Week 7 Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscle System
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
in BIO SCI
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Cell of organ
compose of different kinds of tissue
this group of organ joins together to carry out vital now called as your organ system ( with simmlar ) that become system
different kinds of tissue
epithelia tissue
connective tissue
muscle tissue
nervous tissue
Different function of our organ system
communication ( it can communicate from outside environment )
responsible for the nervous system sensory organs and the endocrine system
Support And Movement
responsible for skeletal and muscular
Maintain and regulate
responsible for the digestive circulatory repertory and secretory system
defense
responsible for organs integumentary and the immune system
reproduce
responsible for the reproductive system
Digestive System:
Circulatory System:
Respiratory System:
Secretory System:
This system breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
This system transports nutrients, oxygen, and waste products throughout the body.
This system is responsible for taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
This system produces and releases substances like hormones and enzymes that regulate various bodily functions.
integumentary system ( under defense category )
its all about our skin
from the latin word “inte“ means whole and “gument” means covering
consist of skin and accessory organ
provides sensory information about the surrounding environment
function of integumentary
Prediction and cover
absorption
excretion
regulation
sensation
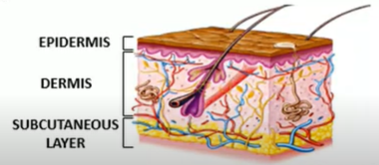
Skin
epidermis
dermis
subcutaneous layer
epidermis
made up of stratified squamous layers of epithelial tissue and consist 10 to30 thick so it is the most superficial layer
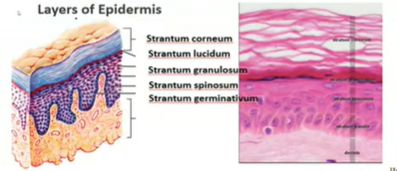
skin epidermis- epidermal cells
Types of cell
Detaching squame: These are dead skin cells that are about to flake off.
Keratinized squame of cornified layer: These are dead skin cells that are filled with keratin, a protein that makes your skin tough.
Granular layer: This layer contains cells that produce keratin and other substances that help protect your skin.
Langerhans cell: These are immune cells that help protect your skin from infections.
Prickle cell layer: This layer contains cells that are connected to each other by spiny-looking projections.
Merkel cell: These cells are sensitive to touch.
Dermis
it is made up of fibrous connective tissues containing collagen and elastic fiber it also contains your fiber glands and blood cell
it thicker than the epidermis
Skin Dermis
Papillary Dermis:
Reticular Dermis:
Includes blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, smooth muscle, glands and lymphatic tissue
This is the upper layer of the dermis. It has tiny bumps called dermal papillae that help to connect the epidermis to the dermis. These bumps also contain blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to the skin cells.
This is the lower layer of the dermis. It's thicker and contains mostly connective tissue, which gives the skin its strength and elasticity. It also contains hair follicles, sweat glands, and oil glands.
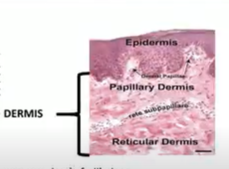
Skin- Dermis – Sensory Receptors
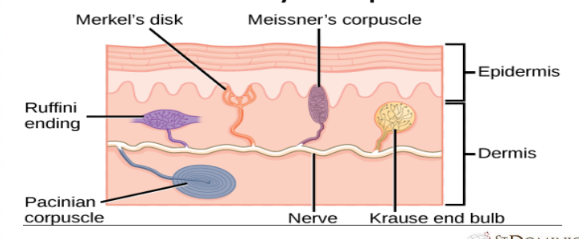
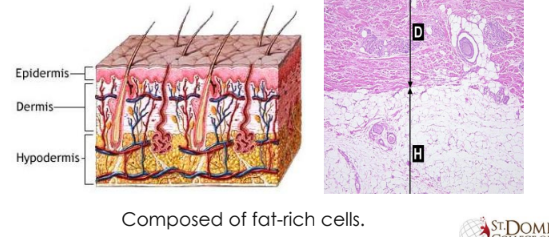
Skin- Hypodermis
Epidermis: The outermost layer of skin, composed of multiple layers of epithelial cells.
Dermis: The middle layer of skin, containing blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
Hypodermis: The innermost layer of skin, composed of fat-rich cells (adipocytes) that provide insulation and energy storage.
