Business - 1.5 Growth and Evolution
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Reasons for businesses to grow
Survival: large firms have a greater chance of surviving, less likely to fail, less likely to be taken over
Economies of scale: large firms enjoy economies of scale, translates into lower costs, greater profit, higher returns, healthier balance sheet
Higher status: larger reach and brand awareness
Market leader status: market leader, dominance
better deals
attract better staff
Increased market share: large market share allows companies to control the market by determining prices and deciding which services will be the industry standard, more revenue
Reduce competition
Access to finance
Reasons for businesses to stay small
Control - control costs and keep profits, stay true to values, won’t need too much money to buy, low overheads (cost of electricity, gas, expenses)
Good relations - good connections with customers, personalized service
Financial risk of being bigger
Government aid is available - can get advice
Local monopoly power
Flexibility and adaptive to change
Cater for limited or niche markets
The main reason many people choose to set up a small business is because it gives them independence. They also reap the rewards for themselves; theses are two powerful incentives
Ansoff’s Matrix
strategic framework and market development strategy that helps businesses identify growth opportunities by considering existing and new products or services in new or existing markets
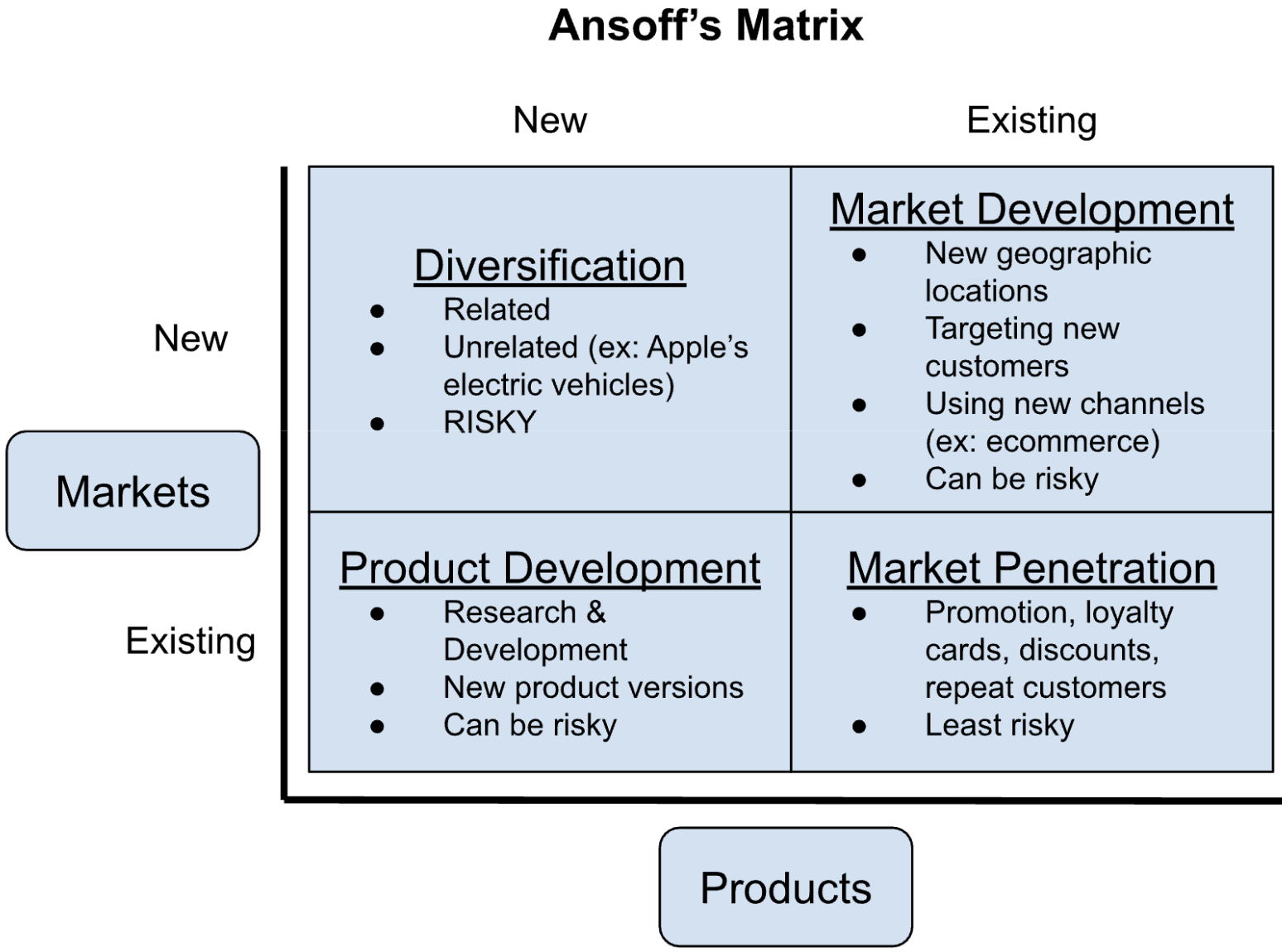
Market Penetration
(Selling more of existing products in existing markets)
✅ Benefits:
Lower risk since the market is familiar.
Economies of scale due to increased production.
Strengthens brand loyalty and market share.
Often requires minimal investment compared to other strategies.
❌ Drawbacks:
Market saturation may limit growth potential.
Price wars and competitive pressures can reduce profitability.
May require heavy promotional spending to attract more customers.
Limited innovation, making the business vulnerable to market changes.
Market Development
(Expanding into new markets with existing products)
✅ Benefits:
Opens new revenue streams and customer bases.
Utilizes existing products, reducing development costs.
First-mover advantage in new or emerging markets.
Spreads business risk across different regions.
❌ Drawbacks:
Higher costs due to market research and localization.
Cultural and regulatory differences may create barriers.
Existing competitors in the new market may be well-established.
Potential brand dilution if expansion is not well-executed.
Product Development
(Creating new products for existing markets)
✅ Benefits:
Strengthens customer loyalty and brand image.
Meets evolving customer needs, staying competitive.
Can differentiate the brand from competitors.
Potential for higher profit margins with innovative products.
❌ Drawbacks:
High research and development (R&D) costs.
Risk of product failure or rejection by customers.
Requires effective marketing to create demand.
May lead to cannibalization of existing products.
Diversification
(Launching new products in new markets)
✅ Benefits:
Spreads business risk across different industries/markets.
Opens entirely new revenue opportunities.
Can boost brand recognition and corporate reputation.
Potential for high returns if successful.
❌ Drawbacks:
Highest risk due to unfamiliar products and markets.
Requires substantial investment in R&D and market research.
Challenging to manage different business operations.
Higher chance of failure due to lack of expertise.
Cash Flow: Definition
cash movement in and out of a business
cash inflows and outflows
Profit: Definition
TR - TC: Total Revenue - Total Cost
financial gain remaining after all expenses are deduced from revenue