PHAR301 - Placebo Effect [2025 COPY]
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is a placebo treatment?
An inert treatment, given as if it were a real treatment
Beecher stated that placebos could produce a real therapeutic effect of 35.2% in all placebo cases. What were the problems with his statment and evidence?
1. He discussed 15 published trials, none of which were to test for placebo effects.
2. Failed to recognize the difference between placebo effect and placebo response
3. The studies referenced did not have a randomized design
4. Some studies used questionable measures
5. Some of the drugs prescribed in the study were not helpful in itself or may have even been toxic.
What is the difference between placebo response and placebo effect?
Response: Change over time within placebo treatment group
Effect: Change over time CAUSED by the placebo treatment
Large placebo response can mask drug effects, causing a clinical trial to fail. T or F.
True
What is a failed clinical trial?
means that the comparator (a.k.a. "gold standard") drug (here, SSRI) has no detectable effect
Why might there be a placebo response if it is not due to the placebo effect?
• patient wants to be polite
• patient is getting additional treatment elsewhere
• spontaneous improvement
• regression to the mean
• etc
What may explain spontaneous improvement in disease?
The body may have naturally recovered OR the disease may be cyclical in nature
What is the regression of the mean?
the tendency for extreme random values to be closer to the mean when they are repeated
• assume disease severity varies randomly with time
• each line in figures is a single patient measured before and after
• extreme values at one time point will tend to be less extreme at another time point
In a study examining placebos, two conditions were tested. One where the patient was given a injection of sumatriptan or placebo and another where the patient was given sumatriptan or a placebo orally. What were the results of the experiment? What was the explanation behind the results?
The experiment results showed an observable placebo response in the injected patients, yet no difference in response in the oral patients.
This indicates that there DOES appear to be a placebo effect that is modulated by the complexity of the modality of the treatment.
How do we isolate the placebo effect?
Studies should include a no treatment group to identify the change caused by the placebo effect.
What is a no treatment group?
Subjects are told they are on a waiting list to enter the study. Meanwhile, take baseline measures and measure again at end of study
What is the challenges with the no treatment group?
• Patient is still contracting with clinicians (feeling cared for)
• Negativity of having to wait for treatment
Draw a summary of the placebo effect.
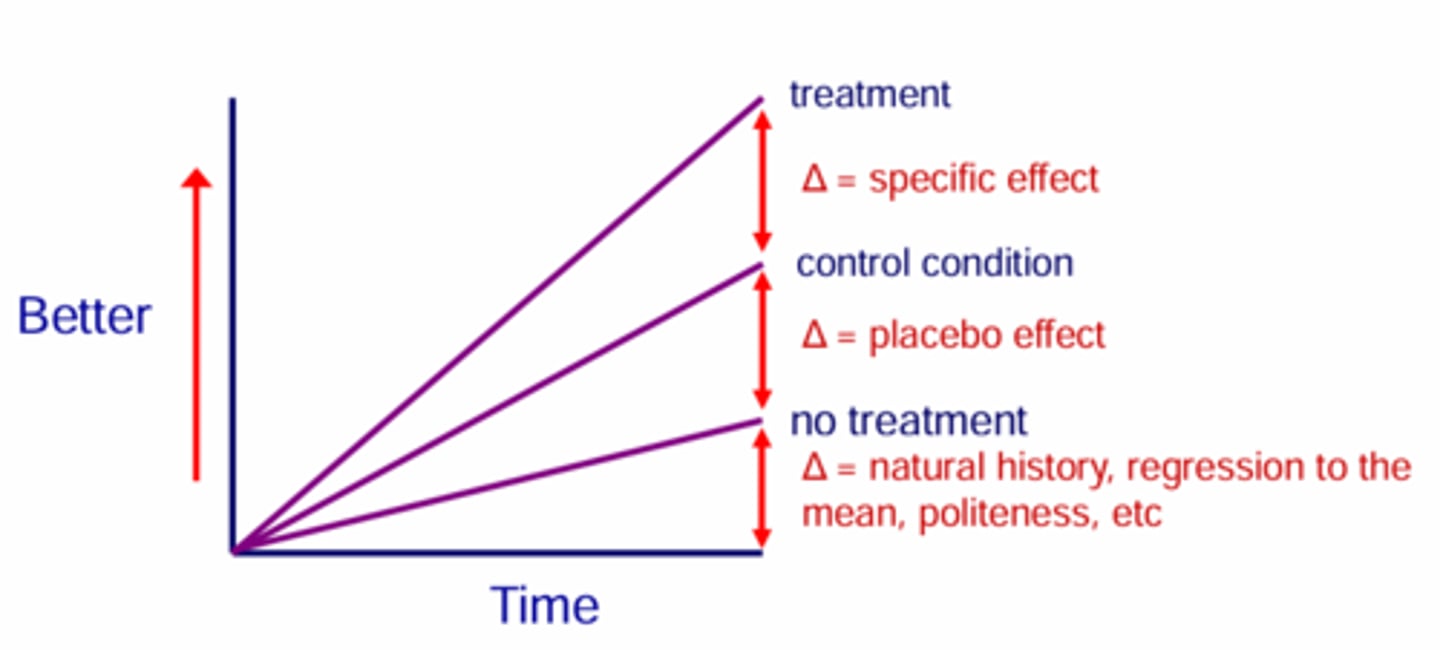
What is the change between homeopathy and the placebo (vehicle)?
