Chapter 3: Cellular Regeneration and Regulation
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
embryo
An early stage of development in multicellular organisms following fertilization and before becoming a fetus
conception
the process when a sperm cell fertilized an egg cell to begin the development of an organism
foetus
the unborn offspring of a mammal more than 8 weeks after conception
Gestation period
The time between fertilization and birth during which the embryo and fetus develop in the uterus.
Zygote
A single cell formed by the fertilization of an egg by a sperm, containing a complete set of genetic material
Uterus
A muscular organ in female mammals where the embryo implants and develops during pregnancy.
Morula
An early stage of embryonic development where the zygote has divided into a solid ball of cells
Blastocyst
Structure of a hollow ball of cells that forms a few days after fertilization. Inside are the inner cell mass which will develop into the embryo. The blastocyst attaches to the uterine wall to continue development.
Gastrulation
A process during embryonic development in which the blastocyst reorganizes into three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Embryonic germ layers
The three primary layers of cells (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) formed during gastrulation, which give rise to all tissues and organs.
Ectoderm
The outermost germ layer that forms the nervous system, skin, and sensory organs.
Mesoderm
The middle germ layer that develops into muscles, bones, the circulatory system, and internal structures.
Endoderm
The innermost germ layer that forms the digestive system, lungs, and other internal organs.
Critical periods
Specific time frames during development when an organism is particularly sensitive to environmental influences.
Stem cell
Cell that can divide and develop into specialised cell types.
Embryonic stem cell
Type of stem cell taken from the early embryo that can differentiate into any cell type
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
The molecule that carries genetic information in cells
Nucleotide
The basic structural unit of DNA and RNA, consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Purine
A type of nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA, including adenine (A) and guanine (G).
Pyrimidine
A type of nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA, including cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) in RNA.
Complementary base pairing
The specific hydrogen bonding of nucleotide bases in DNA (A-T and G-C) and RNA (A-U and G-C).
DNA packaging/structure
DNA molecules are wrapped around 8 histones (special type of protein), which is called the nucleosome, then many nucleosomes forms the chromatins and then many chromatins make up the chromosomes, which are found inside the nucleus
Chromatin
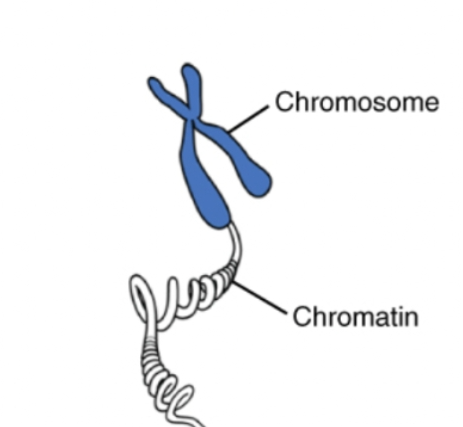
The complex of DNA and proteins in the nucleus that condenses to form chromosomes during cell division

Nucleosome
The fundamental unit of chromatin structure, consisting of DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins.
Chromosomes
Thread-like structures made of condensed DNA that carry genetic information and found inside the nucleus
Mitosis
A type of cell division that produces two genetically identical daughter cells for growth, repair damaged cells and replace dead cells.
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in prokaryotes where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
chromatid
One of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome.
Centromere
The middle region of a chromosome that links sister chromatids and where spindle fibers attach during mitosis.
G0 phase
A resting phase where cells do not divide but carry out normal functions.
G1 phase
The first growth phase of interphase where the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication.
S phase
DNA replication occurs, doubling the genetic material.
G2 phase
The second growth phase where the cell prepares for mitosis by producing proteins and organelles.
M Phase
The stage of the cell cycle where mitosis and cytokinesis occur.
Sister chromatids
The replicates of the chromosomes (two of them combine)
Diploid
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent).
Full set of chromosomes (46 in humans)
The symbol '2n' refers to being diploid. Body cells are diploid.
Haploid
is used to describe sex cells/gametes (23) to function. Symbol ‘n’ refers to being a haploid.
Homologous Chromosomes
Pairs of chromosomes, one from each parent, that have the same genes but may have different alleles.
Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows, performs normal functions, and replicates DNA in preparation for division.
Prophase
replicated chromosomes and chromatids become visible and spindle fibers start to form from the centrosomes, and chromatin begins to condense into chromosomes.
In between prophase + metaphase (last on prophase)
The nuclear membrane begins to break down, microtubules continue to extend and attach to the centromere of chromosomes.
Metaphase
replicated chromosomes line up along the equator
Anaphase
The stage of mitosis where sister chromatids are pulled apart toward opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase
The final stage of mitosis is when the nuclear membrane forms around two new nuclei, each number the same as the parent cell. Spindle microtubules begin to retract, and chromosomes begin to decondense back into chromatin, slowly entering cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis
The final step in cell division where the cell splits into two new daughter cells.
Cell plate
A structure formed in plant cells during cytokinesis that develops into a new cell wall.
G1 Check point
Checks for
Cell size
Nutrients
Growth factors
DNA damage
Organelles have double
G2 Check point
Checks for
DNA damage
DNA replication completeness
M Check point
A checkpoint in mitosis ensuring proper chromosome alignment and attachment to spindle fibers for division at the metaphase plate
Fail discovered in the check points?
Repair damage (attempt)
Cell goes through programmed cell death (Apoptosis)
what is Apoptosis
A programmed cell death process that removes damaged or unnecessary cells.
what triggers apoptosis (a receptor-mediated response) by?
internal or external signalling molecules
Major steps of Apoptosis:
Cell strinkage (cytoskeleton break down)
Breakdown of oganelles + nucleus
Blebbing of plasma membrane
Formation of apoptosis bodies
Phagocytosis of apoplotic bodies
Two pathways for apoptosis:
Extrinsic and Intrinstic
where does intrinsic occur?
mitochondria → released from → cytochrome
where does extrinsic occur
death receptor
what does extrinsic pathway activate
Extrinsic pathway can activate apoptosis on its own and activate the intrinsic pathway.
what does the intrinsic pathway activate?
This pathway acts independently, but can also be activated by the extrinsic pathway in some situations
Caspase
a special enzyme that helps break down a cell during apoptosis. They are already present as inactive precursors within the cell
cancer formation occurs via check points
errors at checkpoints can cause cancer or the inability to form death receptor proteins.
Necrosis
Uncontrolled cell death caused by external factors such as injury or infection.
Phagocytic cell
A type of immune cell that protects the cell as it eats and digests germs, dead cells, and debris.
Benign
A harmless tumor that does not spread.
Malignant
A dangerous tumor that can invade other parts of the body (cancerous).
Culture
The process of growing cells in a controlled laboratory environment.
Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells from the original tumor to other parts of the body.
Angiogenesis
The formation of new blood vessels, often stimulated by tumors to supply oxygen and nutrients.
Spindle microtubules
They attach to centromeres and help separate chromatids into daughter cells during cell division.
centrosome
spindle fibers start to form