Geo C.O.5
1/234
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
235 Terms
Plate Tectonics
A unifying theory that states that the earth is composed of lithospheric crustal plates that move slowly, change size and interact with each other
Plate Boundaries
Plates move away, toward, or past each other through intense geologic activity
1. Pacific
2. North American
3. Eurasian
4. African
5. Antarctic
6. Indo- Australian
7. South American
Seven Largest tectonic plates (Descending Order)
Alfred Wegener
German meteorologist, presented the first comprehensive and detailed theory of continental drift.
glossopteris (plant), Lystrosaurus and Cynognathus animals) fossils
found on all five continents
Mesosaurus (reptile)
found in Brazil and South Africa Only
Pangaea
Supercontinent
Laurasia
Northern Supercontinent (North America and Asia- excluding India)
Gondwanaland
Southern supercontinent (South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia)
Late Paleozoic
Glaciation patterns were evident on the southern continents
Late Paleozoic
Coal beds deposited in the northern continents from swampy, probably warm environments
Paleoclimate Belts
suggest polar wandering as potential evidence for continental drift.
Polar Wandering
the apparent movement of the poles
1. The continents remained motionless, and the poles moved (polar wandering)
2. The poles did not move, and the continents moved
3. Both occurred
Evidence
Skepticism about Continental Drift
Land Bridges
Winds or Ocean currents
Polar Wandering
Mechanism
Land Bridges
could explain the distribution of land-dwelling reptiles on scattered continents.
Winds or Ocean currents
could explain distribution of fossil plants on separate continents.
Polar Wandering
could be explained by moving poles rather than moving continents
Mechanism
Wegner’s proposed mechanism was not accepted by most geologist in the northern hemisphere
Curie Point
The mineral magnetite becomes magnetized in cooling lava once its temperature drops below the _____.
mineral magnetic
Uses _____ properties to determine direction and distance to the magnetic pole when rocks formed.
Steeper dip angle
_____ indicate rockets formed closer to the magnetic poles
increasing
Rocks with _____ age point to pole locations increasingly far from present magnetic pole positions.
The Revival of Continental Drift
The mineral magnetite becomes magnetized in cooling lava once its temperature drops below the Curie Point.
Uses mineral magnetic properties to determine direction and distance to the magnetic pole when rocks formed.
Steeper dip angle indicate rockets formed closer to the magnetic poles
Rocks with increasing age point to pole locations increasingly far from present magnetic pole positions.
Evidence from Paleomagnetism
Apparent polar wander curves for different continents suggest real movement relative to one another.
Permian rocks in every continent show a different pole position which seems highly unlikely.
By reconstructing their locations to form Pangae, the polar wandering paths are nearly identical, indicating that the continents were once joined together.
relative
Apparent polar wander curves for different continents suggest real movement _____ to one another.
Permian rocks
in every continent show a different pole position which seems highly unlikely.
identical
By reconstructing their locations to form Pangae, the polar wandering paths are nearly _____, indicating that the continents were once joined together.
Fitting of Continents
Redefined the edge of each continent as the middle of the continental slope greatly improved the fit.
Fitting of Continents
Isotopic ages, glacial striations, rock types, structure, and sequence match.
History of Continental Positions
Paleomagnetic data indicate the direction and rate of movement
History of Continental Positions
Pangaea split apart 200 millions years ago but the continents have been in motion for much longer (2 to 4 billion years)
Geologic Evidence for Continental Drift
Fitting of Continents
History of Continental Positions
Seafloor Spreading
Takes place at divergent plate boundaries.
Seafloor Spreading
The concept that the _____ like a conveyor belt away from the crest of the midoceanic ridge.
Seafloor Spreading
Proposed in 1962 by Harry Hess
Hess’s Driving Force
Deep Mantle Convection
Deep Mantle Convection
Circulation pattern driven by rising of hot material (hot mantle rock) and/or the sinking of cold material (oceanic crust)
The Mid-Oceanic Ridge
Hot mantle rocks rie beneath
The Mid-Oceanic Ridge
Decompression melting occurs
The Mid-Oceanic Ridge
Circulation pattern diverges moving rock away from the ridge
Oceanic Trenches
Rocks have cooled and become denser
Oceanic Trenches
Crust sinks beneath a continent or island arc back into the mantle.
Age of the Sea Floor
<200 million years
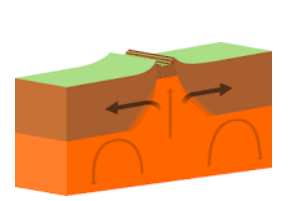
Divergent Boundaries
plates move apart.
