BIOL 1020 Chapter 7
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fluid Mosaic Model
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Amphipathic
membranes that have both a hydrophilic and hydrophobic region
hydrophobic tails
hydrophilic heads
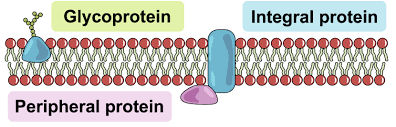
Glycoproteins
Embedded with the membrane and have a sugar molecule attached
used for cell recognition and signaling
Integral Proteins
penetrate fully through the membrane
Peripheral Proteins
loosely bounded to the surface of membrane or part of an integral protein
Functions of Proteins
transport
signaling
cell-to-cell recognition
intercellular joining
attachment to cytoskeleton
Passive Transport
Diffusion (net movement) across a membrane from high to low concentration
no energy
gradient represents potential energy
Osmosis
the diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane
water moves from areas of high solute concentration to low
Osmotic Pressure
tendency of water to move into the solution
Tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
compares two solutions
Isotonic
Same osmotic pressure
no net movement of water
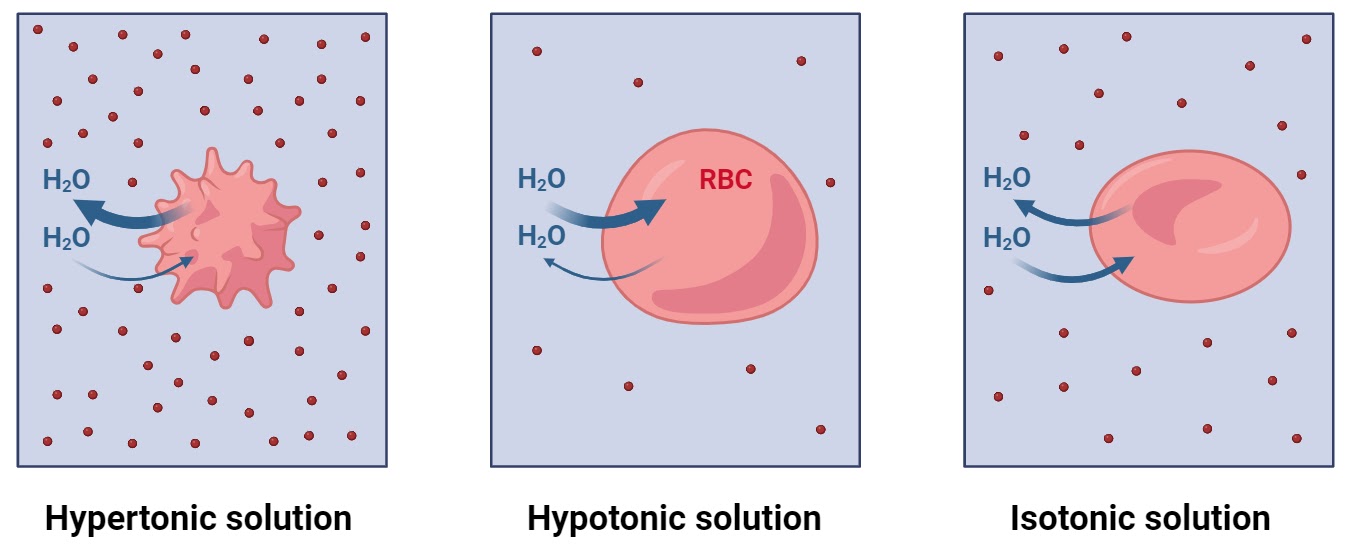
Hypertonic
higher osmotic pressure
water flows into a solution
Hypotonic
lower osmotic pressure
water flows out of a solution
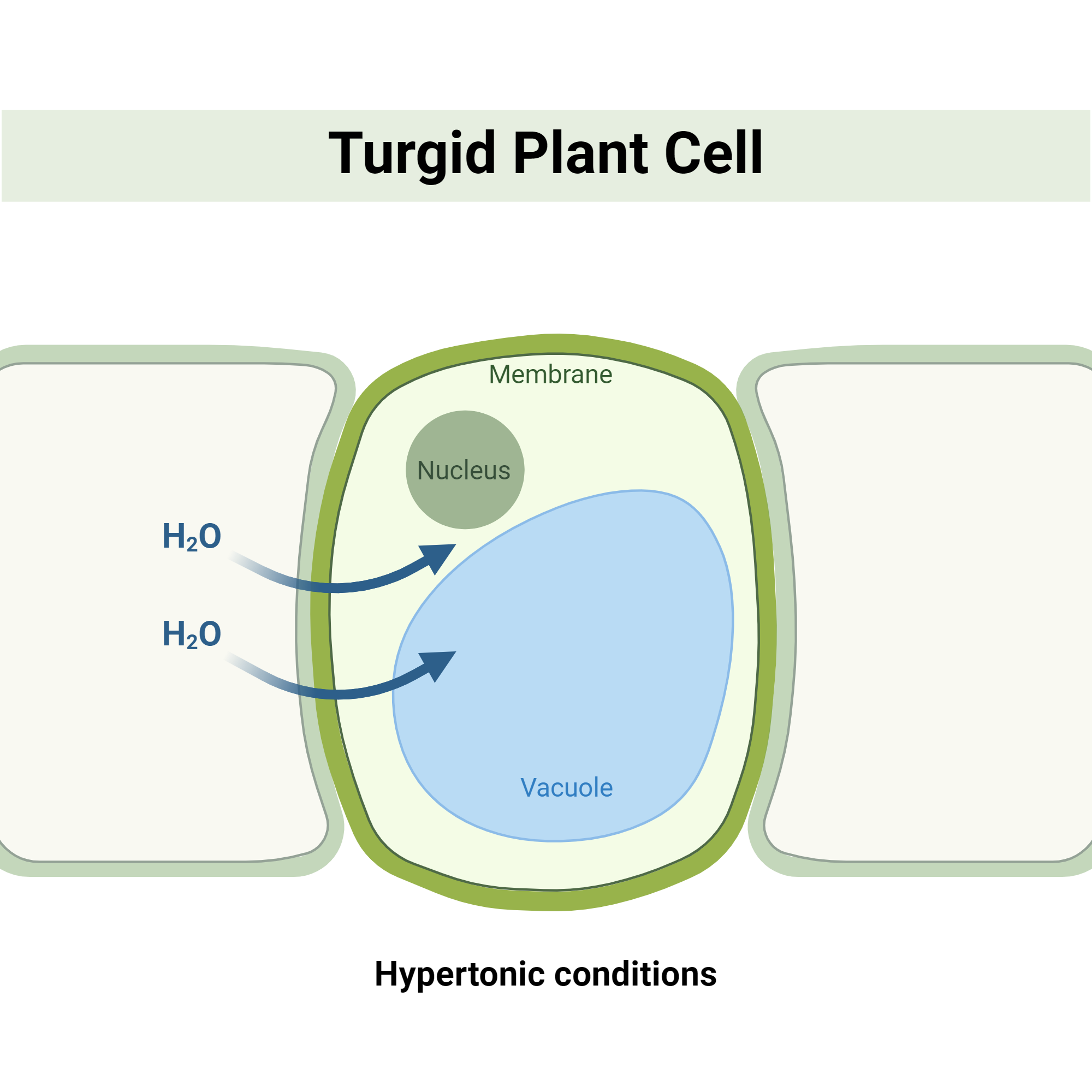
Turgor Pressure
the force within plant cells where water inside cell pushes the membrane against the cell, keeping cell rigid by providing structural support
Turgid
very firm plant cell
healthy state
kept by being in a hypotonic solution
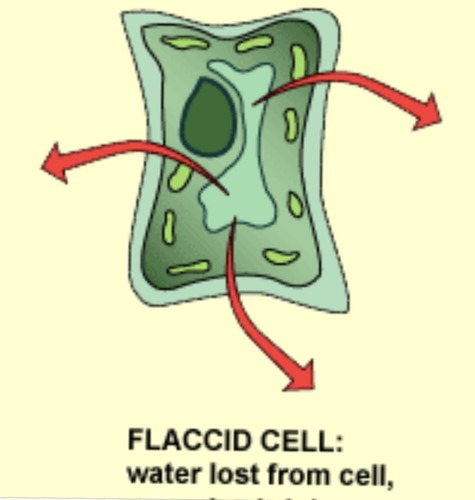
Flaccid
limp
happens when plant is in an isotonic solution
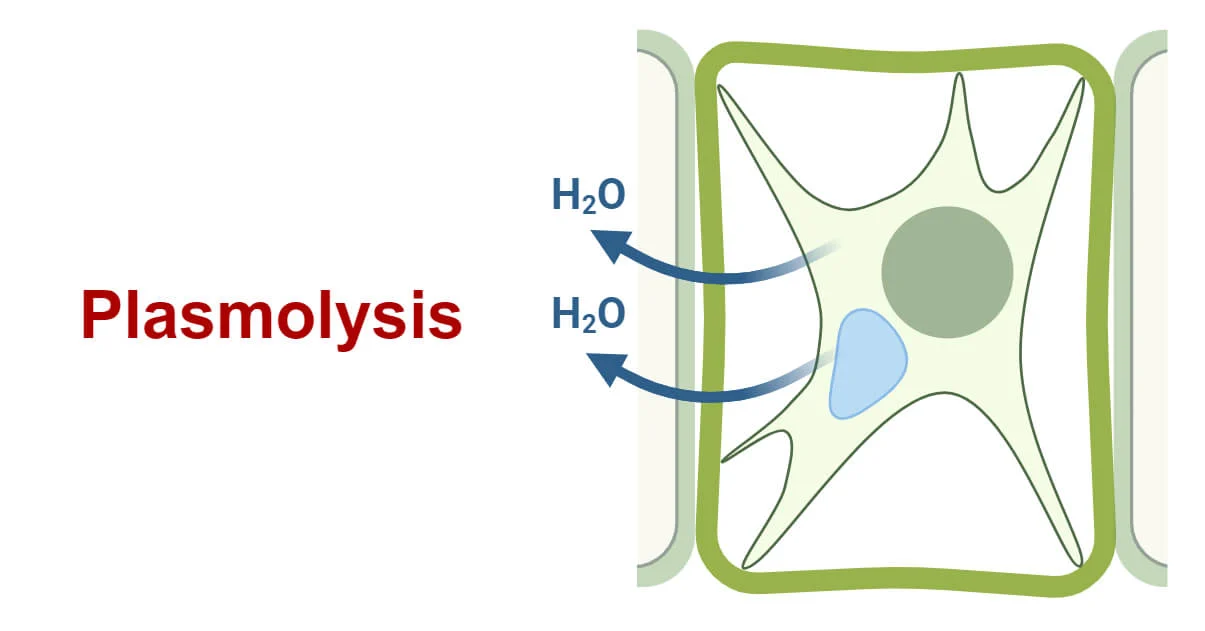
Plasmolysis
cell membrane pulls away from wall
