AP Human Geography - Unit 1 Vocabulary
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All of the vocabulary needed in Unit 1, done for summer work.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
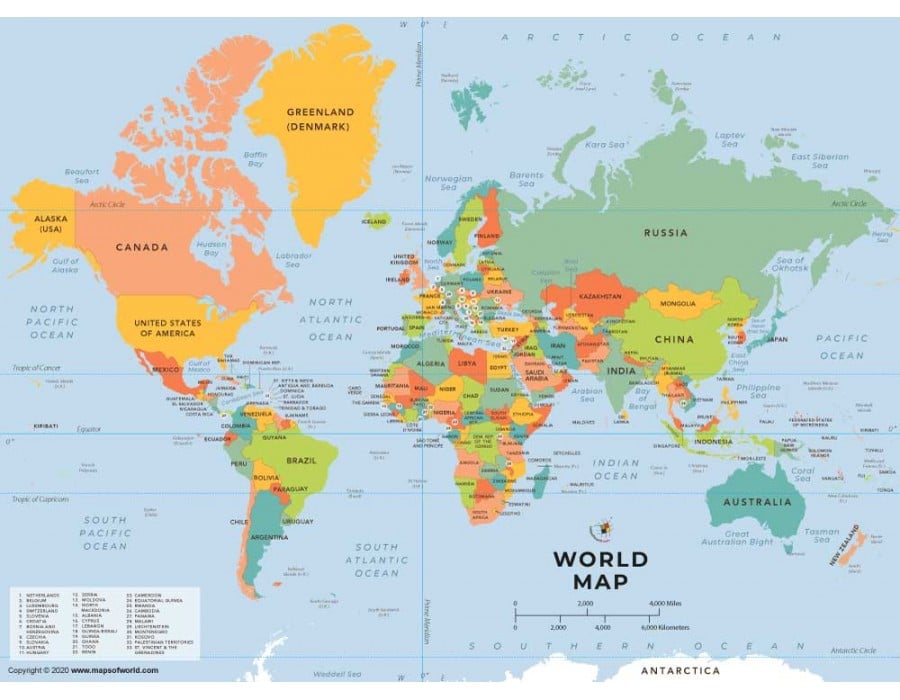
Reference Map
Maps that provide general geographic information, such as the location of features and boundaries.
Thematic Map
Maps that tell stories by displaying spatial patterns and quantitative data related to a particular theme.
Example: heat maps, dot density maps, and choropleth maps.
Absolute Distance
The exact distance between two places, usually in miles or kilometers.
Example: The distance between Washington, D.C. and New York City is 203.55 miles.
Relative Distance
An approximate measurement between two places, usually in time or direction.
Example: New York City is about three hours and 50 minutes away from Washington, D.C.
Clustered Spatial Distribution
A pattern where objects in an area are close together with little to no space.
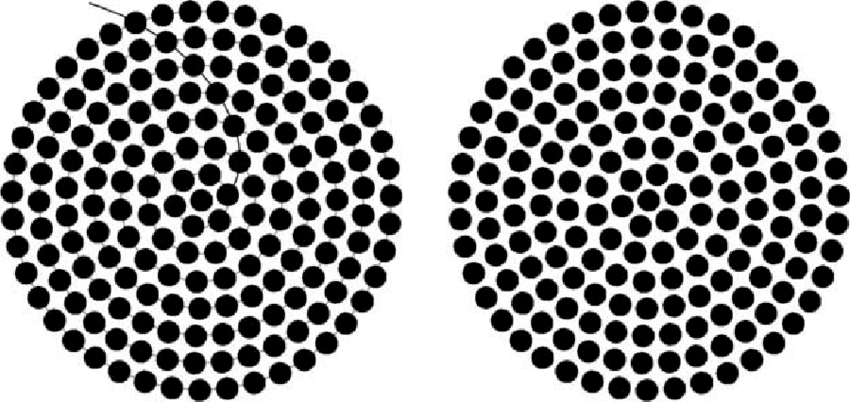
Dispersed Spatial Distribution
A pattern where objects in an area are spread out.

Elevation
The altitude of a location above sea level.
Example: The elevation of Memphis, Tennessee is 338 feet.