Structural Basis
of Skin Color
• Melanin
• Carotene
• Hemoglobin
Accessory Structures of the Skin
• Nails
• Hair
• Skin Glands
HAIR
• A protein filament
• Only in mammals
• Entire skin
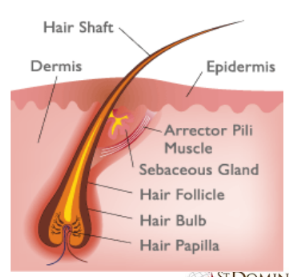
ANATOMY OF A HAIR
• HAIR SHAFT
• HAIR ROOT
• HAIR FOLLICLE
• HAIR BULB
• ARRECTOR PILI
Skin Glands
• Sudoriferous Gland (Sweat glands)
• Ceruminous Gland (Ear wax)
• Sebaceous Gland (Sebum)
• Mammary Gland (Milk)
Nails
• Found in finger tips
• Claws and hooves
Parts of a Nail
• Nail Matrix
• Nail Bed
• Nail Plate
• Nail Folds
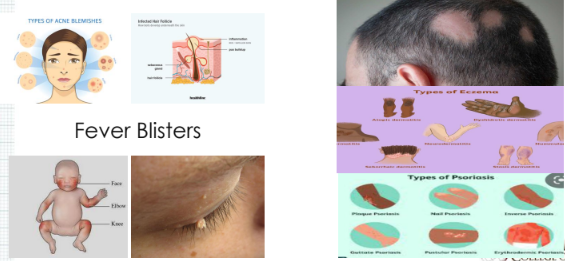
Contagious Disorders
Fever Blisters
Non- Contagious Disorders
Skeletal System
• Consist of bones, cartilages and joints
• Osteology
• Bone is considered as an organ.
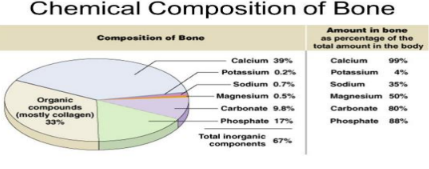
BONE COMPOSITION
• 25% water, 25% collagen fibers, and 50%
Functions of Skeletal System
• Support the body
• Attachment of muscles
• Gives stability and shape to the body
• Acts a levers for movement
• Protection of internal organs
• Production of blood cells
BONE CELLS
Osteoprogenitor Cells:
These are stem cells that can differentiate into osteoblasts.
They are responsible for bone growth and repair.
Osteoblasts:
These cells are responsible for bone formation.
They synthesize and secrete the organic matrix of bone, called osteoid, which later mineralizes to form hard bone tissue.
Osteocytes:
Mature bone cells that are embedded within the bone matrix.
They maintain bone tissue and help regulate mineral exchange between the bone and blood.
Osteoclasts:
Large, multinucleated cells that resorb bone tissue.
They break down old or damaged bone, allowing for bone remodeling and calcium release into the bloodstream.
Types of Bone Tissue
COMPACT BONE
• 80% of the skeleton.
• It forms the external layer of all
bones.
• It provides protection, support,
and resists stresses
• It has a functional unit called
“OSTEON”.
SPONGY BONE
• It does not contain osteons.
• It is consist of trabeculae
• Red bone marrow is found between the spaces of the trabeculae of some bones
• Spongy bone tissue is light,
Type of Skeleton Based on Formation
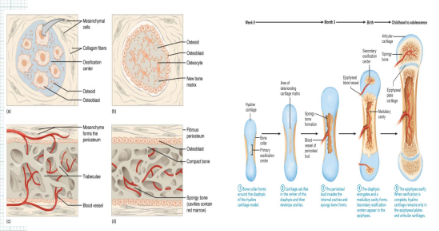
Intramembranous Ossification: Direct bone formation from mesenchymal cells.
Endochondral Ossification: Bone formation through a cartilage model.
Calcification: Hardening of tissue by mineral deposition.
Bone Resorption: Breakdown of bone tissue by osteoclasts.
TYPES OF BONES BASED ON SHAPE
• Long bones: Longer than wide (e.g., femur, humerus)
• Short bones: Cube-shaped (e.g., carpals, tarsals)
• Flat bones: Thin, flat, and curved (e.g., skull, ribs, sternum)
• Irregular bones: Complex shape (e.g., vertebrae, facial bones)
• Sesamoid bones: Small, round bones embedded in tendons (e.g., patella)
DIVISION OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
• 2 division of the skeletal system:
Axial skeleton: Bones forming the central axis of the body (skull, vertebral column, rib cage).
Appendicular skeleton: Bones of the limbs and girdles (shoulder and pelvic girdles, arms, legs, hands, and feet).
