7.6: Test: Bohr to Quantum Model of Atoms, Electron Configurations, Periodic Table and Periodicity
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/79
Last updated 1:16 AM on 10/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
energy levels
the fixed energies an electron can have
2
New cards
What did Bohr propose in his model of the atom?
Bohr proposed that an electron is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around the nucleus.
3
New cards
Quantum (of energy)
the amount of energy required to move an electron from one energy level to another energy level
4
New cards
quantum mechanical model
the modern description of the electrons in atoms
5
New cards
Where did the quantum mechanical model come from?
the mathematical solutions to the Schrodinger equation
6
New cards
What does the quantum mechanical model determine about the electrons in an atom?
The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus of an atom
7
New cards
what do atomic orbitals describe?
describes the probability of finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus
8
New cards
What are atomic orbitals?
mathematical expressions from the Schrodinger equation
9
New cards
How do sublevels of principal energy levels differ?
each energy level corresponds to one or more orbitals of different shapes. The orbitals describe where an electron is likely to be found.
10
New cards
What is the shape of an s orbital?
sphere
11
New cards
What is the shape of a p orbital?
dumbbell
12
New cards
what is the shape of a d orbital?
four-leaf clover
13
New cards
how many sublevels are in principal energy level n=1?
1 sublevel
14
New cards
how many sublevels are in principal energy level n=2?
2 sublevels
15
New cards
how many sublevels are in principal energy level n=3?
3 sublevels
16
New cards
how many sublevels are in principal energy level n=4?
4 sublevels
17
New cards
how many electrons can be stored in an s orbital?
2 electrons
18
New cards
how many electrons can be stored in a p orbital?
6 electrons
19
New cards
how many electrons can be stored in a d orbital?
10 electrons
20
New cards
how many electrons can be stored in an f orbital?
14 electrons
21
New cards
What is the maximum number of electrons principal energy level n1 can hold?
2 electrons maximum
22
New cards
What is the maximum number of electrons principal energy level n2 can hold?
8 electrons maximum
23
New cards
What is the maximum number of electrons principal energy level n3 can hold?
18 electrons maximum
24
New cards
What is the maximum number of electrons principal energy level n4 can hold?
32 electrons maximum
25
New cards
electron configurations
the ways in which electrons are arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms
26
New cards
what are the three rules for writing the electron configurations of elements?
the aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund's rule
27
New cards
Aufbau Principle
electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first
28
New cards
Pauli Exclusion Principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons (with opposite spin)
29
New cards
Spin
a quantum mechanical property of electrons that may be thought of as clockwise or counterclockwise (indicated with arrows)
30
New cards
Hund's Rule
electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as large as possible
31
New cards
P Block
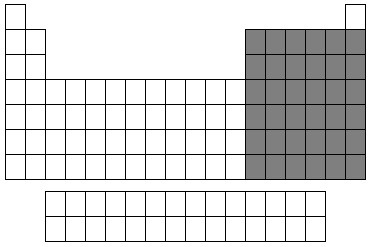
32
New cards
What is the orbital order?
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p
33
New cards
S Block
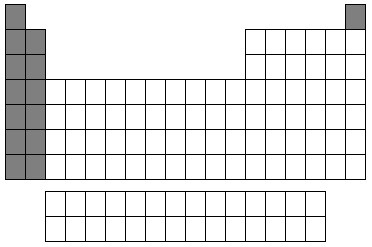
34
New cards
D Block
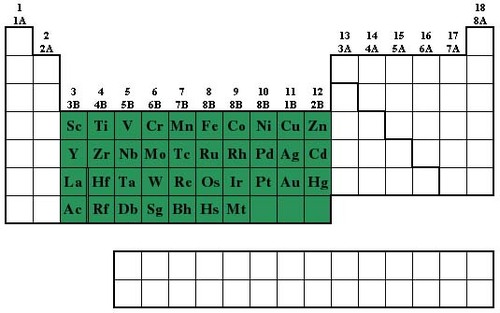
35
New cards
F Block
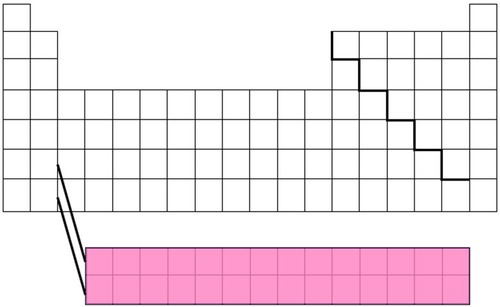
36
New cards
amplitude
the wave's height from zero to the crest
37
New cards
Wavelength (λ)
the distance between crests of a wave
38
New cards
frequency (ν)
the number of wave cycles to pass a given point per unit of time
39
New cards
Hertz (Hz)
Unit for frequency, SI unit of cycles per second
40
New cards
electromagnetic radiation
energy waves that travel in a vacuum at a speed of 2.998 x 10^8 m/s; includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays
41
New cards
spectrum (of colors)
wavelengths of visible light that are separated when a beam of light passes through a prism; range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation
42
New cards
What causes atomic emission spectra?
When atoms absorb energy, their electrons move to higher energy levels. These electrons lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels.
43
New cards
atomic emission spectrum
the pattern formed when light passes through a prism or diffraction grating to separate it into the different frequencies of light it contains
44
New cards
Planck's Constant (h)
(6.626 x 10^-34 Js) Used to calculate the radiant energy absorbed or emitted by a body based on the frequency of radiation
45
New cards
Photoelectric Effect
the ejection of electrons by certain metals when they absorb light with a frequency above a threshold frequency
46
New cards
How did Einstein explain the photoelectric effect?