GIS
a computer system that analyzes and displays geographically referenced information.
Example: A city uses this to map out flood-prone areas and plan emergency responses.
Remote Senseing
Acquisition of data from a satellite or other long-distance method.
Example: Satellites use remote sensing to monitor deforestation in the Amazon forest.
Census
Process of collecting, compiling, and publishing data about the population and housing of a country or region.
Example: The population of Memphis, Tennessee is 613,110, latest U.S. census released May 2024.
Distance Decay
The effect distances have on cultural or spatial interactions. Interaction is less likely with increased distance.
Example: I hang out more with my friends from Millington rather than Arlington because Arlington is further away.
Space-time Compression
With more ways to connect with things further away, with advances in technology, the effect of distance decay reduces.
Example: I can still FaceTime and text friends regardless of where they live, increasing how much we interact, lowering the effect of distance decay.
Human-environment interaction
How people modify or adapt to their environment.
Example: Cutting down trees to make houses.
Sustainability
Using the earth to meet your wants and needs while ensuring resources in the future.
Example: Using renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions.
Environmental Determinism
The idea that the environment is the driver for societal development.
Example: Colder climates drive people away from living in certain areas.
Possibilism
People have the ability to adjust to the physical environment.
Example: A home built on stilts in Florida to protect it from flooding.
Global Scale
The scale of the world in a global setting. Entire planet.
Example: The Mercator projection.
Regional Scale
The scale to the level of the region/regional setting.
Example: A map of Asia Minor.
National Scale
The scale to the level of a specific country or nation.
Example: A map of France.
Local Scale
The scale to the level of a specific community or neighborhood.
Example: A map of zoning regulations.
Region
An area with common physical and cultural characteristics.
Example: On the national scale, the United States of America.
Formal Region
A geographic area with common traits usually defined by economic, social, political, or environmental characteristics.
Example: The Himalayan mountain range.
Functional Region
A geographic region organized around a node or central point.
Example: Delivery zones for restaurants.
Vernacular/Perceptual Region
A geographic region that has no perfect definition. A place that exists due to people's beliefs, feelings, and attitudes.
