Pedigree Analysis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Why are human genetics difficult to study?
We are not model organisms (do what we want when we want, long generations, free will)
‘Single-gene’ human traits
attached/free earlobe, dimples, chin cleft, widow’s peak, finger hair, hitchhiker’s thumb
Family histories can reveal much about the _________ pattern of traits
inheritance
unaffected person

person affected with trait

obligate carrier (carries gene but doesn’t have trait)

asymptomatic carrier (currently unaffected but may exhibit trait later)

autosomal recessive traits
Appear with equal frequency in males and females and tend to ‘skip’ generations
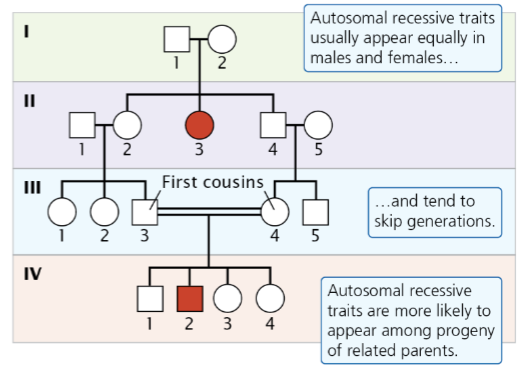
autosomal recessive traits often arise from _________ parents
unaffected
If two affected individuals with autosomal recessive traits have offspring, how many offspring will show the trait?
all
Autosomal dominant traits
Appear with equal frequency in males and females and tend to be present in all generations
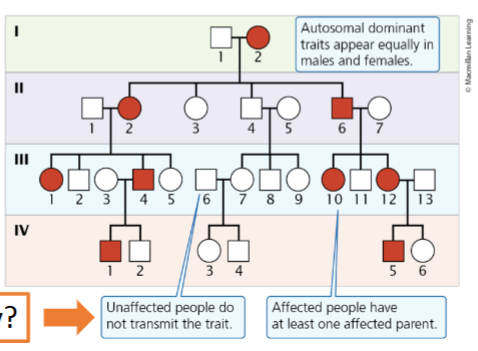
Why don’t unaffected people transmit autosomal dominant traits?
they can’t be unaffected if they carry the trait; they don’t carry it so they can not transmit it
X-linked recessive traits
Appear with higher frequency in males than in females and tend to skip generations
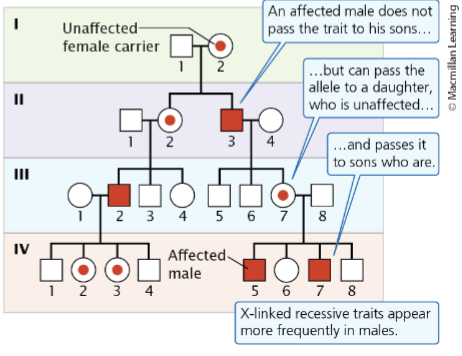
___-______ recessive traits are always passed from mother to son, never from father to son
X-linked
Female carriers of X-linked recessive traits and affected males can produce _________ _________
affected females
X-linked dominant traits
Appear with higher frequency in females than males and do not skip generations
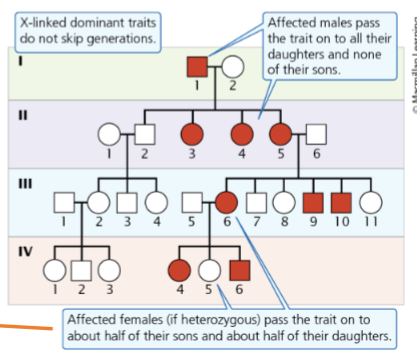
A father affected by an X-linked dominant trait who mates with an unaffected female will produce…
all affected daughters and no affected sons
a mother affected by an X-linked dominant trait who mates with an unaffected male will produce…
50% affected offspring (male or female)
Y-linked traits
Only appear in males and appear in all generations regardless of dominance
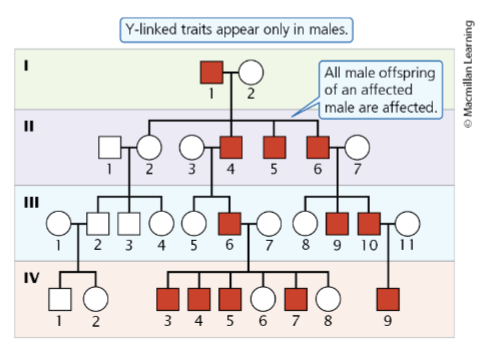
Pedigrees with more ____ are generally more useful for analysis, and can be constructed from ancient DNA
data
studies on concordance of twins and adoption of a child reveal the relative influence of ____ and __________ on traits
genes and environment
Concordance in twins
the likelihood that both twins exhibit the same trait or characteristic
Monozygotic (identical) twins share 100% of DNA (any difference in phenotype are _____________)
environmental
Dizygotic (nonidentical) twins share ___% of DNA
~50%
If concordance is higher for monozygotic twins than dizygotic twins, then it has a ______________ component
genetic (inherited)
examples of traits where there is not much difference in % occurrence in monozygotic vs dizygotic twins (% concordance is around the same)
cancer and death from acute infection (caused by environment)
examples of traits where there is a difference in % occurrence in monozygotic vs dizygotic twins (% concordance is higher for monozygotic than dizygotic)
epilepsy and rheumatoid arthritis (caused by genetics)
If a child has similar characteristics to their adopted parents, it suggests _____________ __________
environmental influence
If an adopted child has similar characteristics to their biological parents, it suggests _____________ __________
genetic influence
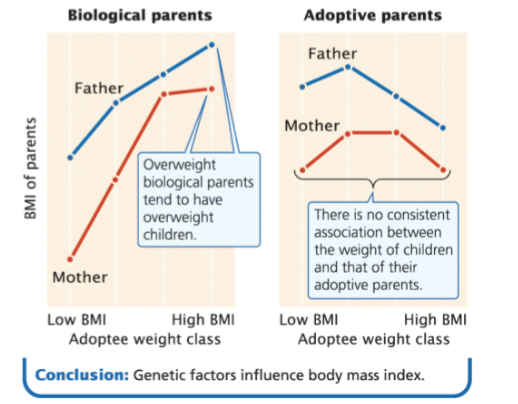
BMI example of an adoption study
BMI is influenced by genetics