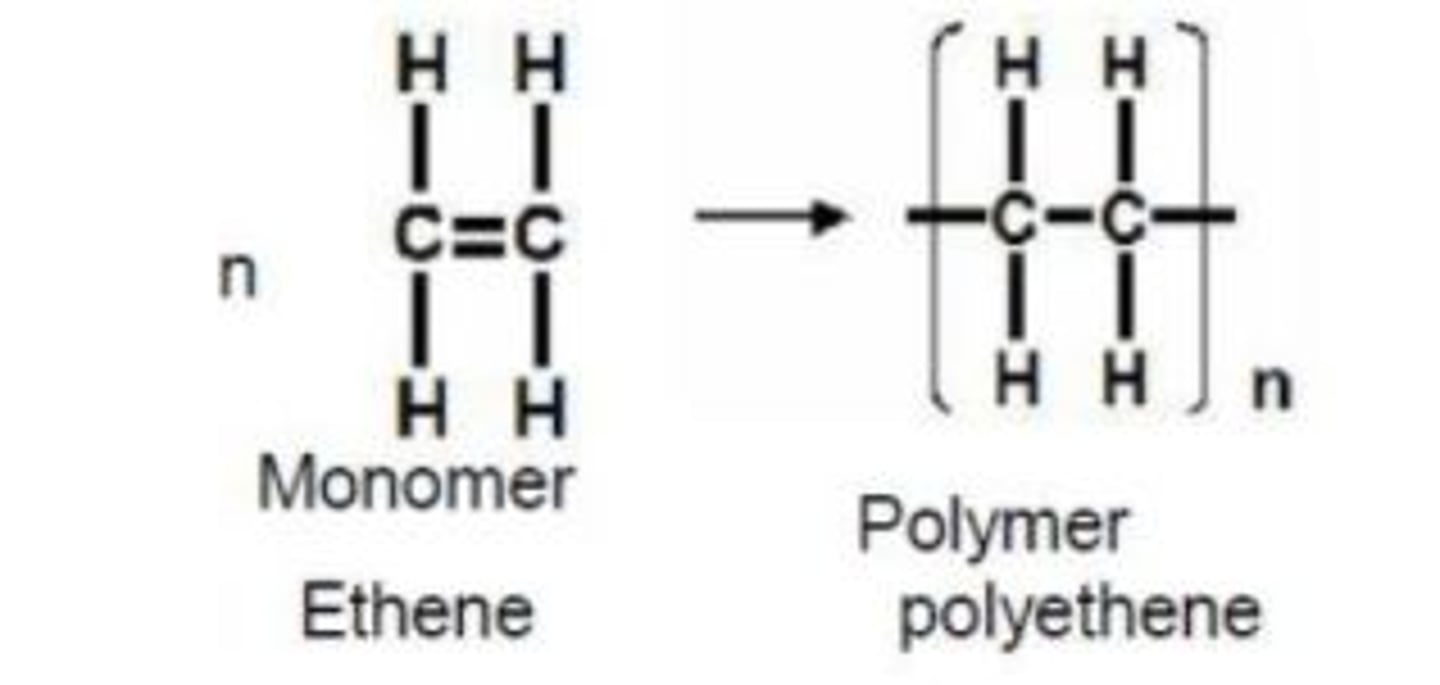
What is addition polymerisation? (1)
The joining/adding of momomers to form a polymer
What is the requirement for the monomer to have to become an addition polymer? (1)
Has to contain a C=C bond
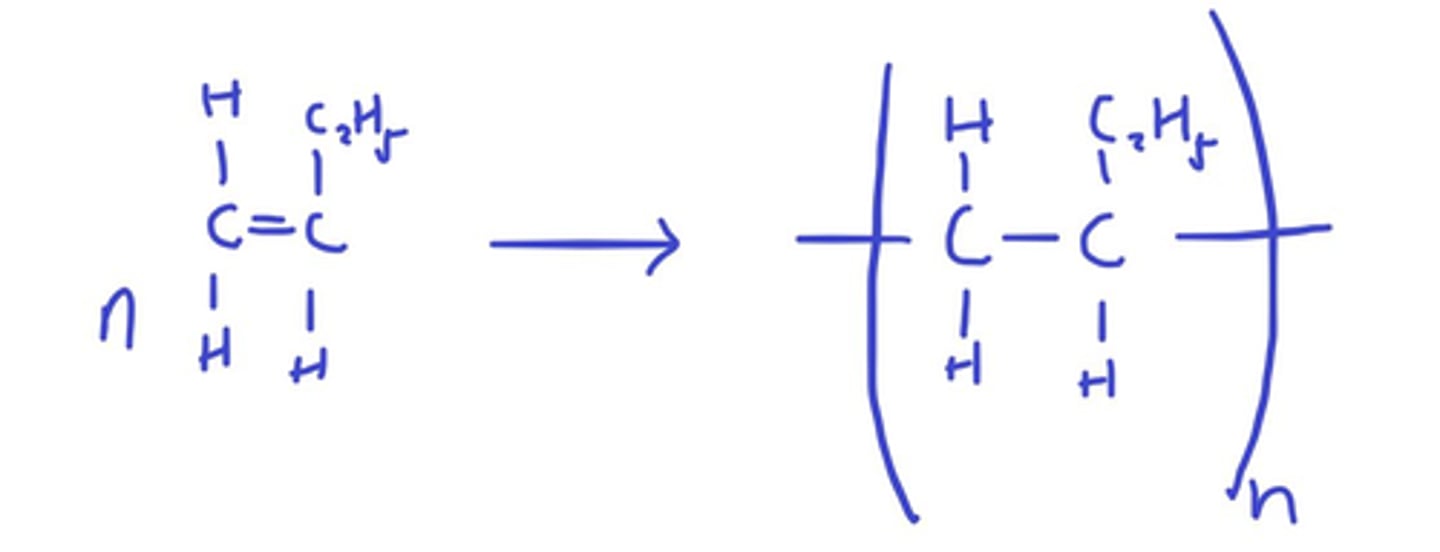
Draw the equation for the formation of (poly)but-1-ene
What shape and bond angle do alkanes have? Explain why (5)
- Tetrahedral
- 109.5 degrees
- Electron pairs repel
- C has 4 bonding pairs and 0 lone pairs
- Bonding pairs repel equally
What reactions will alkanes undergo? (1)
Combustion and reactions with halogens
What is incomplete combustion and what does this form? (1)
Combustion under limited oxygen forming CO and/or C (soot)
What are the problems of combusting polymers? (2)
- Can lead to toxic fumes (e.g HCl)
-Or emission of CO2 which can increase global warming and enhance the greenhouse effect
Give 3 ways of dealing and processing waste polymers? (3)
1. Combustion for energy production
2. Use as an organic feedstock for the production of plastics and other organic chemicals
3. Removal of toxic waste products
Suggest how the HCl can be removed from the gases during the combustion of PVC (3)
1. React with an alkali in order to neutralise
2. React base/carbonate
3. Bubble the HCl through water to make HCl (aq)
What are biodegradable polymers? (2)
Polymers in which micro-organisms recognise specific parts of a molecule and decomposes it
What are the benefits to the environment of developing biodegradable and photodegradable polymers? (2)
1. Reduced dependency of finite resources
2. Reduce problems from disposal e.g Emission of CO2, toxic gases, plastic waste
What does a curly arrow show? (1)
The movement of an electron pair
What bond is broken during addition polymerisation? (1)
Pi bond
What carbocation intermediate is the most stable? (1)
Tertiary carbocation
Why is HBr an electrophile? (1)
HBr breaks by heterolytic fission to form H+ which accepts a lone pair of electrons
What type of bond fission occurs when alkenes react with halogens via electrophilic addition? (1)
Heterolytic fission
Disposal of polymers causes environmental damage. Describe 2 ways in which chemists can reduce this environmental damage (1)
- Develop use of photodegradable polymers
- Develop use of biodegradable polymers
State 2 ways in which chemists are trying to minimise the damage to the environment caused by the disposal of halogenated plastics (3)
- Develop and increase use of biodegradable polymers