Example: The South in the United States. People have different ideas of which states are included.
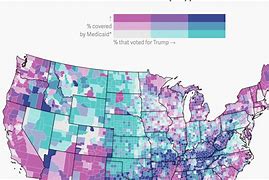
Choropleth (map)
A thematic map based on color coding to represent data. Different shades show different degrees and amounts.
Example: A map showing the population density in the USA with darker shaded areas being more dense.
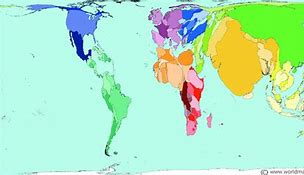
Cartogram (map)
Data represented with values corresponding to the size of the area.
Example: A population map at the global scale where China is seen much bigger than Canada.
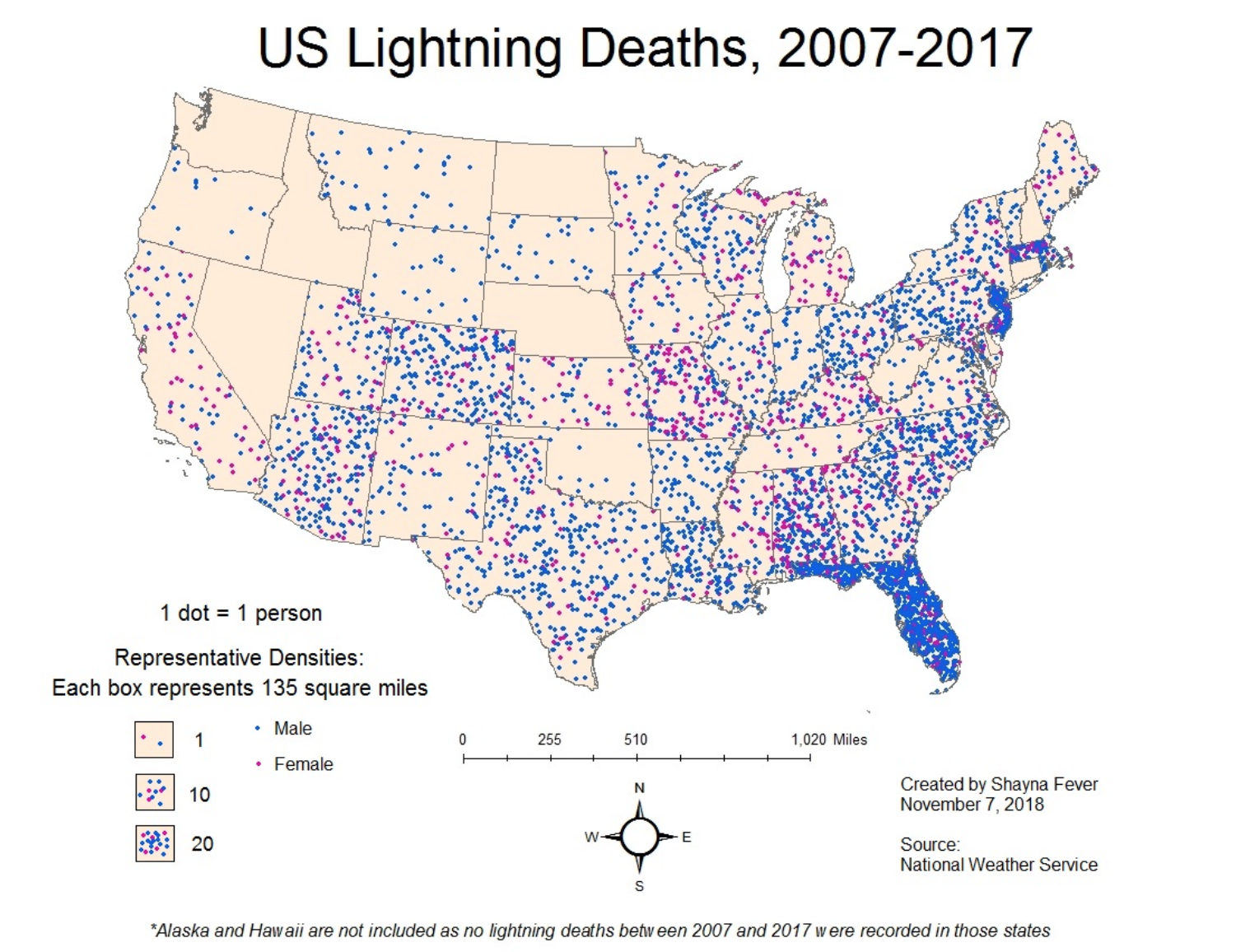
Dot Density (map)
Represents data with points where the data is occurring.
Example: A map showing the distribution of Walmarts across Tennessee.
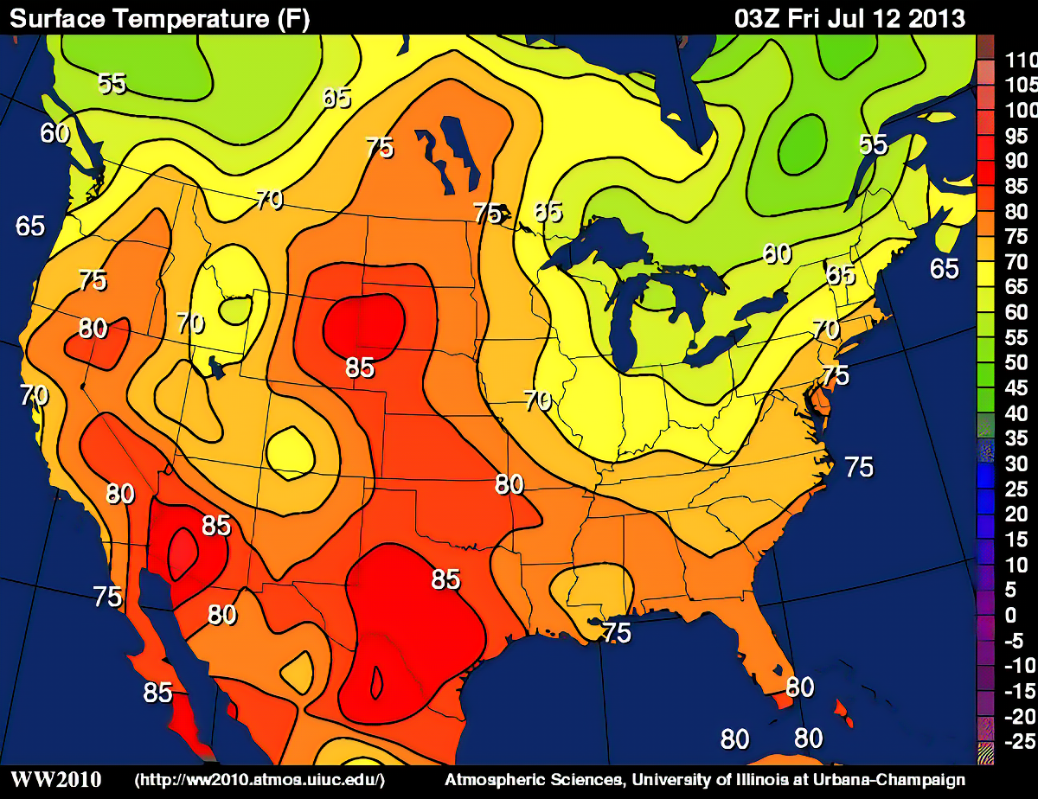
Isoline (map)
A map that connects similar or equal amounts of data by using lines.
Example: A weather map on a national scale.
Latitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of a parallel on a globe measuring distance north and south of the equator.
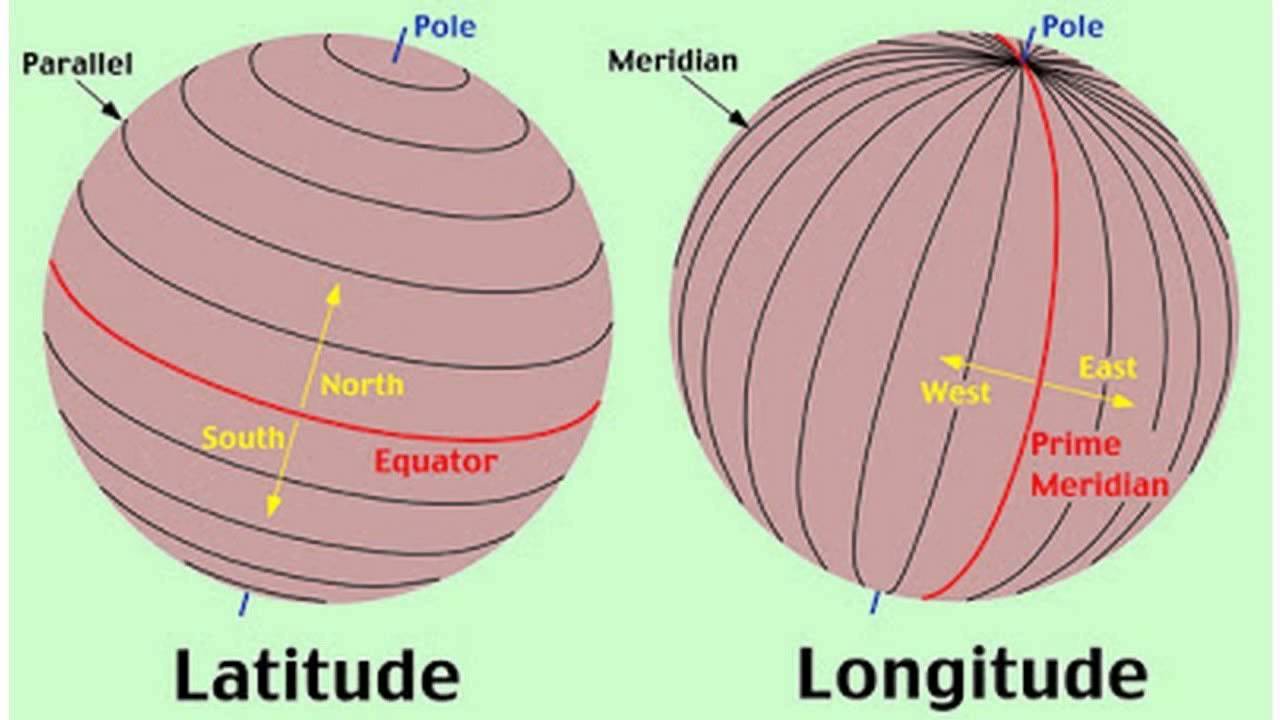
Longitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians on a globe measuring distance east and west of the prime meridian or zero degrees.
