Sleep
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by @agreyr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Standard sleep measures
Electroencephalogram (EEG), Electrooculogram (EOG), Electromyogram (EMG)
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Allows us to look at brain activity through wave patterns
Electrooculogram (EOG)
Analyzing specific muscle movements around the eye (REM vs NREM)
Electromyogram (EMG)
Identifying muscle activity (or lack thereof) in the neck
EEG patterns
Wakefulness, stage 1 sleep EEG, stage 2 sleep EEG, stage 3 sleep EEG
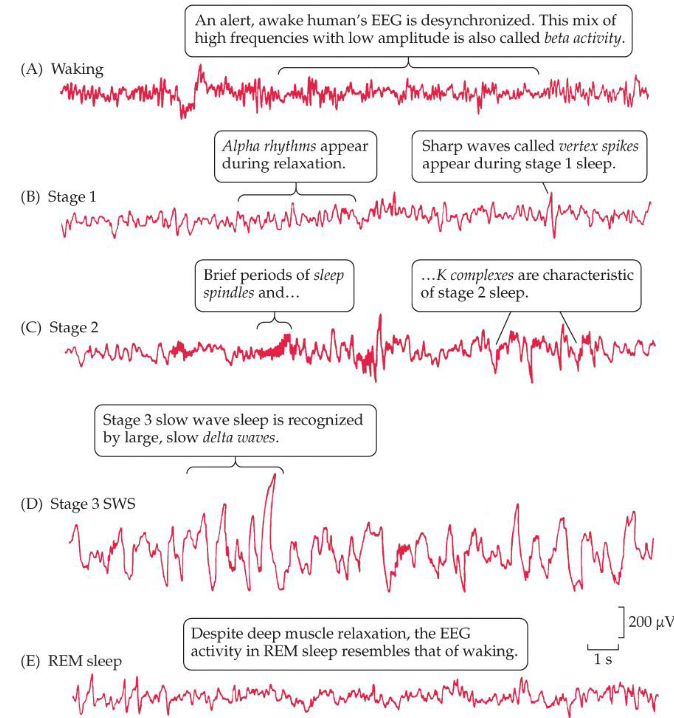
Wakefulness (EEG)
Desynchronized EEG (beta activity)
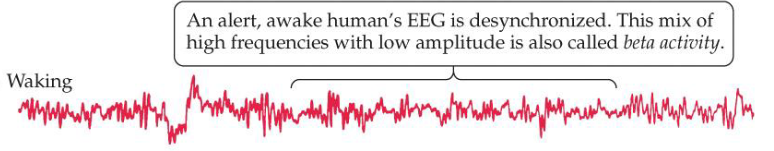
Stage 1 sleep EEG
Alpha waves and vertex spikes; slowing of the heart rate and relaxation of the muscles
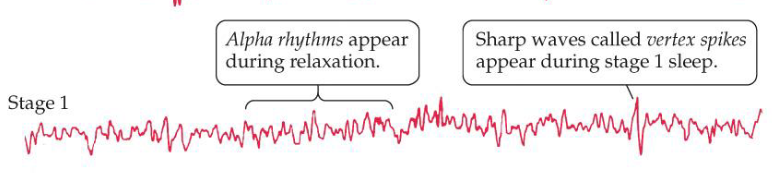
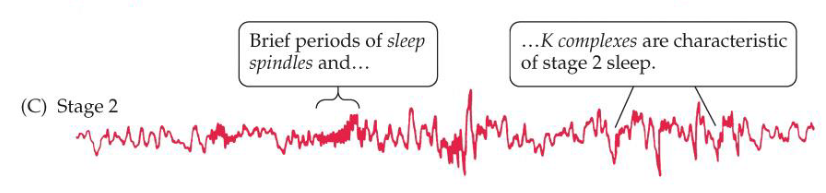
Stage 2 sleep EEG
K complexes and sleep Spindles
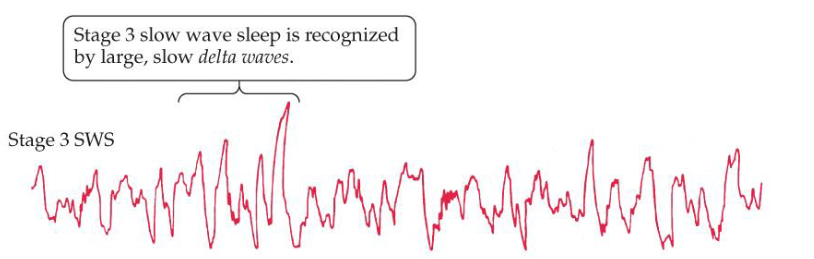
Stage 3 sleep EEG
Slow wave sleep; delta waves
REM sleep
Rapid eye movements; loss of core muscle tone (atonia), brainstem regions inhibit motor neurons; low amplitude, high frequency EEG; cerebral activity increases to waking levels; general increase in ANS activity; occasional muscle twitching in extremities; more prominent in later half of sleep cycle
REM and dreaming/dream recall
If you wake people up during REM or NREM sleep, 80% of awakenings from REM sleep but only 7% of awakenings from NREM sleep led to dream recall
Dream interpretation theories
Freudian theory and Hobson’s activation-synthesis theory
Freudian theory of dream interpretation
Dreams represent unacceptable wishes; can determine real desires by understanding the meaning of the dreams we experience
Hobson’s activation-synthesis theory
Information supplied to the cortex during dreaming is largely random and the dream is the cortex attempting to make sense of it; meaning comes from what the people add to the random jumble
Theories on the purpose of sleep
Recuperation theories and adaptation theories
Recuperation theories of sleep
Being awake disrupts homeostasis and sleep is required to restore it
Sleepiness triggered by deviation from homeostasis caused by wakefulness; sleep is terminated by the return to homeostasis
Adaptation theories of sleep
Sleep is the result of an internal timing mechanism
Humans programmed to sleep at night to avoid accidents and predation and to save energy
Purpose of sleep
It fulfills some necessary physiological function; probably not some complex higher order one, as most mammals and birds sleep
Sleep is essential for survival but not necessarily needed in massive quantities
Sleep patterns across the lifespan
Infants sleep a lot, with decreases throughout childhood
REM sleep likely important for nervous system and brain development in infants; high proportions of REM sleep in infants
Increased need for sleep in adolescence
Shift in circadian rhythms for sleep/wake cycles; research shows benefits when these shifts are built into society with later school start times (increased academic performance, fewer driving accidents, and reduced depression rates)
Effects of sleep deprivation in humans
Increase in sleepiness, irritability, difficulty concentrating
Severe sleep deprivation can result in occasional hallucinations
REM rebound (sleep recovery)
You won’t make up for the sleep you lost but you may have more intense sleep for a few days
Sleep functions
Energy conservation, niche adaptation, body & brain restoration, memory consolidation
Energy conservation
Reduced metabolic activity when we sleep
Niche adaptation
Sleep is part of an organism’s ecological niche; emphasizes the role of natural selection
Body & brain restoration
Prolonged deprivation leads to lower immune function; people more susceptible to pain after sleep deprivation
Memory consolidation
Slow wave sleep and REM may plan an important role; synaptic rearrangement occurs during REM