Immunology Final
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Are the tumor antigens specific? Nonspecific? Sensitive?
Specific
Which mechanism is involved in peripheral tolerance to self-antigens?
Inhibition of co-stimulatory signals from antigen presenting cells
Central tolerance, in which lymphocytes learn to distinguish between self-antigens and foreign antigens, takes place in the thymus and:
Bone Marrow
Which histocompatibility system activates gamma or delta T-cell receptors?
MHC Class-I related chain A (MICA) antigen
A transplantation patient suffers an organ rejection within hours after the procedure. What type of rejection occurred?
Hyper acute
Which of the following is characteristic of an acute graft-versus-host disease episode?
The reaction involves the skin, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and liver
In a patient who is exhibiting signs of graft-versus-host disease, which cell type is most likely responsible for the reaction?
T cells
A transplant patient has been prescribed corticosteroids as part of his post-transplant medication regimen. What class of drug is the patient taking?
Immunosuppressive
A tumor that is classified as malignant is described as:
A disorganized mass that is not encapsulated and can invade nearby organs
What is the definition of a carcinoma?
A cancer that is derived from skin or epithelial linings or internal organs or glands
What is the definition of a sarcoma?
A cancer that is derived from muscle, bone, fat, or soft tissue
A tumor-specific antigen is:
Unique to the tumor of an individual patient
Which of the following is a clinical application for tumor markers?
Diagnosis, screening, and monitoring
In which of the following conditions would you not see an increase in alpha-fetoprotein?
Hypercholesterimia
A woman who has a history of ovarian cancer in her family goes to her physician for a "cancer test." What is the test that is most likely to be positive if the woman has ovarian cancer?
Cancer antigen 125
Which type of gene is required for cell growth and division but can cause malignant transformation when altered?
Proto-oncogene
Which statement regarding myelogenous leukemias is true?
They originate from a common myeloid precursor cell
Polyclonal gammopathies can be exhibited as a secondary manifestation of all the following EXCEPT:
Multiple myeloma
A CA-125 assay was performed on a woman with ovarian cancer. After treatment, the levels xxxl significantly. How can this finding be explained?
Increased = treatment is not working; can increase during menstruation, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine fibroids, and pregnancy; rising concentrations over time can predict reoccurrence of the disease, poor prognosis,
Decreased = treatment is working; high dose hook effect (false decrease in measurement in an area antigen excess)
A patient had surgery for colorectal cancer, after which he received chemotherapy for 6 months. The test for CEA was normal at the time. One year later, the bimonthly CEA was elevated (above 10ng/mL). An examination and biopsy revealed the recurrence of small tumor. What was the value of the results provided by the CEA test in the clinical situation?
Information for further treatment
Which cytogenetic abnormality is associated with an excellent prognosis in children with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)?
t(12:21)(p13;q22)
Which marker is highly specific for hairy-cell leukemia?
CD103
A patient whose malignant clone is positive for the CD markers CD15 and CD30 is most likely to have what clinical disease?
Hodgkin lymphoma
Which of the following is not a characteristic in the identification of lymphoma of B-cell origin?
Presence of CD14 and CD15
Which of the following findings is a diagnostic criterion for monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance?
Plasma cell count lower than 10% of total cells in bone marrow
Malignant plasma cells exhibiting CD38, CD56, and CD136 are found in:
Multiple myeloma
What is the correct order of protein migration, starting at the anode and moving to cathode, following serum protein electrophoresis?
Gamma, beta, alpha 2, alpha 1, albumin
A patient’s immunofixation electrophoresis shows excessive amounts of free monoclonal light chains. These light chains are referred to as:
Bence Jones proteins
Decreased CD3-positive lymphocytes and a lack of responsiveness to phytohemagglutinin in the circulation are typically associated with:
DiGeorge anomaly
Which of the following statements about severe combined immunodeficiency is true?
It may be associated with a signal transduction defect.
A 9-month-old boy is suspected of having an immune deficiency because he had many recurrent infections with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Laboratory tests reveal a normal percentage of T cells and T-cell subsets but a lack of mature B cells and immunoglobulins. This boy most likely has:
X-linked agammaglobulinemia
Which of the following diseases results in an acquired or secondary immunodeficiency?
HIV infection
A patient with hereditary angioedema will present with swelling in the tissues and has deficiencies in which of the following?