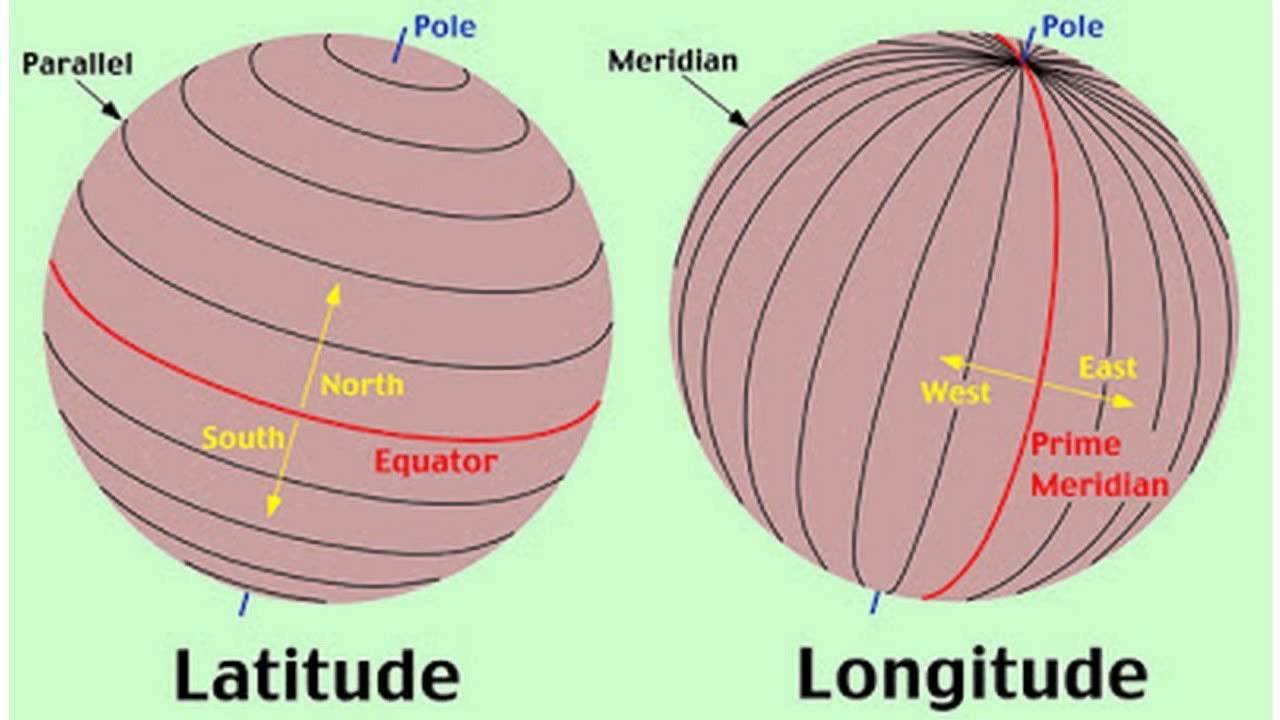
Prime Meridian
The meridian at zero degrees longitude splitting the western and eastern hemispheres. Used for time zones.
