control of gene expression
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Does every cell have the same genotype in humans?
yes
Why is gene expression regulated?
Cells express only genes needed for their function
amount of Protein vary with cell type and cell cycle stage
Making proteins uses lots of energy, so unnecessary synthesis is avoided
When is gene expression regulated?
during differentiation
during development
as a ressponse to environemnt
depending on the function of the cell
what are the stages of gene expression and when can it be regulated
DNA is unfolded from histones to make genes accessible
Transcription factors bind and start transcription (DNA → mRNA)
mRNA is processed (splicing, capping, poly-A tail added)
Translation factors help make protein from mRNA
Protein modified or broken down after it’s made
What are the 2 levels at which gene expression can be regulated?
Epigenetics and transcriptional regulation
What is epigenetics and transcriptional regulation?
epigenetics changes gene activity and expression without changing the DNA sequence,
transcriptional regulation controls when and how much a gene is transcribed into RNA.
why do epigentic factors affect chromatin and not DNA sequence
epigenetic factors mean changing in gene activity without changing DNA sequence
epigenetic factors change how tightly the DNA is wrapped around the histone the more tighter packed ( heterchromatin) makes the gene less transcriptionally active the more loosley packed ( euchromatin) makes the gene more trancriptionally active
What is a nucleosome
8 histones + DNA wrapped around it
1 unit of chromatin
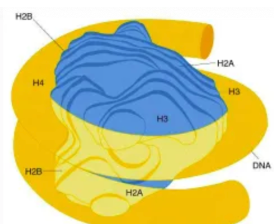
what chemical changes make epigenetic code
it controlls whether a gene is swithced on or off
DNA methylation – addition of methyl groups (–CH₃) to cytosine bases in DNA
Histone modification – addition or removal of chemical groups (like acetyl, methyl, or phosphate) to histone proteins
How are histone tails modified and what does it cause
Histones have N-terminal tails that stick out from the nucleosome.
These tails can be chemically modified by acetylation ( add acetyl group) methylation ( add methyl group ) , or phosphorylation ( add phosphate group ).
The modifications change chromatin condensation, affecting how tightly DNA is wrapped around histones.
This alters DNA accessibility, making genes easier or harder to transcribe.
Through these changes, cells can switch large regions of chromosomes on or off, allowing global gene regulation.
How does DNA methylation workAKA cytosine methylation
Where: Occurs at CpG sites (cytosine next to guanine).
What happens: An enzyme called DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) adds a methyl group (–CH₃) to the cytosine base.
Effect:
Prevents transcription factors from binding.
Attracts proteins that condense chromatin, making DNA tightly packed (heterochromatin).
Result: The gene is silenced (turned off) — less or no mRNA is made.
Reversible: Methyl groups can be removed (demethylation), allowing gene reactivation.
What is dual inheritance?
organism inherit genes in ways:
Genetic inheritance: genes passed from parent to offspring.
Epigenetic inheritance: chemical tags or chromatin marks (like DNA methylation, histone modification) that control how those genes are expressed, not the genes themselves.
How is epigenetics and disease linked?
chemical changes to DNA or histones can turn genes on or off without changing the DNA sequence ( methylation, histone ,modification)
these changes can be influenced by the environment and sometimes passed to offspring, affecting their risk of disease.
How can problems with gene expression cause cancer?
The absence of transcription off switch leads to the wrong genes being expressed and it causes cell division
How can problems with gene expression cause chronic diseases (e.g obesity)?
Abnormal gene expression because of the wrong signals in the
cell can cause inflammation and increased risk of other diseases
How can problems with gene expression cause developmental diseases?
Mistakes in early protein synthesis can lead to organ developmental problems
What external stimulus can alter gene expression?
Exposure to toxins or drugs
how and by what is transcription initiation controlled
a regulatory protein control how much and wen a gene is transcibed
they have to binding sites the DNA binding domain and a transcription activation domain, that attach to the DNA
the regulatory protein is made in the cell and diffuses to the nucleas and binds to th DNA it either allows or blocks RNA polymerease
What is needed for transcription initiation?
General transcription factors (GTFs)
what are the 2 types of regulatory sequences and explain
cis- they influence genes on the same molecule of DNA
trans - act on other DNA molecules to regulate gene expression.
Where are regulatory sequences found in the genome?
the non-coding regions of the genome
what is the differnce between regulatory sequences and regulatory proteins
Regulatory sequences are DNA regions (like promoters, enhancers, silencers) that control gene expression.
Regulatory proteins (like transcription factors) are proteins that bind to these DNA sequences to turn genes on or off.
What do regulatory sequences do?
they interact with DNA binding proteins e.g. transcription factors resulting in induction or repression of transcription initiation
What is the TATA box?
a DNA sequence in eukaryotic promoters in the 5' region that helps form the transcription initiation complex, allowing RNA polymerase II to start transcription.
What happens if transcription initiation goes wrong?
if the sequence is missing to switch the gene off and you keep expressing a protein which is going to lead to cell growth and cancer
How is gene expression regulated by hormones?
hormones bind to receptors which can switch genes on or off
some hormones can enter the cell making a hromon-receptor complex which can move to the nucleas and bind to DNA
What are 2 ways that mRNA processing is regulated?
Polyadenylation (rare) and splicing (common)
how is polyadenylation regulated
normally the poly A tail is added
but U1A is a protein that binds just before the polyA site
U1A bidns to its own mRNA which means it stops translation down stream also stopping the translation that woudl of made the poly A tail
this is negatuve feedback so when there alot fo U1a protein then it stops makig more as the mRNA is blocked
if there is low u1A then not much mRNA is blcoked so it cna make more
what is splicing and alternative splicing
introns removed by splicing
alternative splicing can remove specific exons
Explain alternative splicing in gene regulationusing the example of fibronectin
liver and fibroblast make fibronectin but the protein they make has different properties because of alternative splicing
liver makes soluble fibronectin for clotting
fibroblast make insolube fibronecting for tissue structure
regulation of protein synthesis summary
1. Epigenetic level – DNA accessibility (chromatin structure)
- doesnt change the DNA sequence only the activity
- it affects chromatin not DNA sequence
- heterochromatin ( tighter) - gene offf
- euchromatin (looser) - gene on
how?
1. DNA methylation → adds –CH₃ to cytosine → gene off
2. histone modification → acetyl, methyl, phosphate groups change how tightly DNA wraps → controls transcription
2. Transcriptional level – control of mRNA production
- controlled by regulatory proteins ( transciption factors)
- transcription factors have a DNA binding domain and a activation domain
- trancription factors bind to regulatory sequences which are found in the non coding region ( e.g promoters)
- cis- the transcption factor acts on the same DNA strand
- trans- the transcription factor acts on another DNA molecule
-TATA box where the RNA polymerease binds
3. Post-transcriptional – splicing, capping, poly-A tail
-polyandylation: added to ther 3' end and it helps mrna go to translation but when there U1A protein this is just before the poly A tail and it binds to its own mRNA stopping translation of the poly A tail
splicing: remove introns
alternative splicing: remove certain exons
capping:
cap added to 5' end this stabalised the mrna moving it to be translated
4. Translational – control of protein synthesis
- controls how much protein is made from mRNA
5. Post-translational – protein modification or breakdown
hormone control:
- hormones bind ot receptors
- some hormones eneter the cell making a hormon-receptor complex which canbidn to dna switching genes on/off