Lecture 11: Pain and Temperature Pathway
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AHHHHHHH
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Nociception is what?
The detection and localization of a stimulated pain receptor
Pain is what?
The emotional or arousal aspects of such stimulation
Pain is these 3 things…
A sensory, subjective, and emotional experience
Can pain arise without nociceptor stimulation?
Yes
Nociceptors are or are not free nerve endings?
They are
Where does pain perception crossover? (Decussate)
In 2nd order spinal cord, proceeding to the thalamus
Axons that conduct pain/temp are ____ and myelinated and ____ and unmyelinated
Small, Small
What is the fastest pain fiber?
A-delta
What is the slowest pain fiber?
C fiber
What is a ganglion?
A bundle of nerve cells/fibers in the peripheral
What is a fasciculus?
A bundle of nerve cells/fibers in the central nervous system
What is a commisure?
A bundle of nerve fibers connecting through the midline
1st order pain pathway
Dorsal root ganglion
Nucleus Proprius (Via the Dorsolateral fasciculus)
Spinothalamic tract
What connects the nucleus proprius to the spinothalamic tract?
The anterior white commisure
Pain withdrawal reflex excites and inhibits what?
Excites flexor and opposite extensors
Inhibits extensors
What is involved in the spinothalamic tract?
Medulla → Medulla → Pons → Midbrain → Ventral Posterolateral (VPL)
Pain Neuron 3 is located in…
The ventral posterolateral of the thalamus
Axons of Neuron 3 travel in what?
The internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the cortex. Ending there
What 3 areas does the spinothalamic tract terminate in?
The postcentral gyrus
The cingulate Gyrus
Insula
Termination in the poscentral gyrus means
A location and duration of the pain stimulus
Termination in the cingulate gyrus and insula
Indicates unpleasant, emotional qualities of pain such as burning or throbbing
Along with the postcentral gyrus, what also detects the location of pain stimuli?
The paracentral lobule
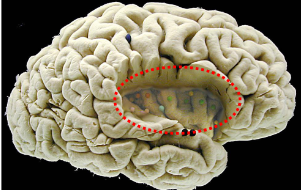
What is this?
The insula
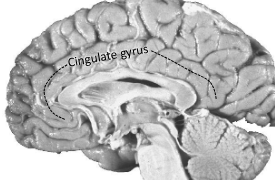
What is this?
The cingulate gyrus
_____descending pathways from brainstem can decrease spinothalamic tract activity. Where are they from?
Two. One from the periaqueductal gray matter and another from substantia gelantinosa.
What transmission is inhibited in these two descending pathways?
Transmission from neuron 1 to 2
Axons release ____ and _____ onto opiate interneurons that inhibit which order neuron in the pain pathway?
Serotonin, norepinephrine, 2nd neuron
Genetic Mutations such as…
Prevention of action potentials in sodium channels can prevent pain sensations
Neuropathic pain
Trauma that directly damages pain fibers, chronic pain
Hyperalgesia
Increases pain caused by mildly noxious stimulus
Allodynia
Pain caused by a stimulus that is NOT noxious
Syringomyelia
Formation of a cavity in the spinal cord
Brown-Sequard syndrome
Sensory deficits caused by injury to one half of the spinal cord
In syringomyelia, if the cavity interrupts the anterior white commissure what happens?
Both sides of the body will have affected pain sensation/temperature sensation