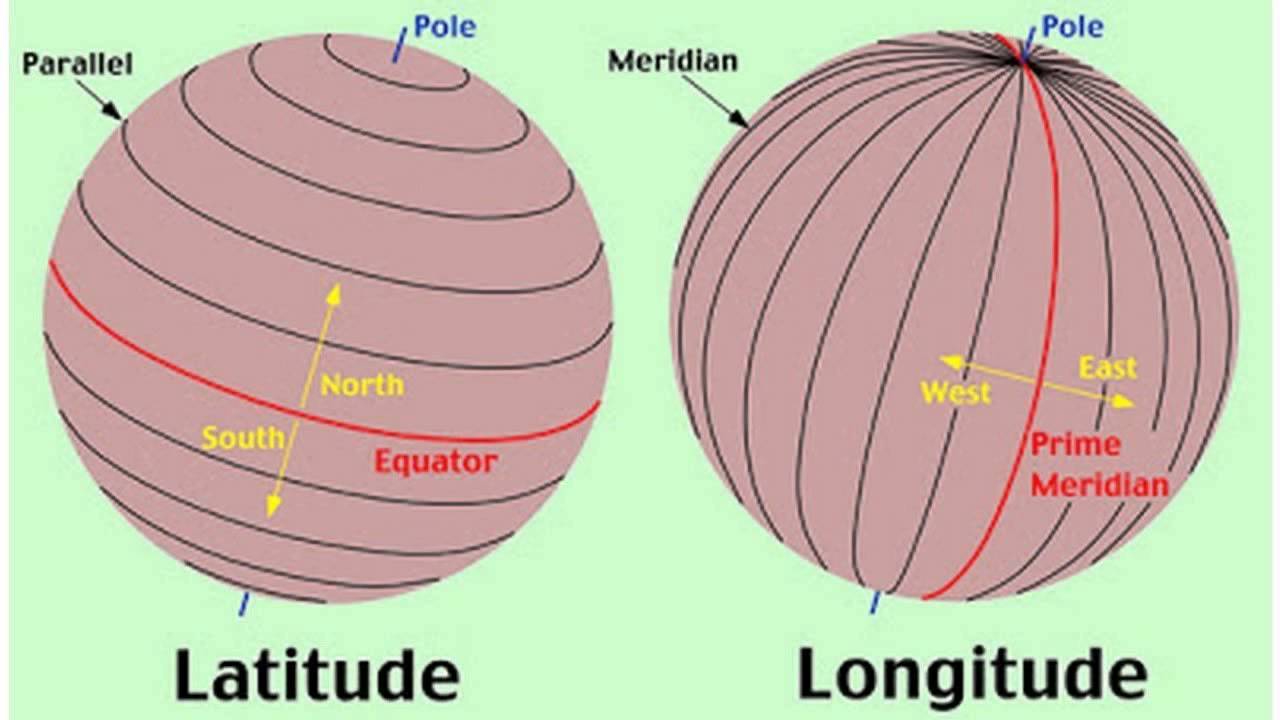
Equator
The latitude at zero degrees parallel with the largest circumference of the earth and divides northern and southern hemispheres.
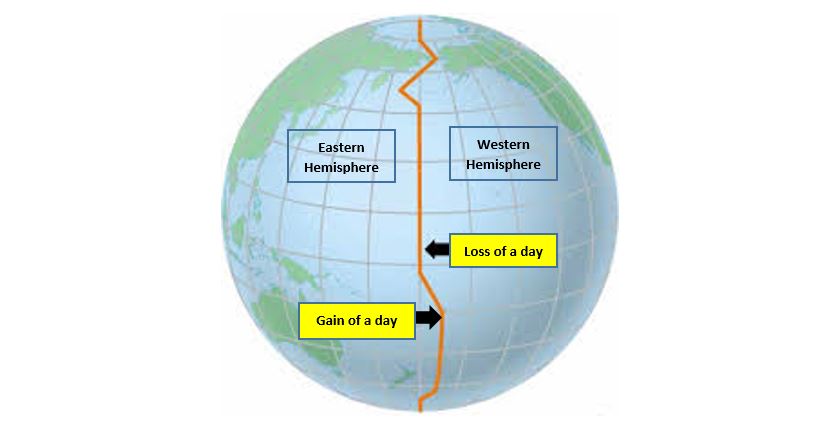
International Date Line
Line at the 180 degrees longitude east (or west) that separates one day from the next. West to east gain one day. East to west lose one day.
Scale
Relationship between a feature's size compared to its actual size on earth.'
Example: A map of France displays France at a national scale in comparison to the earth.
Toponym
The names given to a place on earth especially derived from topographical features.
Example: Los Angeles, California.