There should be no difference, as homeopathy is just a significantly diluted solution.
What is the change between acupuncture and the placebo?
Several studies have shown that acupuncture needles are no more effective than sham needles that do not penetrate the skin.
What was Kirsch's arguements against the efficacy of antidepressants?
Irving Kirsch argued that antidepressant drugs act as "super-placebos".
Randomized receive antidepressant drug --> Notice side effects --> Guess correctly which group you are in --> Expect drug to reduce depression --> Feel better!
Hrobjartsson and Gotzsche conducted an experiment to determine how powerful the placebo effect is in conventional medicine. What were their findings?
Reviewed 114 trials and 40 clincial conditions.
• generally no convincing evidence of a placebo effect, except
• a significant but small effect on pain
• even this could reflect publication bias or patient's desire to please •
no justification for use of placebos outside of clinical trials
What are the two greatest effects of placebos?
Alleviate pain and nausea.
(But not other conditions such as tumour shrinkage or lowering cholesterol)
What were the challenges with Hrobjartsson and Gotzsche findings?
• Even the "no treatment" group may be subject to placebo effects
• Expectations of patients often differ between clinical trials and clinical practice in the real world
• No firm conclusions for many diseases
• "No treatment" patients may seek treatment outside study
• They only analyzed clinical trials, not studies where expectations were deliberately manipulated...
20 asthmatic subjects were given either a bronchodilator or a bronchoconstrictor in a double blind test. They were either told the truth about their treatment or told the opposite. Measured the airway resistance at the end. What were the results?
• isoproterenol - dilator
• carbachol - constrictor
The results suggest that expectations of the treatment can affect airway reacitivty.
