Exam 2: Adverse Drug Reactions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is true of medical management of aging patients?
it will be more complex
(age 65+ --> 85% of population will have one chronic illness and 30% will have three)
What is the % of prescriptions use in the elderly?
% use taking 3-7 drugs
1992 --> 19.6%
2010 --> 38%
What do drugs act on?
biologic system to bring things back to normal
What do drugs lack? What happens because of this?
absolute specificity
they act on many organs and tissues
(ex: want to target finger blood vessels to dilate them, but drug will target all blood vessels)
Define adverse effects
clinically undesirable reactions and potentially harmful (5-10% are hospitalized)
all drugs cause ADR!
What are the types of ADRs? (6)
1. exaggerated effect on target tissues (hypoglycemia, works too well on diabetes patient)
2. effects non-target tissues (aspirin for body ache, targeting knee but causes stomach upset)
3. effect on fetal development --> teratogenic effect
4. local effect (death of tissue where injection occurs, ex insulin delivery)
5. hypersensitivity (allergic reaction)
6. idiosyncrasy (possible genetic cause, we have no idea why)
What are local ADRs?
characterized by local tissue irritation
What are examples of local ADRs?
1. Injectable drugs at site of injection --> kill tissue there
2. Topically applied agents --> thinning of skin
3. Drugs taken orally can produce gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea or dyspepsia
What are the three sub categories of adverse reactions?
side effects
toxic reactions
allergic reactions
Describe side effects
predictable - we know what will happen when they take it bc of FDA testing
dose related - depends on how much of the drug you take, ADR's can happen at a high level, but usually you are taking a lower level
acts on non-target organs
Describe toxic reactions
predicted
dose related
acts on target organs - ex: if target organ is the liver, liver toxicity is checked to make sure it can handle the med
extensions of pharmacological effects - not doing anything unplanned, but more dose = more chance for reactions
Describe allergic reactions
not predictable - allergies can develop
not dose related - if you are allergic to it, you can't take it
does not include nausea/puking!! (this would be adverse reaction or sensitivity)
What is an allergic reaction? How does it work?
immune system response to drug
drug acts as antigen
stimulates antibody production in a previously sensitized area
What are the 4 types of allergic reactions determined by?
determined by the type of antibody produced or the type of cell mediated reaction
Describe how the Type I Immediate reactions occurs
1. Mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies
2. Drug antigen binds to IgE antibody
3. Histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins released and start these processes --> vasodilation, edema, and inflammation
What are the targets of Type I Immediate reaction?
1. Bronchioles (branching off in lungs) --> anaphylactic shock, hard to breath
2. Respiratory System -->
rhinitis (runny nose) and asthma
3. Skin --> urticaria (hives) and dermatitis (swollen, redness)
multiple can happen at the same time
What are some reactions that occurs with Type I Immediate reactions?
Anaphylaxis --> acute, life-threatening allergic reaction, includes:
Hypotension --> blood pressure drops
Bronchospasm --> hard to breath
Laryngeal edema --> throat swells
Cardiac arrhythmia --> irregular heart beat, fluttering
What are the reaction times of Type I Immediate reactions?