Common Diseases and Disorders
Arthritis – general term meaning joint inflammation
• Osteoarthritis – degenerative joint disease, primarily of weight-bearing joints
• Rheumatoid Arthritis – chronic systemic inflammatory disease of smaller joints and surrounding tissues
Common Diseases and Disorders (cont.)
• Bursitis – inflammation of a bursa (fluid- filled sac that cushions tendons)
• Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – overuse of wrist; the median nerve in the wrist becomes compressed
• Ewing’s Family of Tumors (EFT) – a group of tumors that affect different tissue types; primarily bone
• Gout – a type of arthritis; deposits of uric acid crystals in the joints
Common Diseases and Disorders (cont.)
• Kyphosis – abnormal curvature of the spine (humpback)
• Lordosis – exaggerated inward curvature of the lumbar spine (swayback)
• Osteogenesis imperfecta – brittle-bone disease
• Osteoporosis – a condition in which bones thin (become porous) over time
Muscular system
Functions of Muscle
• Movement
• Stability
• Control of body openings and passages
• Heat production
Functions of Muscle
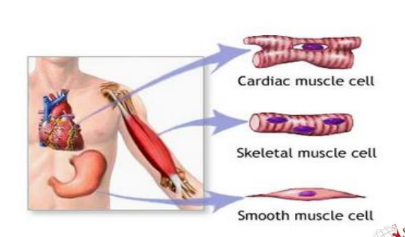
Cardiac Muscle: Found only in the heart, it is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Cardiac muscle cells are striated (have a striped appearance) and involuntary, meaning they contract without conscious control.
Skeletal Muscle: Attached to bones via tendons, it allows for voluntary movement and maintains posture. Skeletal muscle cells are also striated but are under voluntary control.
Smooth Muscle: Found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels, it helps with various functions such as digestion, blood flow regulation, and childbirth. Smooth muscle cells are not striated and are involuntary.
Function of muscle: Stability
1. Postural Muscles:
2. Joint Stabilization:
3. Dynamic Stability:
These muscles, such as those in the back and core, work continuously to maintain upright posture and balance.
They counteract gravity and keep us from toppling over.
Muscles surround joints and work in pairs to provide stability.
For example, the quadriceps and hamstrings work together to stabilize the knee joint.
Muscles enable us to perform complex movements while maintaining balance.
For instance, when walking, muscles in the legs and core work together to keep us upright and prevent falls.
Function of muscle:
• Sphincters
control of body openings and passages
• Control movement of substances in and out of passages
Function of muscle: heat production
Muscle Contraction:
Heat Production:
This is the fundamental function of muscles.
It allows for movement, from simple actions like blinking to complex ones like running.
Muscle contraction involves the sliding of protein filaments within muscle cells, generating force.
As a byproduct of muscle contraction, the body generates heat.
This heat is essential for maintaining body temperature, especially in cold environments.
Shivering, an involuntary muscle contraction, is a prime example of the body's mechanism to generate heat.
Types of Muscles: As to structure
Striated Voluntary Muscle Tissues:
Striated Involuntary Muscle Tissues:
Smooth Involuntary Muscle Tissues:
Skeletal Muscle: These muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for voluntary movements. They appear striated due to the arrangement of protein filaments within the muscle cells.
Cardiac Muscle: This specialized muscle tissue is found only in the heart. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. While it appears striated, it is involuntary, meaning it contracts without conscious control.
Smooth Muscle: This muscle tissue is found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. It is responsible for involuntary movements, such as digestion and blood flow regulation. It lacks the striated appearance of skeletal and cardiac muscle.
Types of muscles: As to action
• Agonist or prime mover
• Antagonist
• Principal mover for specific action
• For opposite movement
Types of muscles: As to action
• Synergist
• Fixator
• Helps stabilize the movement of one joint
• Fixes the position when movement is occurring
Types of muscles: As to specific function
Flexors:
Extensors:
Function: These muscles cause a joint to bend or decrease the angle between bones.
Examples: Biceps brachii (flexes the elbow), hamstrings (flex the knee).
Function: These muscles cause a joint to straighten or increase the angle between bones.
Examples: Triceps brachii (extends the elbow), quadriceps (extend the knee).
Types of muscles: As to specific function
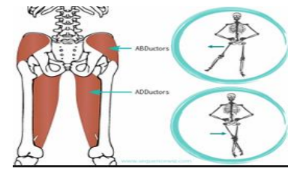
• Adductors and abductors
Function: These muscles pull a limb or body part towards the midline of the body.
Example: Adductor muscles in the inner thigh pull the legs together.
Function: These muscles move a limb or body part away from the midline of the body.