He proposed that light could be described as quanta of energy that behave as if they were particles.
47
New cards
Equation for energy
E = hv
48
New cards
Photons
a quantum of light; a discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy that interacts with matter similarly to particles
49
New cards
Ground State
The lowest possible energy of an atom (described by quantum mechanics)
50
New cards
How are the frequencies of light emitted by an atom related to the changes of electron energies?
the light emitted by an electron moving from a higher to a lower energy level has a frequency directly proportional to the energy change of the electron
51
New cards
How does quantum mechanics differ from classical mechanics?
Classical mechanics adequately describes the motions of bodies much larger than atoms, while quantum mechanics describes the motions of subatomic particles and atoms as waves
52
New cards
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know exactly both the velocity and the position of a particle at the same time
53
New cards
How did chemists begin to organize the known elements?
used the properties of elements to sort them into groups
54
New cards
How did Mendeleev organize his periodic table?
Arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass
55
New cards
How is the modern periodic table organized?
arranged in order of increasing atomic number
56
New cards
periodic law
when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties
57
New cards
What are 3 broad classes of elements?
metals, nonmetals, metalloids
58
New cards
Metals
elements that are good conductors of heat and electric current. tend to be ductile, malleable, and shiny
59
New cards
Nonmetals
elements that tend to be poor conductors of heat and electric current. properties opposite of metals.`
60
New cards
Metalloids
elements that tend to have properties of both metals and nonmetals
61
New cards
What information can be displayed in a periodic table?
The periodic table usually displays the symbols and names of the elements along with information about the structure of the atom
62
New cards
alkali metals
any metal in Group 1A of the periodic table
63
New cards
alkaline earth metals
any metal in Group 2A of the periodic table
64
New cards
halogens
a nonmetal in Group 7A of the periodic table
65
New cards
transition metal
one of the Group B elements in which the highest occupied s sublevel and a nearby d sublevel generally contain electrons
66
New cards
How can elements be classified based on electron configurations?
elements can be sorted into noble gases, representative elements, transition metals, or inner transition metals based on their electron configurations
67
New cards
noble gases
an element in Group 8A of the periodic table; the s and p sublevels of the highest occupied energy level are filled
68
New cards
representative elements
an element in an "A" group in the periodic table; as a group these elements display a wide range of physical and chemical properties. In their atoms, the s and p sublevels in the highest occupied energy level are partially filled
69
New cards
inner transition metals
an element in the lanthanide or actinide series; the highest occupied s sublevel and nearby f sublevel of its atoms generally contain electrons; also called inner transition element
70
New cards
atomic radius
one-half the distance between the nuclei of 2 atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined (r = d/2) (r = bonded atomic radius)
71
New cards
What are the trends among the elements for atomic size?
In general, atomic size increases from top to bottom within a group and decreases from left to right across a period
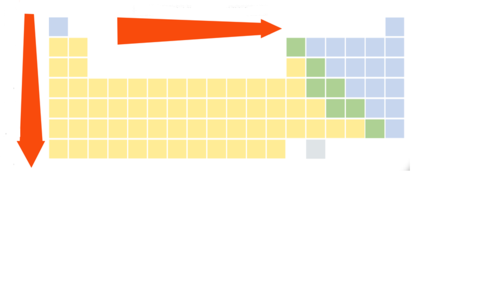
72
New cards
ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
73
New cards
how do ions form?
Positive and negative ions form when electrons are transferred between atoms
74
New cards
cation
any atom or group of atoms with a positive charge
75
New cards
anion
any atom or group of atoms with a negative charge
76
New cards
ionization energy
the energy required to remove an electron from its atom in its gaseous state
77
New cards
What are the trends among the elements for first ionization energy?
first ionization energy tends to decrease from top to bottom within a group and increase from left to right across a period
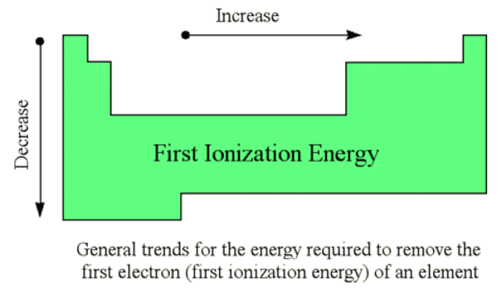
78
New cards
what are the trends among the elements for ionic size?
ionic size tends to increase from top to bottom within a group and (the size of cations and anions) decrease from left to right across a period
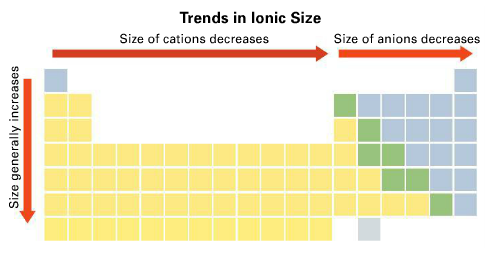
79
New cards
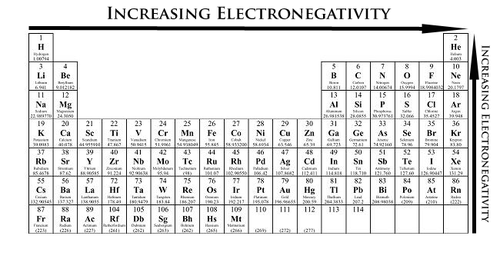
Electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound
80
New cards
what are the trends among the elements for electronegativity?
In general, electronegativity values decrease from top to bottom within a group. For representative elements, the values tend to increase from left to right across a period