C1 inhibitor
A 7-month-old boy is seen by a specialist because of hypocalcemia, viral pneumonia, a history significant for recurrent diarrhea, and oral candidiasis. An x-ray reveals the lack of a thymic shadow. A likely diagnosis for this boy is:
DiGeorge anomaly
A child suspected of having an inherited humoral immunodeficiency disease is given a diphtheria/tetanus vaccine. Two weeks after the immunization, his level of antibody to the specific antigens is measured. Which result is expected for this patient if he does have this deficiency?
No change in the level of specific antibody
Defects in oxidative burst activity can be detected using flow cytometry by labeling patient neutrophils with:
Dihydrorhodamine (DHR)
Which is true of selective IgA deficiency?
Patients may develop an anti-IgA antibody
A 9-month-old infant is seen by a physician because of a persistent skin infection. His white and red blood cell counts are normal. However, immunofixation electrophoresis indicates a low level of IgG. When the infant returns to the physician for a follow-up visit in a month, his IgG level has increased. What condition do these results indicate?
Transient hypogammaglobulinemia
A 6-month-old baby has suffered from recurrent bacterial infections. Flow cytometry results indicate a lack of B cells but the presence of normally functioning T cells. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
Bruton's tyrosine kinase deficiency
Which test should be performed when a patient has a reaction to transfused plasma product?
Immunoglobulin levels
Which of the following statements best describes common variable immunodeficiency?
There is a deficiency of IgA, IgG, or both.
A male baby who has suffered from persistent Candida fungal infections and several bouts of pneumonia before the age of 6 months is found to have some developmental problems as well as low-set ears. Laboratory testing reveals an absence of T cells. What is the most likely diagnosis?
DiGeorge syndrome
Which of the following is associated with DiGeorge syndrome?
Small or missing thymus
Delayed-type hypersensitivity skin tests are used to screen for:
Cell-mediated immunodeficiencies
A nitroblue tetrazolium test shows little color in cells observed under a microscope. What disease does this finding correlate with?
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)
A patient’s total IgG is in the normal range, but he suffers from recurrent infections with encapsulated bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenza. T-cell functions are all normal. What is the most likely cause of the infections?
IgG subclass deficiency
The most common form of severe combined immunodeficiency disease results from an X-linked mutation in the gene that codes for:
a receptor subunit involved in signaling for interleukins-2, -4, -7, and -9.
An autosomal-recessive form of severe combined immunodeficiency can be caused by a deficiency in:
JAK3
The buildup of toxic purine metabolites that impair B- and T-cell proliferation is the result of a mutation in the gene coding for:
adenosine deaminase
Patients with recombinase activating gene 1 (RAG-1) or RAG-2 deficiencies have decreased numbers of:
Lymphocytes
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency is caused by a defect in:
CD18
Which enzyme deficiency causes moderate to severe impairment of cell-mediated immunity, with little or no effect on humoral immunity?
Purine-nucleoside phosphorylase
A defective kinase needed for DNA repair and cell cycle control leads to involuntary muscle movements and dermal capillary swelling in which syndrome?
Ataxia telangiectasia
Which syndrome is characterized by defective apoptosis, leading to survival of lymphocytes that can react with self-antigens?
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative
A specific defect in innate immunity leading to bacterial infections could involve a deficiency in:
toll-like receptors
An inflammatory syndrome involving recurrent fevers (periodic fever syndrome) is
Hyper IgD
The accumulation of immune complexes in renal glomeruli or joints (lupus-like syndromes) can be caused by a deficiency in the complement component:
C2
The most serious impairment of opsonization and antimicrobial defense is caused by a deficiency in complement component:
C3
The most common complement component deficiency is:
C2
From the following, identify a specific component of the adaptive immune system that is formed in response to antigenic stimulation:which tweo
Immunoglobulin
Which MHC class of molecule is necessary for antigen recognition by CD4-positive cells?
Class II
Which of the following cell surface molecules is classified has an MHC class II antigen
HLA-DR
A 3-year-old boy is seen by his physician because of many recent bacterial infections. Flow cytometry indicates normal levels of T and B cells. The nitroblue tetrazolium test for oxidative burst reduction is negative. The most likely cause is
Chronic granulomatous disease
A patient with hereditary angioedema has which of the following deficiencies?
C1 esterase inhibitor (C-1 INH)
A 2-week-old baby is seen for a possible infection with CMV. Which of the following statements is false?
An initial titer of anti-CMV IgG would need to be established
an initial titer of 4 followed by a subsequent titer of 16 for the same patient , drawn 2 weeks later, is indicative of which of the following?