leads to cell death
occurs in a hypertonic solution
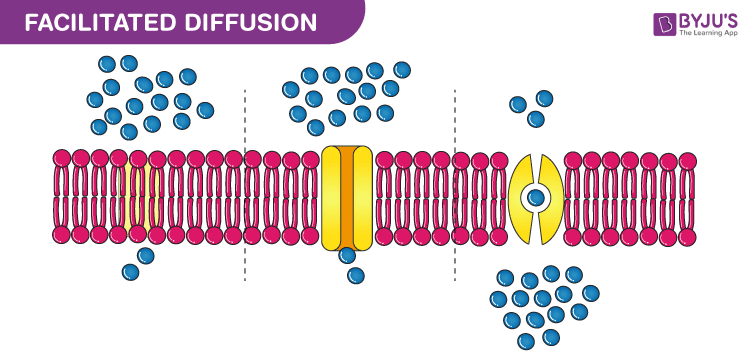
Facilitated Diffusion
polar molecules and ions travel through membrane with the help of a transport protein
ions and large molecules (glucose)
no energy
Active Transport
uses energy to pump solute against its gradient
allows cell to maintain internal concentrations
sodium potassium pump
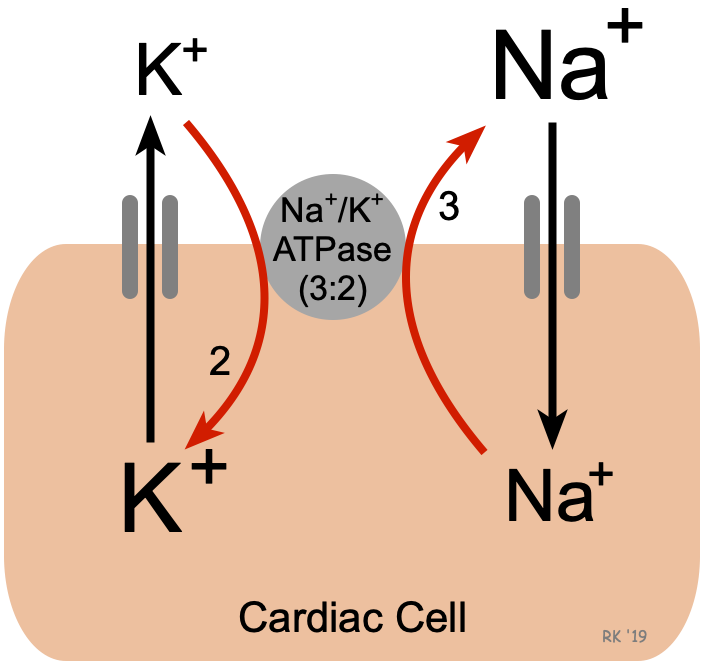
Sodium Potassium Pump
active transport via ATP
linked co-transport
cell moves 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in
ions are transported down their concentration gradient
causes an electrochemical gradient
Charge of the cytoplasmic side
relatively negative
Electrochemical Gradient
The two forces that drive diffusion of ion
chemical force: ion’s gradient
electrical force
Proton Pump
electrogenic pump where protons (H+) are transported out of the cell