- Remove HCl by reacting with an alkali/base/bubbling through water
What is an essential condition for the hydration of alkenes? (2)
- Temperature ≥ 100oC
- As you are reacting the alkene with steam
What is a homologous series? (1)
A series of organic compounds having the same functional group but with each successive member differing by CH2
If a compound contains a benzene ring then it is? (1)
Aromatic
If a compound does not contain a benzene ring then it is (1)
aliphatic
If an aliphatic compound contains a non-aromatic ring then it is (1)
alicyclic
What is the reaction between an acid and a base called (1)
A neutralisation reaction
What are isomers? (1)
Two molecules with the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms
What are structural isomers? (1)
Two molecules with the same molecular formula different structural formula
What forces act between alkane molecules? (1)
London forces
Why do longer chained hydrocarbons have stronger London forces? (1)
There are more surface contact areas and more electrons to interact
Why do branched chained alkanes have lower boiling points? (1)
Cannot pack closely together So, smaller molecule surface area
Why is producing carbon monoxide a problem? (3)
- Carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin
- Less oxygen can be carried around the body
- Oxygen deprivation
What is breaking a covalent bond called? (1)
Bond fission
What is heterolytic fission? (3)
- Bond breaks unevenly
- One bonded atom receives both electrons from COVALENT bond
- Two different substances are formed
What is homolytic fission? (3)
- Bond breaks evenly
- Each bonding atom receives one electron from COVALENT bond
- Two uncharged radicals are formed
What are radicals? (1)
Species with an unpaired electron
Why are radicals very reactive? (1)
They have an unpaired electron
What do Halogens react with Alkanes to form? (1)
Haloalkanes
What is a free radical substitution reaction? (1)
When a hydrogen atom is substituted by chlorine or bromine
Why is a lack of reactivity in everyday polymers an issue? (1)
Makes them non biodegradable and so difficult to dispose of
When is landfill used? (2)
- Plastic is difficult to separate
- Too difficult to recycle
How can plastics be reused? (4)
- Recycled by melting and remoulding
- Cracked into monomers and used as organic feedstock
- Combustion for energy production
Why is burning carefully controlled? (1)
To reduce toxic gases e.g HCl
What do scrubbers do? (1)
They neutralise gases such as HCl allowing them to react with base