Example: Abductor muscles in the outer thigh move the legs apart.
Types of muscles: As to specific function
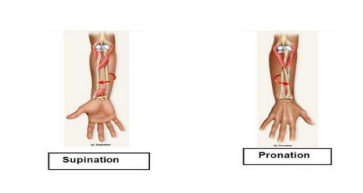
Pronators:
Supinators:
Function: These muscles rotate the forearm so that the palm faces downward.
Example: Pronator teres and pronator quadratus muscles.
Function: These muscles rotate the forearm so that the palm faces upward.
Example: Supinator muscle.
Types of muscles: As to specific function
• Elevators/ levators and depressors
Function: These muscles raise or elevate a body part.
Examples: Levator palpebrae superioris (raises the eyelid), masseter (elevates the mandible for chewing).
Function: These muscles lower or depress a body part.
Examples: Depressor anguli oris (pulls the corner of the mouth downward), platysma (pulls the lower lip and corner of the mouth downward).
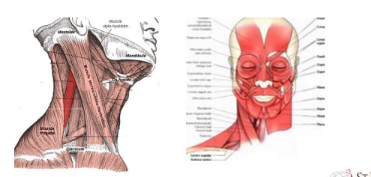
Types of muscles: As to specific function
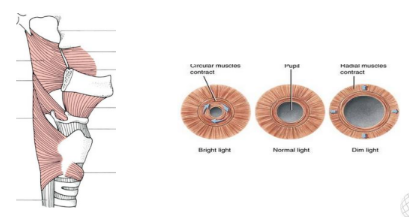
Constrictors
Dilators
:
Function: These muscles narrow or constrict openings.
Examples: Muscles in the digestive tract that help propel food, muscles in the blood vessels that regulate blood flow.
:
Function: These muscles widen or dilate openings.
Examples: Muscles in the iris of the eye that control pupil size, muscles in the respiratory tract that help regulate airflow.
Major Skeletal Muscles: The Head
Sternocleidomastoid
• Pulls the head to one side
• Pulls the head to the chest
Frontalis
• Raises the eyebrows
Splenius capitis
• Rotates the head
• Allows it to bend to the side
•• Orbicularis oris
• Allows the lips to pucker
Orbicularis oculi
• Allows the eyes to close
Zygomaticus
• Pulls the corners of the mouth up
• Platysma
• Pulls the corners of the mouth down
• Masseter and temporalis
• Close the jaw
Major Skeletal Muscles: Upper Arm
• Pectoralis major
• Latissimus dorsi
Pulls the arm across the chest
Rotates and adducts the arms
• Extends and adducts the arm and rotates the arm inwardly
Major Skeletal Muscles: Upper Arm
Deltoid
Subscapularis
Infraspinatus
•
• Abducts and extends the
arm at the shoulder
•
• Rotates the arm medially
•
• Rotates the arm laterally
Major Skeletal Muscles: Forearm
• Biceps brachii
• Brachialis
• Brachioradialis
• Flexes the arm at the elbow • Rotates the hand laterally
• Flexes the arm at the elbow
• Flexes the forearm at the elbow
Major Skeletal Muscles: Forearm (cont.)
• Triceps brachii
• Supinator
• Pronator teres
)
• Extends the arm at the elbow
• Rotates the forearm laterally (supination)
• Rotates the forearm medially (pronation
Major Skeletal Muscles: Wrist, Hand, and Fingers
• Flexor carpi radialis and flexor carpi ulnaris
• Palmaris longus
• Flexor digitorum profundus
• Flex and abduct the wrist
• Flexes the wrist
• Flexes the distal joints of the fingers, but not the thumb
Major Skeletal Muscles:
Wrist, Hand, and Fingers (cont.)
• Extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis
• Extensor carpi ulnaris
• Extend the wrist and abduct the hand
• Extends the wrist
• Extensor digitorum
• Extends the fingers, but not the thumb
Major Skeletal Muscles: Respiratory
• Diaphragm
• External and internal
intercostals
• Separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity • Its contraction causes inspiration
• Expand and lower the ribs during breathing
Major Skeletal Muscles: Abdominal
• External and internal obliques
• Transverse abdominis
• Rectus abdominis
l
• Compress the abdominal wall
• Also compresses the abdominal wall
• Flexes the vertebral column • Compresses the abdominal wal
• Trapezius
• Pectoralis minor
• Raises the arms • Pulls the shoulders downward
• Pulls the scapula downward • Raises the ribs
Major Skeletal Muscles: Leg
• Psoas major and iliacus
• Gluteus maximus
• Gluteus medius and minimus
• Flexes the thigh
• Extends the thigh
• Abduct the thighs • Rotate them medially
Major Skeletal Muscles: Leg (cont.)