Convergent Boundaries
plates move together
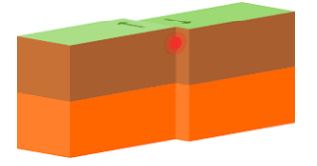
Transform Boundaries
plates slide past one another
Marine magnetic anomalies
refer to alternating positive and negative magnetic patterns, forming stripe-like features that run parallel to the mid-oceanic ridges.
The Vine- Matthews Hypothesis
New basaltic magma continually extrudes at the ridge crest and cools to record the earth’s magnetism including magnetic field reversals.
Matches pattern of reversals seen in continental rocks allow us to measure the rate of movement and to predict the age of the sea floor
New basaltic magma
continually extrudes at the ridge crest and cools to record the earth’s magnetism including magnetic field reversals.
reversals
Matches pattern of _____ seen in continental rocks allow us to measure the rate of movement and to predict the age of the sea floor
Rates of Motion and Seafloor Age
Examining the magnetic polarity of the seafloor, scientist can deduce its age
Measuring the Rate of Motion
Compared to known magnetic reversals from lava flows on land.
Rate of plate motion – equals the distance from ridge divided by age of rocks.
Rate of plate motion
equals distance from ridge divided by age of rocks.
Predicting Seafloor Age
Seafloor age increases with distance from mid-oceanic ridge.
The symmetric age pattern reflects plate motion away from the ridge.
increases
Seafloor age _____ with distance from mid-oceanic ridge.
symmetric
The _____ age pattern reflects plate motion away from the ridge.
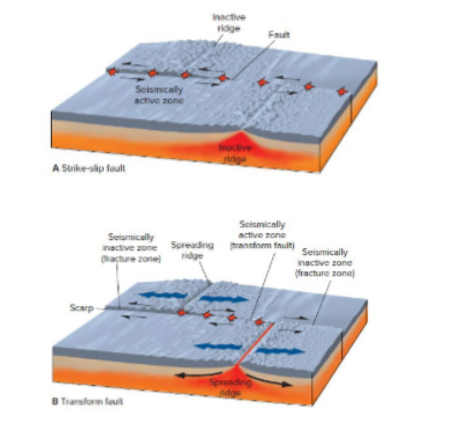
Fracture Zones
Zones that marks left within plate interiors because of transform faults displacing segments of mid-ocean ridges
Transform Faults
Occur at the edges of spreading segments.
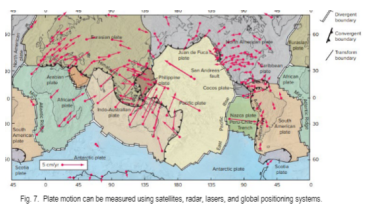
Measuring Plate Motion Directly
Are most accurately measured using satellite-based methods. The three frequently employed space-based techniques are very long baseline interferometry (VLBI), satellite laser ranging (SLR), and the Global Positioning System (GPS)
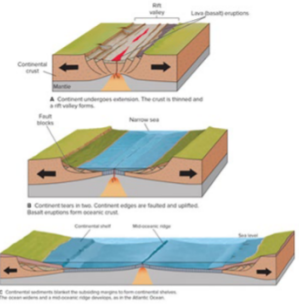
Divergent Plate Boundaries
Drift Apart
Often associated with frequent earthquakes, magma ascends from the earth’s mantle to the surface. It cools and solidifies, forming a fresh oceanic crust
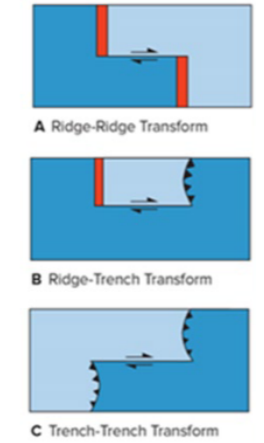
Transform Plate Boundaries
Slides horizontally past one another
Transforms may connect:
two offset segments of mid-oceanic ridge and a trench. Two trenches
Transform offsets of mid-oceanic ridges allow series of straight-line segments to approximate curved boundaries required by spheroidal earth.
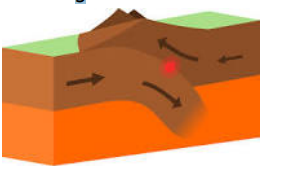
Convergent Plate Boundaries
Two tectonic plates collide.
Collision can lead to the edges of one or both plates crumpling upward, forming mountain ranges.