reactions can occur quickly after drug exposure - immediate hypersensitivity reactions
can occur later - delayed response
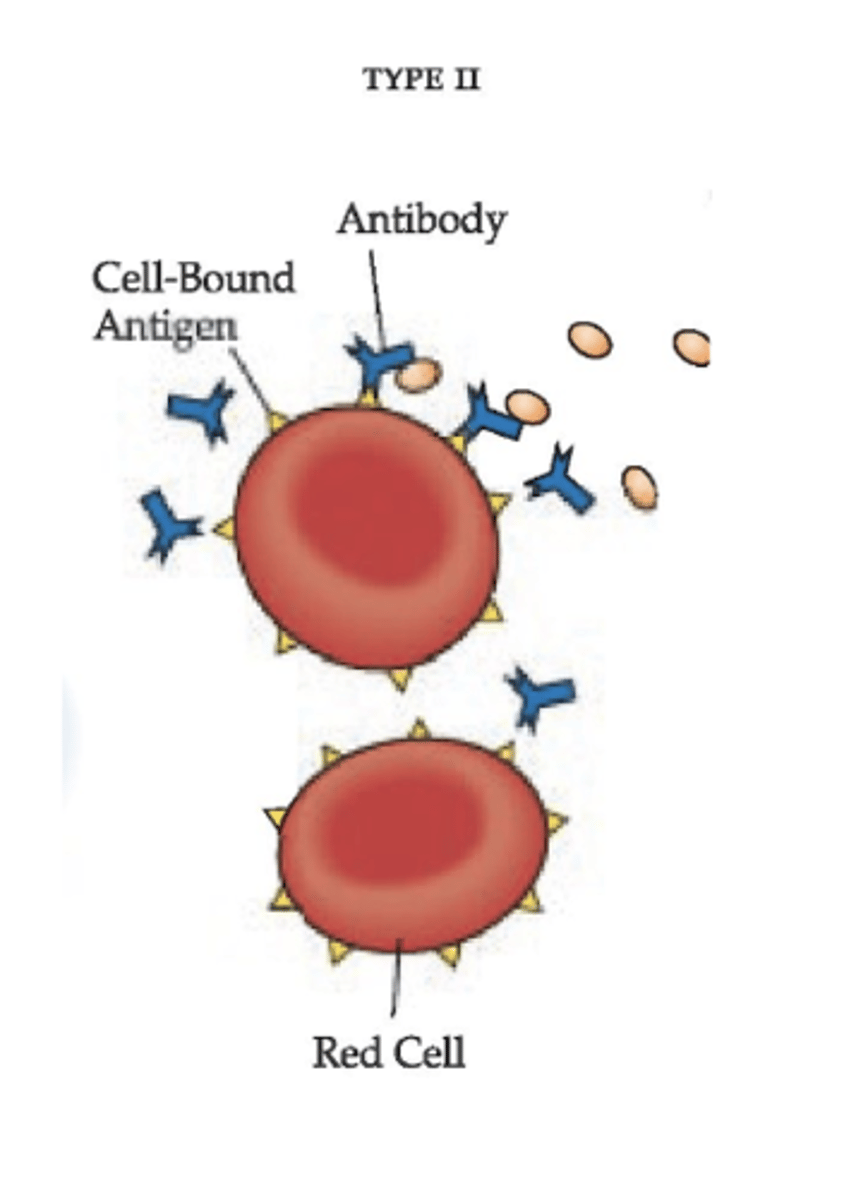
Describe Type II Cytotoxic/Cytolytic reactions
Complement-dependent involving IgG or IgM antibodies (round tan circles are complement, released by immune system to attack drug bc body senses something bad has come into the blood, but end up attack the RBC's)
(Mediator: Antibody)
Antigen-antibody complex is fixed to circulating RBCs resulting in lysis of cells
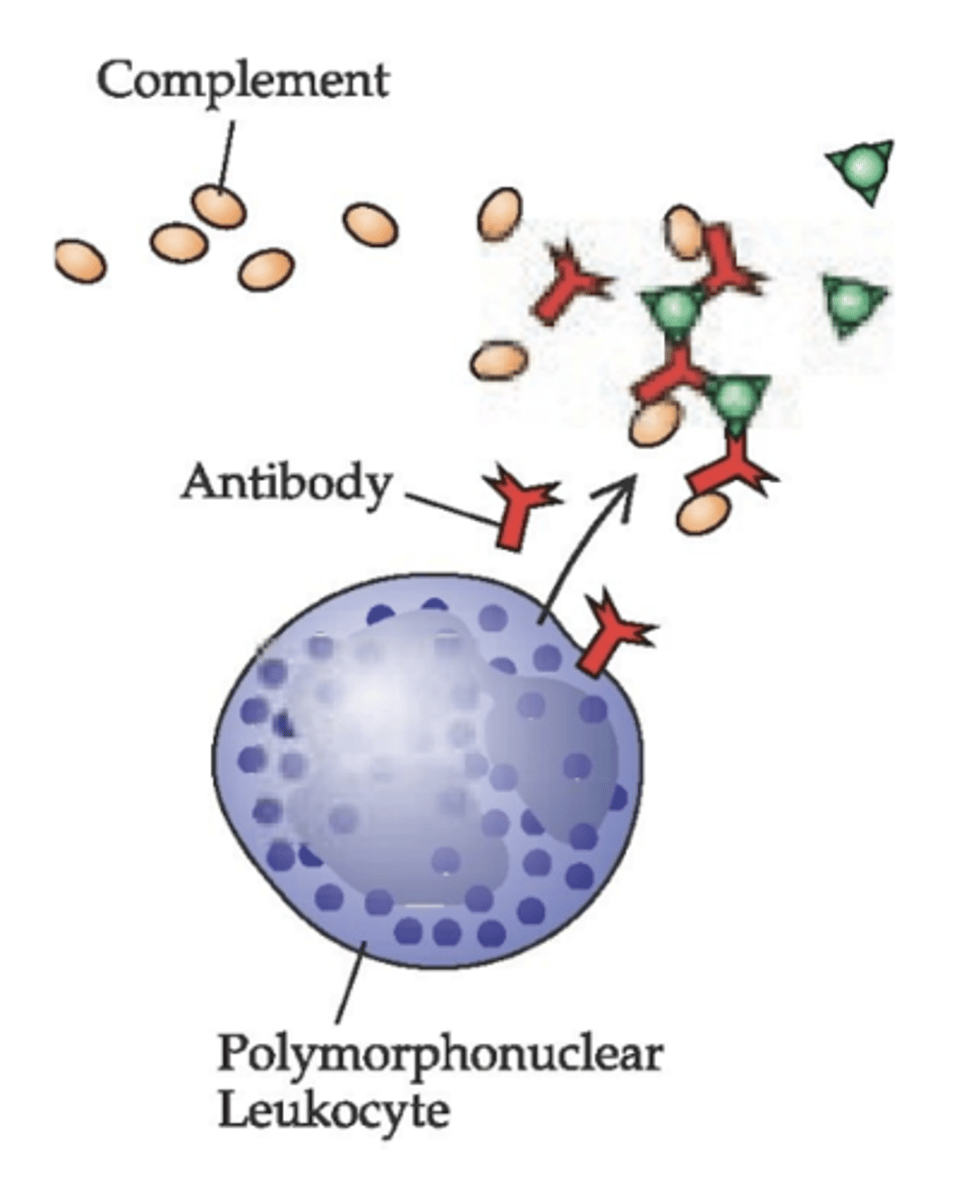
Describe Type III Immune Complex reaction
Mediated by IgG antibodies
complements and antibodies attack to PNM leukocytes instead of the drug
Manifested as serum sickness and can cause:
1. Urticaria (hives)
2. Arthritis
3. Lymphadenopathy (lymph node swelling)
4. Fever
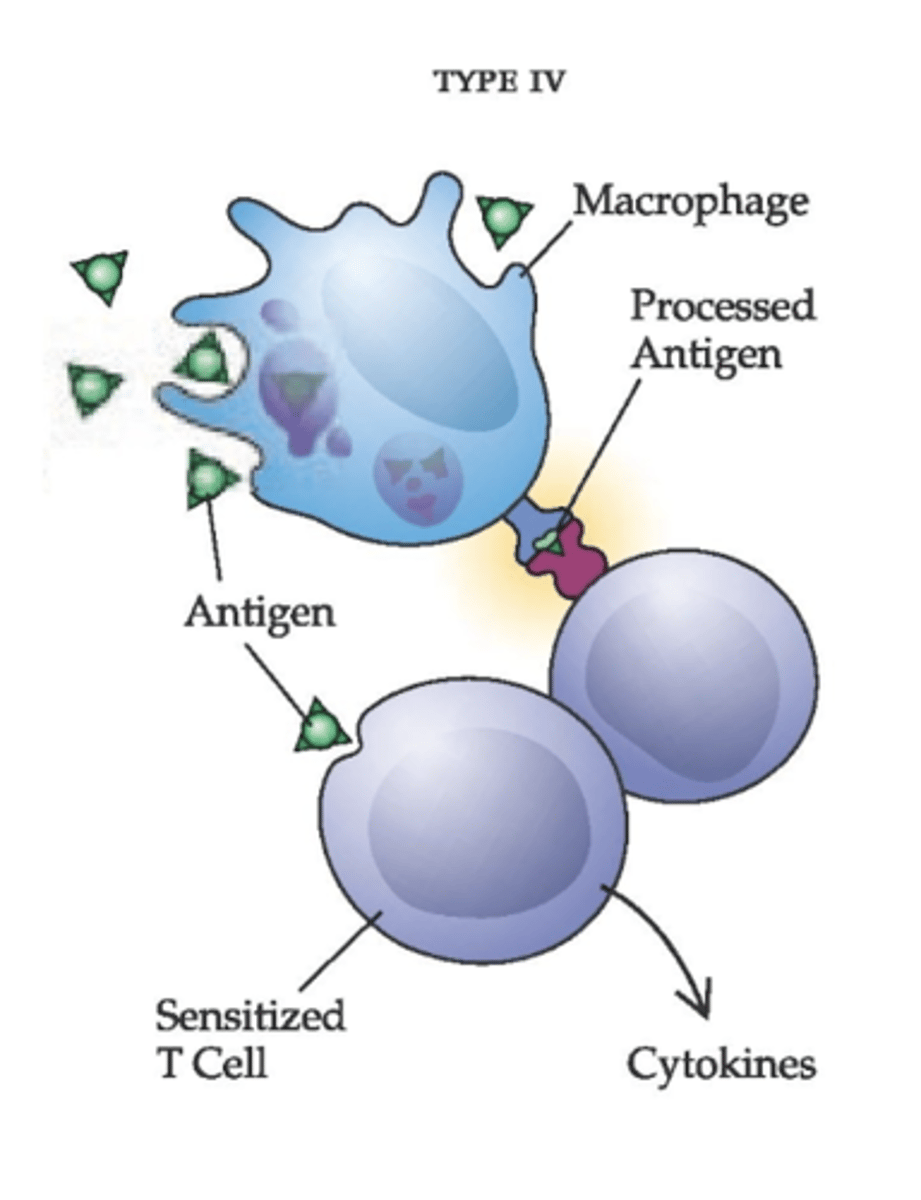
Describe Type IV Delayed Hypersensitivity Reaction
Only one mediated by the sensitized T lymphocytes and macrophages
causes inflammatory reaction produced by lymphokines, neutrophils, and macrophages (no hives, fever, etc)