Cotransport
the coupling of “down hill” diffusion of one substance to the “uphill” transport of another against its own gradient
uses a co-transporter
Exocytosis
Fusion of vesicles with plasma membrane that results secretion of molecules outside of the cell
often packaged from Golgi
Endocytosis
Cell takes in molecules by forming new vesicles from plasma membrane
Phagocytosis
“cell eating”
cell engulfs large particles by extending pseudopodia around and packing it within a membranous sac
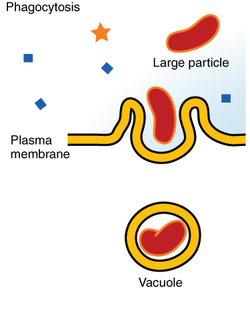
Pinocytosis
“cell drinking”
smaller molecules (fluid) is gulped up into tiny vesicles

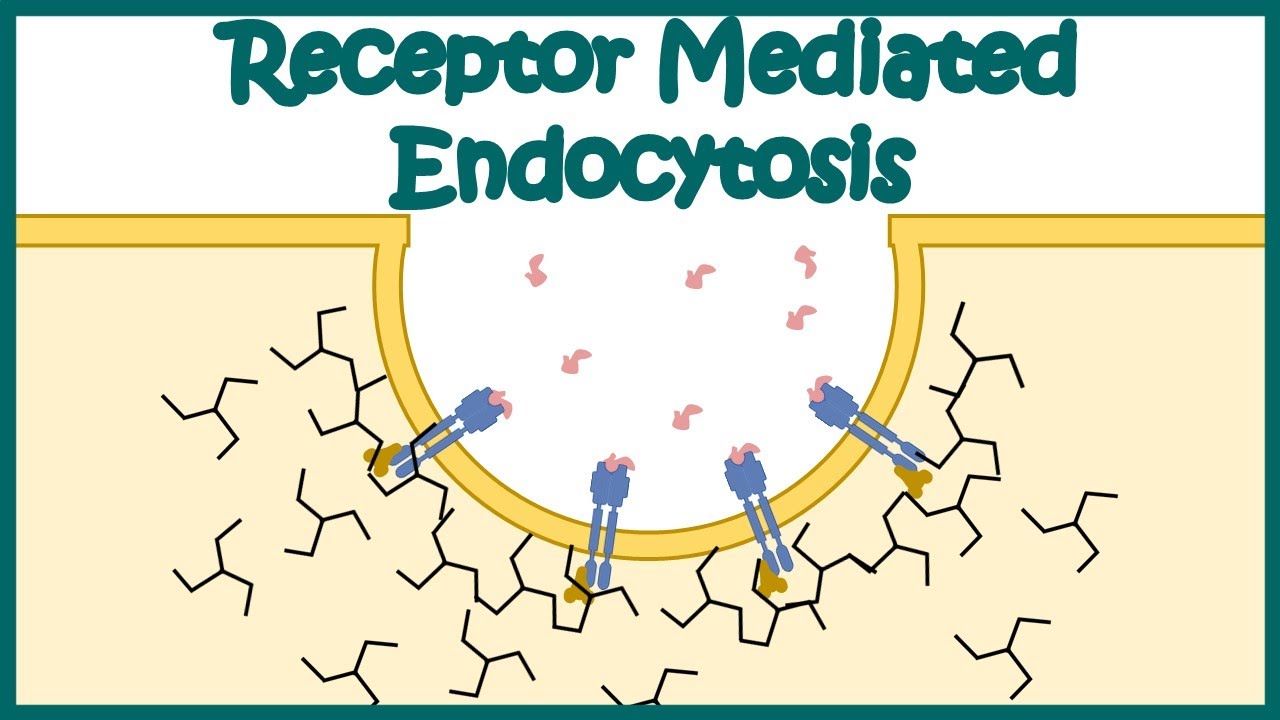
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
specialized types of pinocytosis that acquires bulk quantiles of specific substances
receptor proteins bind to molecules, causing protein to change shape