One of the plates may bend downward and create a deep seafloor trench
Ocean-ocean
marked by ocean trench, benioff zone, volcanic island arc
Ocean-continent
ocean trench, benioff zone, volcanic arc and mountain belt
Continent- continent
mountain belts and thrust faults
Plate boundaries
can move over time
Mid-oceanic ridge crests
can migrate toward or away from subduction zones or abruptly jump to new positions.
Convergent boundaries
can migrate if subduction angle steepens, or an overlying plate has a trench ward motion of its own.
Transform boundaries
can shift as slivers of plate shear off.
Plates
can change size over time.
The North American plate is increasing in size
A new seafloor is being added on the trailing edge as the Atlantic Sea floor spreads.
Most of the plate is not being subducted.
The Nazca Plate is getting smaller.
Leading edge is being subducted under South America.
Trailing edge is adding sea floor but at a slower rate.
Leading edge
is being subducted under South America.
Trailing edge
is adding sea floor but at a slower rate.
The Attractiveness of Plate Tectonics
Explains distribution and composition of volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountain belts.
Explains the major features of the sea floor.
The Cause of Plate Motions
Convection currents in the mantle involve the heating and upward movement of materials to the surface, while cooler liquids sink.
heating and cooler
Convection currents in the mantle involve the _____ and upward movement of materials to the surface, while _____ liquids sink.
Any proposed mechanism must explain why:
Mid-oceanic ridges are hot and elevated, while trenches are cold and deep.
Ridge crests have tensional cracks.
The leading edges of some plates are subducting sea floor, while others are continents (which cannot subduct).
Mid-oceanic ridges
_____ are hot and elevated, while trenches are cold and deep
tensional cracks
Ridge crests have _____.
The leading edges
of some plates are subducting sea floor, while others are continents (which cannot subduct).
Mantle Convection
May be the cause or an effect of circulation set up by the ridge-push and/ or slab-pull.
Ridge Push
as new plate moves away from the divergent boundary it cools and thickens and subsides.
Slab Pull
cold lithosphere sinking at a steep angle through the hot mantle should pull the surface part of the plate away from the ridge crest.
Trench Suction
if subducting plates fall into the mantle at angles steeper than their dip then trenches, and the overlying plates are pulled horizontally seaward toward the subducting plate.
Mantle Plume
narrow columns of hot mantle rock that rise through the mantle.
Large ______ may spread out and tear apart the overlying plate forming a Hot Spot at the Earth’s surface(examples include Hawaii, Yellowstone, and Iceland)
Flood basalt eruptions.
Drifting apart of continental land masses.
New divergent boundaries may form.
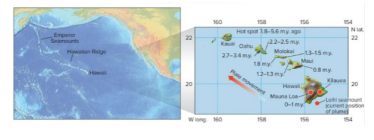
Hot Spot Volcanism
a location on Earth either over a mantle plume or beneath the rocky outer layer, known as the crust, where magma is hotter than the surrounding magma.
Mantle plume hot spots in the interior of a plate produce volcanic chains.
Orientation of the volcanic chain shows direction of plate motion over time.
The age of volcanic rocks can be used to determine the rate of plate movement.
Hawaiian Islands are a good example
How is Earth’s Interior Studied?
the structure of the Earth's interior, scientists depend on seismic waves, which are shock waves generated by earthquakes and explosions, travelling through the planet and across its surface.
The deep interior of the Earth must be studied indirectly.
Direct access only to crustal rocks and small upper mantle fragments brought up by volcanic eruptions or slapped onto continents by subducting oceanic plates.
The deepest drill hole reached about 12 km but did not reach the mantle
indirectly
The deep interior of the Earth must be studied _____.
crustal rocks & small upper mantle fragments
Direct access only to _____ and _____ brought up by volcanic eruptions or slapped onto continents by subducting oceanic plates.
mantle
The deepest drill hole reached about 12 km but did not reach the _____.
Geophysics
Branch of geology that studies the interior of the earth.
Seismic waves
provide evidence that the Earth's interior is composed of several concentric layers
Layers of the earth
a thin outer crust,followed by a mantle, a liquid outer core, and a solid inner core.
P-waves (Primary)
the fastest
S-waves (Secondary
arrive after the P-waves
Seismic Reflection
the return of some waves to the surface after bouncing off a rock layer boundary Sharp boundary between two materials of different densities will reflect seismic waves
Seismic Refraction
Bending of seismic waves as they pass from one material to another having different seismic wave velocities