EX: contact dermatitis - hygienists can get a reaction from gloves from certain companies
Describe idiosyncratic drug reactions
reaction that is neither the drug's side effect nor an allergic reaction
some are genetically determined abnormal reactions
others may be the result of an immunologic mechanism
When does a drug-drug interaction occur?
when the effect of one drug is altered by another drug
When does the likelihood of a drug-drug interactions occurring increase?
increases as the # of drugs a patient is taking increases
What are the possible effects of drug-drug interactions?
1. decrease action of drug(s)
2. increase action of drug(s)
2. cause adverse effects
What are the types of drug-drug interactions with absorption?
changes in GI pH, lower or higher
taking an acid reducer, but taking a drug that needs acidic environment and then affects absorption
What are the types of drug-drug interactions with distribution?
plasma protein binding
the drug is absorbed, but it won't be able to bind to albumin to take the drug to other places
What are the types of drug-drug interactions with metabolism?
increases or decreases how CYP450 works
if you're taking a drug that decreases CYP450, but also taking a drug that requires CYP450 - then drug B won't be broken down as much and won't be effective
What are the types of drug-drug interactions with excretion?
affecting the renal system
if you're not going to the bathroom as much, then the drug won't be eliminated as fast
Give examples of drug-food interactions
1. grapefruit juice and CYP450 --> will inactive CYP450
2. dairy products and tetracycline --> will inactive tetracycline
What is true if a patient if taking a drug for a longer period of time?
increase risk for ADRs
usually they are rare in dentistry and drugs are prescribed for single doses/short duration
Do drugs in dentistry have larger or smaller margins for safety?
larger margins - wide TI, safer
What should we consider when a prescribing a dental patient medication?
Explaining possible drug adverse experience/reactions to patient
carefully assess medical histories --> past ADRs (allergies) and drug interactions