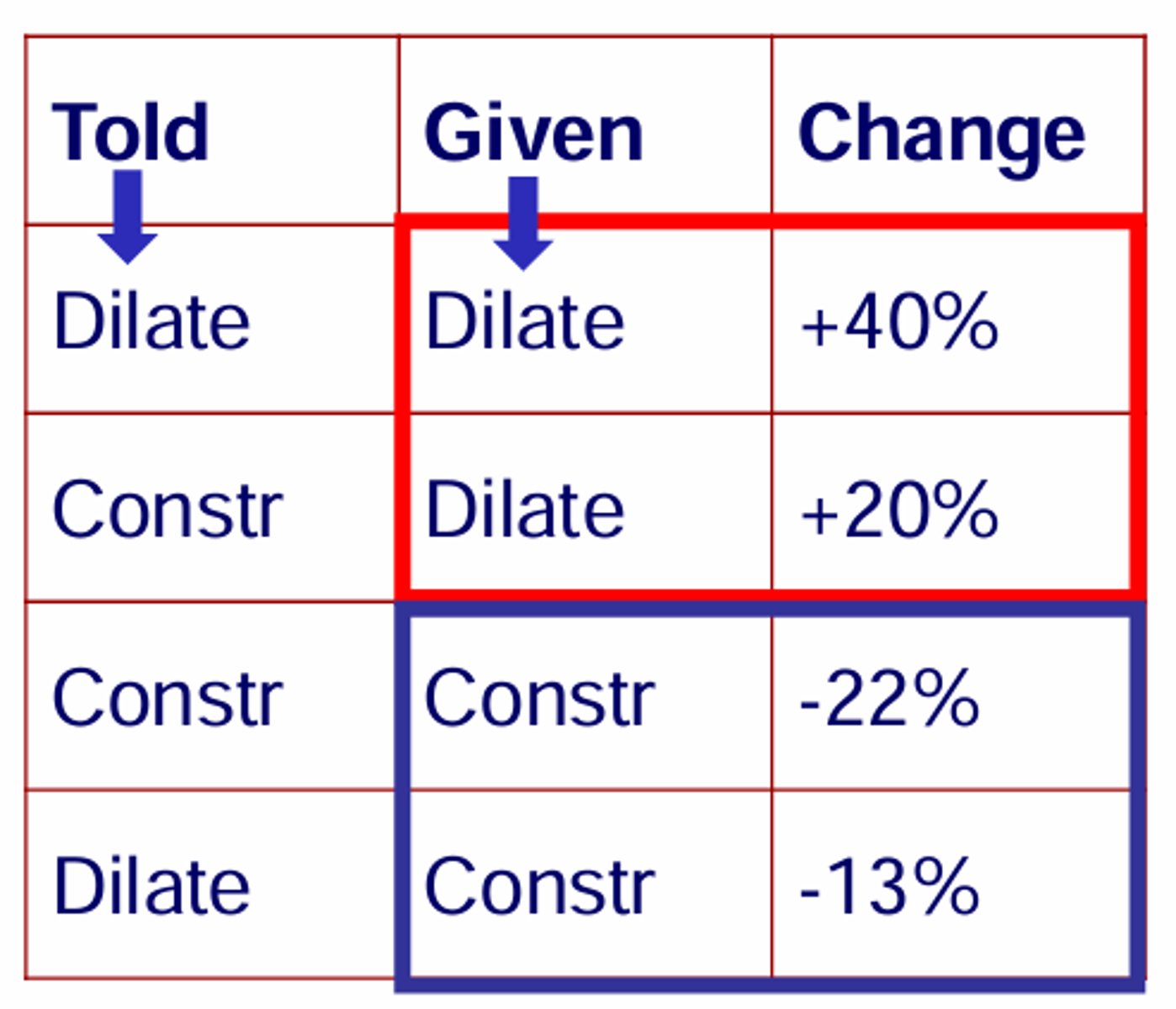
How can we test if expectations can cause a placebo effect?
Have both an objective measure and a subjective measure.
For example, in the same study as before, the asthma patients had their breathing capacity measured after the placebo treatment. It showed that there was no effect on their breathing capabilities. However, subjectively when asked, the patients replied that they felt better.
If morphine is given via infusion, it is more effective if signalled ahead of time. True or false.
True.
What is the wolf, wolfe paradigm?
The phenomenon where the placebo effect does not always persist.
Ex. with the women with dysmenorrhoea, they were given a placebo over sucessive menstrual cycles. The efficacy wore off after the first two cycles.
What are open label placebos? How effective are open label placebos?
"Open-label" placebo means given without deception (tell patients it is placebo) They are effacaious enough for migraines, chronic pain, and irritable bowel syndrome (though less than conventional medicine)
The doctor's authority and interactions with patients can itself act as a placebo. T or F.
True.
The expectations of a practitioner cannot affect the placebo group's response. T or F.
False.
What are psychological mechanisms underlying placebo effects?
Multiple mechanisms exist
• Pavlovian (i.e. classically) conditioned drug effect
• expectation of clinical improvement
• reduced stress and anxiety
• unknown mechanisms
How can Palovian conditioning affect the placebo effect?
If a patient has already been conditioned to feel an effect in an environment, even when placed on a placebo, they may still feel the effect.
Ex. In a randomized crossover design if the patient has been receiving the drug for the first half, they have been conditioned to feel an effect in the hospital. Therefore, even if the drug has been replaced with a placebo, they may still feel effects from conditioning.