Infections
What is the purpose of a C3a, C4a, and C5a?
cause increased vascular permeability, contraction of smooth muscle, and release of histamine from basophils
Which of the following are components of both innate and adaptive immune responses?
Macrophages
Where does the specific immune response to a foreign antigen mainly occur?
Lymph nodes
The most primitive component of the immune response found even in some of the simplest forms of life is the ability to
Identify self from non self
A man opens up an old loaf of bread and inhales Penicillium spores from the organism growing inside. Inside the man’s lungs, phagocytes engulf and digest the spores. The man never gets sick. This is an example of
Innate immunity
Thymocytes start as
Double negative cells - they do not express CD8 or CD4
Mutations causing deficiencies in CD40L expression lead to an inability of helper T cells to:
promote class-switching, resulting in high IgM and low IgA and IgG concentrations.
A critical receptor involved in the second signal for T-dependent B-cell activation is:
CD40
The difference in kinetics between a primary and secondary immune response is caused by the presence of:
Memory cells in the secondary response
All of the following are characteristic of acute-phase reactants EXCEPT:
they are used to diagnose a specific disease
Class II molecules bind to what kind of peptides?
Processed exogenous
A patient with a viral infection to the ABC virus is found to have a high antibody titer to the ABC virus’s RNA, or anti-ABCr. Which of the following is true?
MHC Class I molecules presented antigen to CD 8+ T cells
What is measured in the CH50 assay?
Complement needed to lyse 50% of antibody-sensitized RBCs
If complement CH50 is decreased and complement AH50 is normal in a specimen, the specimen may be deficient in factor(s)
C1, C2, C4
Complement components are completely destroyed if a specimen is
is heated at 56C for 30 minutes
The C5 convertase of the classical pathway of complement activation is:
C4b2a3b
A cytokine “storm” is a:
an overwhelming response to an infection which generates a large, systemic cytokine release
A person steps on a rusty nail, which punctures her skin and activates resident macrophages to secrete IL-1 beta. The fever that develops is an example of what type of cytokine signaling?
Endocrine
A Fab fragment consists of:
One L chain and one half of an H chain
The combination of a plasma cell fused to a myeloma cell is called a:
Hybridoma
Select the statement about secondary response to an antigen that is true.
IgG is increased 100-fold to 1,000-fold
Identify the true statement about the anamnestic response versus the primary response.
The primary response has a long lag phase; the anamnestic response has a short lag phase.
The interaction between an individual antigen and antibody molecule depends upon several types of bonds such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bods, hydrophilic bonds, and van der Waals forces. How is the strength of this attraction characterized?
Affinity
A laboratory is evaluating an ELISA test for detecting and antibody to CCP. The laboratory incudes serum from healthy volunteers and patient with other connective tissue diseases in the evaluation. These specimens determine which factor of the assay?
Specificity
The detection of precipitation reactions depends on the presence of optimal proportions of antigen and antibody. A patient’s sample contains a large amount of antibody, but the reaction in a test system containing antigen is negative. What has happened?
Prozone phenomenon
Which organs are involved in the immune system, which are considered the primary lymphoid organs in which immunocompetent cells originate and mature?
Bone marrow and thymus
A patient has a PSA level of XXX the day before surgery to remove a localized prostate tumor. One week following surgery, the serum PSA was determined to be XXXX by the same method. What is the most likely cause of these results?
Increase = treatment is not working/regrowth or did not take out whole tumor
Decrease = treatment is working/no new growths
A pregnant woman came to her physician with a maculopapular rash on her face and neck. What positive test(s) would reveal a diagnosis of congenital rubella syndrome in her baby after birth?