• Adductor longus and magnus
• Biceps femoris, semitendinosus,
and semimembranosus
• Adduct the thighs • Rotate them laterally
• Known as the hamstring group • Flex the leg at the knee • Extend the leg at the thigh
Major Skeletal Muscles: Leg (cont.)
• Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius
• Sartorius
• Extend the leg at the knee
• Flexes the leg at the knee and thigh • Abducts the thigh, rotating the thigh laterally but rotating the lower leg medially
Major Skeletal Muscles:
Ankle, Foot, and Toes
• Tibialis anterior
• Extensor digitorum longus
• Gastrocnemius
• Inverts the foot and point the foot up (dorsiflexion)
• Extends the toes and point the foot up
• Flexes the foot and flexes the leg at the knee
Major Skeletal Muscles:
Ankle, Foot, and Toes (cont.)
• Soleus
• Flexor digitorum longus
• Flexes the foot
• Flexes the foot and toes
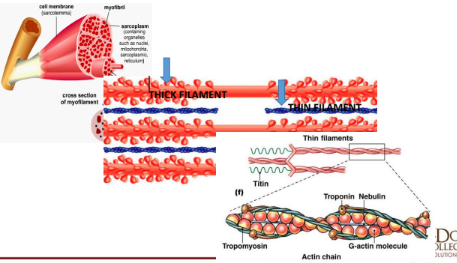
Structure of Skeletal Muscle
Epimysium
Fascicles
Muscle fibers
perimysium
endomysium
Sacroplasmic reticulum
myofibril
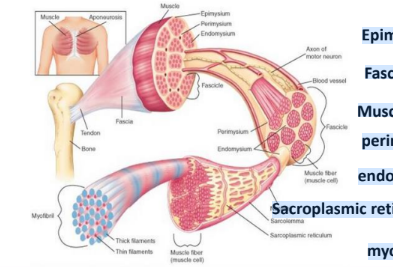
Muscle proteins
• Myosin
• Composed the thick filaments
• Actin
• composed the thin filaments
• Troponin
• Subcomponent of thin myofilaments
• Tropomyosin
• Subcomponent of thin myofilaments
• Myoglobin
• Muscle hemoglobin for transport of
oxygen
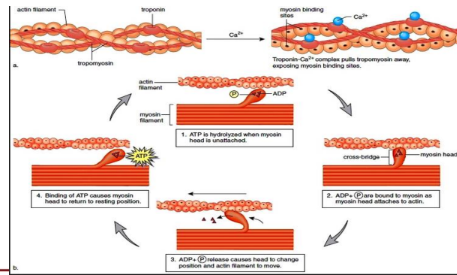
Muscle Metabolism
• Energy - Muscle contraction
• Muscle contraction needed ATP
• ATP - muscle cells
• Hydrolysis, glycolysis, Krebs cycle and oxidation phosphorylation
• Two types of muscle fibers
• White muscle fibers (Glycolysis)
• Red muscle fibers (Krebs cycle)
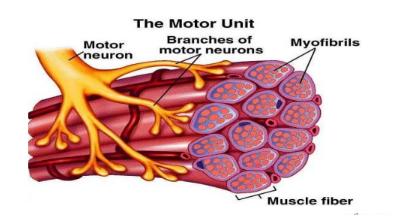
Motor Unit
Composition and Structure of Myofilaments
Muscle contraction
Production of Energy: Muscle Fatigue
• Condition in which a muscle has lost its ability to contract
• Causes
• Accumulation of lactic acid
• Interruption of the blood supply to a muscle
• A motor neuron loses its ability to release acetylcholine
onto muscle fibers
Muscle Strains and Sprains
• Strains
• Sprains
• RICE is recommended treatment for either
– injuries due to over-stretched muscles or tendons
– more serious injuries that result in tears to tendons, ligaments, and/or cartilage of joints
is recommended treatment for either Rest • Ice • Compression • Elevation
Muscle Strains and Sprains (cont.)
• Prevention
• Warm up muscles
• Stretching
• Cooling down or slowing down
Diseases and Disorders of the Muscular
System
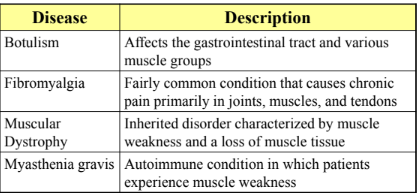
Diseases and Disorders of the Muscular
System (cont.)