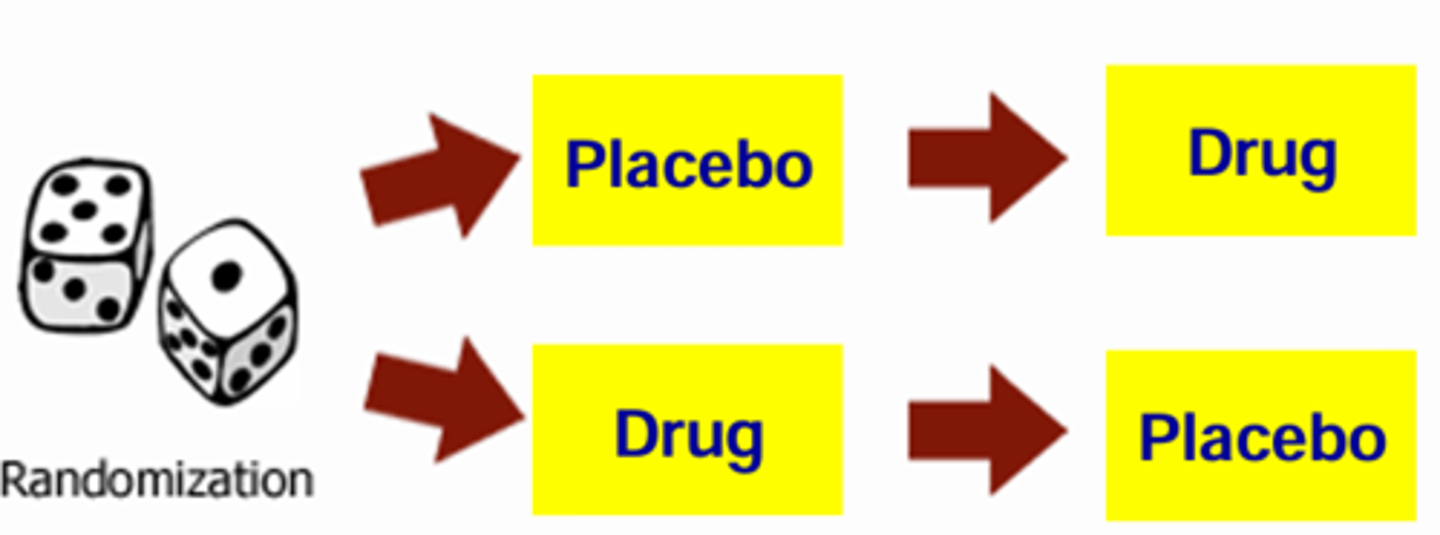
What are the neurobiological mechanisms underlying placebo effects?
Placebo analgesia does not occur by block of ascending pain signals, but rather through altered processing in the brain
What can inhibit the placebo analgesic effects? What was the evidence that supported this claim?
• capsaicin was applied simultaneously to 4 different sites on body
• "powerful local anaesthetic" (placebo cream) applied to 2/4 sites
The patient was then given an opioid antagonist.
An opioid antagonist can inhibit placebo analgesic effects. The placebo effect was anatomically specific. I.V. naloxone did not affect the pain per se but blocked the placebo analgesia
What is the proposed mechanism behind the analgesic effect of the placebo?
Endogenous opiods are released to produce an analgesic effect when a placebo is given. Depending on brain region, opioid activity correlated with expectancy and pain severity
Experiment:
• Subjects were told "medication"
may help the pain
• Inferred endogenous opioid release
from PET imaging of mu receptors- pain alone - vs. - pain + placebo (i.v. saline
Are non-deceptive placebo effect inhibited by the opioid receptor antagonist naloxone?
Method:
Make people do a pain tolerance test
Identify "placebo responders" (i.e. who show analgesia)
Give half of this subgroup a hidden i.v. injection of saline or naloxone
Result:
Even a non-deceptive placebo effect can be blocked by naloxone, so depends on endogenous opioids
Is the analgesic placebo effect only mediated via opiods? How do we know?
No, it can also be mediated via endocannbinoid release.
Method:
• Depending on group, painkiller was morphine or NSAID (ketorolac)
• Give painkiller (orally), then test pain tolerance
• Repeat on a few subsequent days
• Next, give a placebo injection (deceptively) → confirm a placebo effect
• Finally, give an endocannbinoid receptor antagonist (as NSAIDs are known to interact with endocannbinoid receptors)
Results:
The placebo effect in morphine was not disrupted but the placebo effect in NSAIDs were! This indicates that NSAIDs placebo effect is mediated via endocannbinoid release.