Positive rubella test for IgM
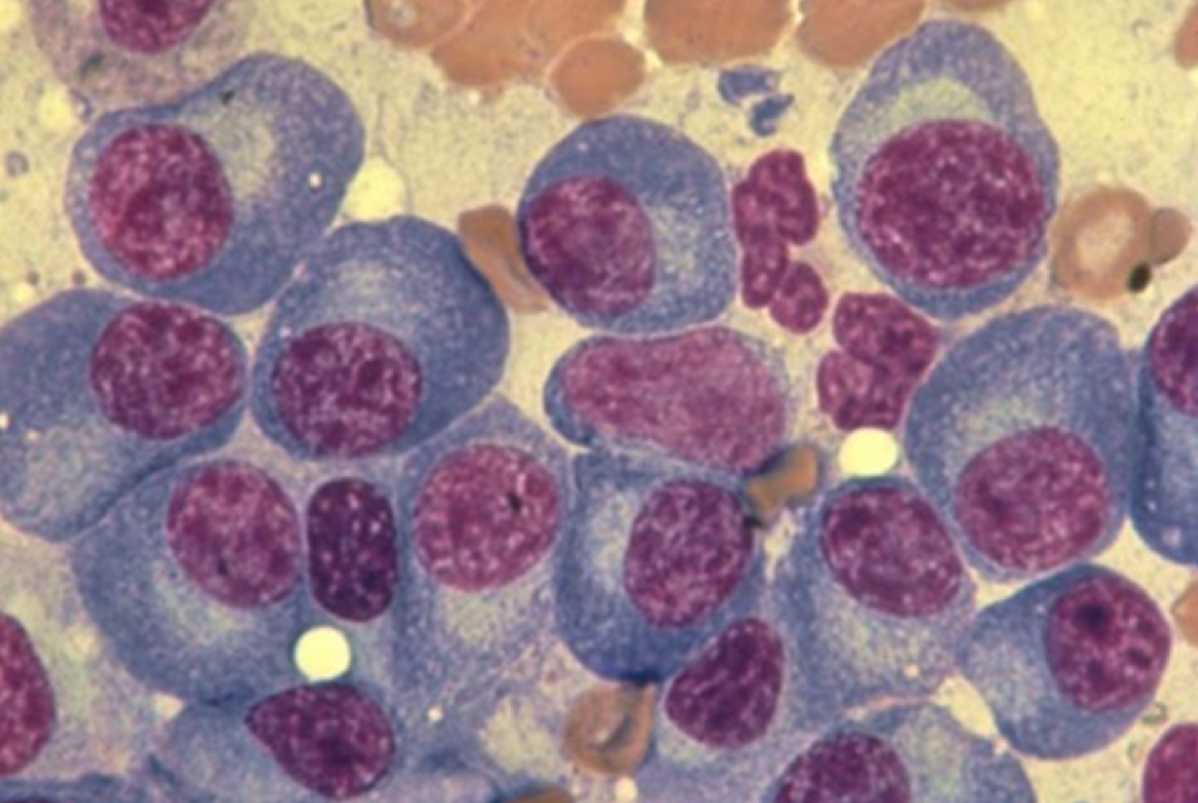
What type of lymphoma is this?
Plasma cell dyscrasias
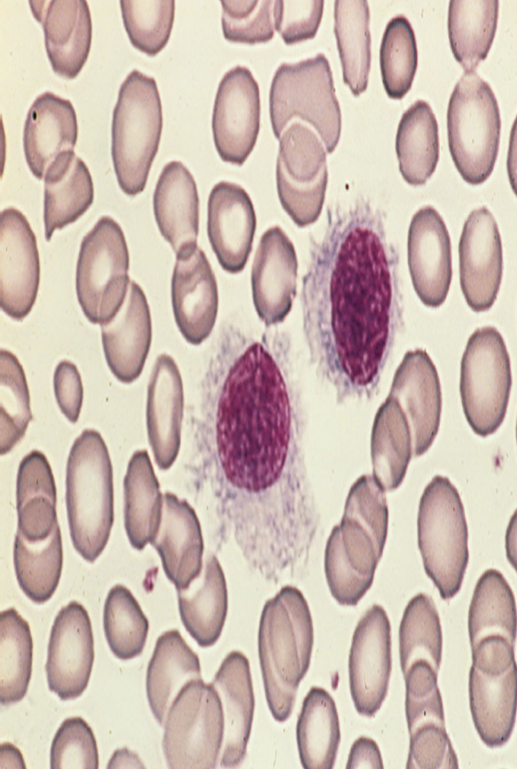
This cell is positive for: CD19, CD20, CD22, IL-2 receptor, and CD25, CD103 (Highly specific marker). Trap +
Hairy Cell Leukemia
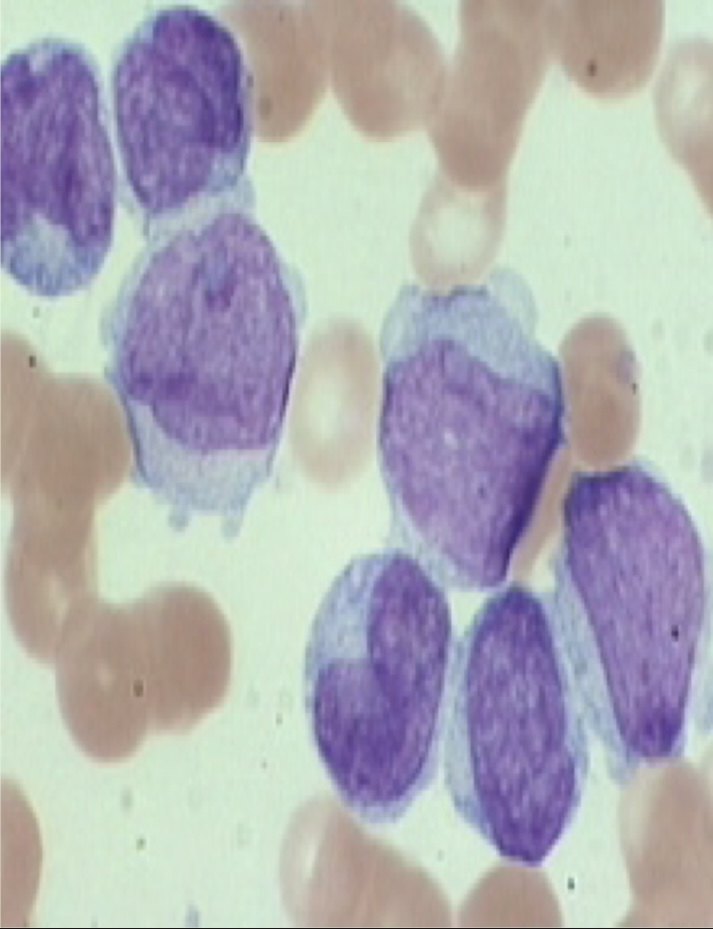
What type of leukemia is this? Acute or Chronic
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
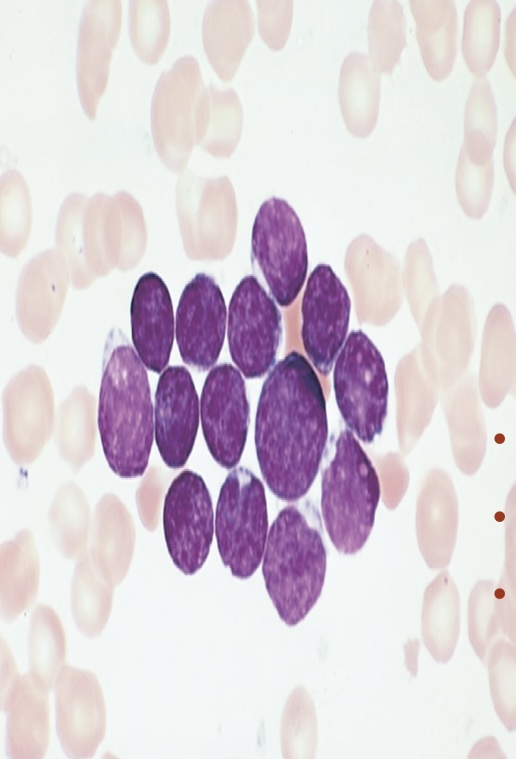
What type of leukemia is this? Acute or Chronic
Acute
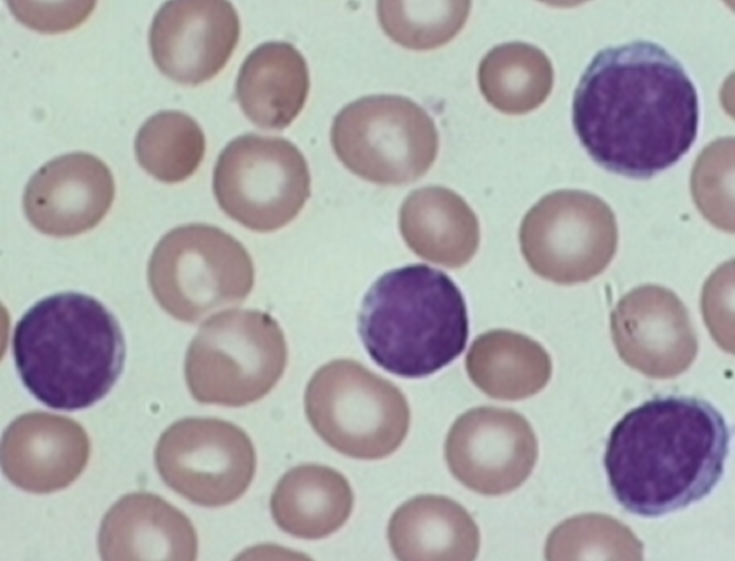
What type of leukemia is this? Acute or Chronic
Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
CD19 +, weakly expressed CD20
CD10 negative
Most common in adults
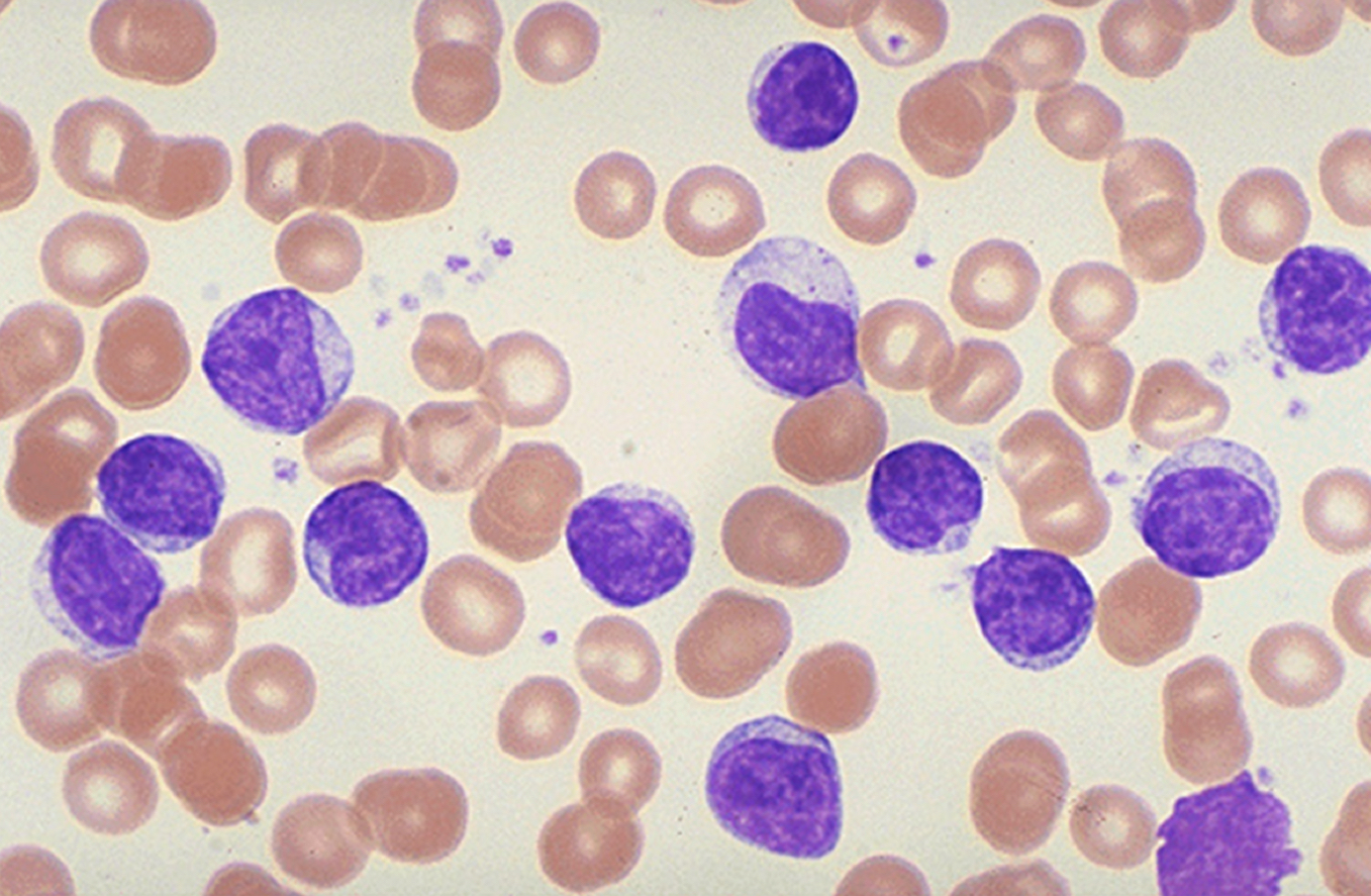
What type of leukemia is this? Acute or Chronic
Chronic - mature