IB Business paper 1- terminology that relates most to pre-seen case
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
private limited company
owned by shareholders
can not raise finance from general public
shares are typically sold to family, or friends
Advantages
Limited liability – when the company is sued or incurs losses, all a shareholder will lose is his stock in the business.
Higher capital, higher capacity for expansion
Disadvantages
More restrictions
Corporate taxes (higher)
public limited company
owned by shareholders
Able to sell shares to the public
Required by law to publish their complete and true financial position
flotation(when the business sells part or all of itself to the public) or an initial public offering (IPO)
Advantages
More capital raised from selling stock
Limited liability
Continuity after death, freely transferable
Higher capacity for expansion
Disadvantages
Possibility of a hostile take-over through shares, control can change unexpectedly and be lost by the original owner
Much more restrictions
Corporate tax
expansion
the growth of a business due to an increase in the size of the organisation itself or/and growth in the market
usually measured by an increase in sales revenue, market share, or profits
Average cost
the cost per unit of production
derived from total cost of output/ number of units produced
this tends to decrease as business increases due to economies of scale
Greenwashing
misleading marketing tactic that falsely portrays sustainable practices or describe products to be more environmentally friendly than they actually are
permanent employees
these workers have an employment contract on a continual basis
contract only ends if workers resign or the employer terminates the contract
Temporary workers
employees hired for a limited period of time or until the completion of a project
freelancer
a self-employed individual who provides services to their clients rather than work for an employer
work on specific projects instead of long-term employment commitments
mission statement
a simple declaration of the company’s underlying purpose and its core values
aims
general and long-term goals of the organisation
objectives
short-to- medium term specific targets to achieve the aims
strategies
medium-to-long-term plans of action to achieve the strategic goals of the organisation
business strategies
operational strategies-
day to day methods to improve efficiency
genetic strategies-
affect business as a whole
to gain competitive advantage
corporate strategies-
long term goals
tactical objectives
survival-
to establish the business
to recover and get back to profitability
prevent hostile takeover
sales revenue maximisation -
grow and achieve recognition
become more efficient through economies of scale
not profitability
strategic objectives
profit maximisation-
maximising profits tends to be the main goal of all businesses
growth-
market share/sales revenues/helps achieving EOS
market standing-
presence in an industry
image and reputation-
Good image helps grow the business, attracts new customers, make employees proud
the need for changing objectives
Companies change objectives when responding to internal and external changes
Internal factors
Corporate culture – way the organisation works
Type and size of organisation – small or big businesses run differently
Age of organisation – change must be consistent with times
Financial status – profit goals, how much money the business has to use
Risk profile of shareholders – If investors are risk-averse or risk-loving
Private/Public sector
External
State of economy – strong or depressed economy affects the company too
Government constraints – government telling you not to expand somewhere
Presence and power of pressure groups – (e.g. not to expand in the endangered locations)
CSR
Concept whereby organizations consider the interests of society by taking responsibility for the impact of their activities on various stakeholders
Benefits:
Better employee recruitment and retention
Boosts company’s image/reputation
Risk management against scandals, accidents, etc.
Brand differentiation and smoother operations
Customer loyalty & goodwill
Disincentives:
High compliance costs can lower profits
Forced to use materials that are specialised and may reduce profit
Ethics are not universal or unchanging anyway
Attitudes change over time; acceptable practices before are unacceptable today.
CSR objectives adapt to changes in social norms
SWOT analysis
Guides management for future strategies- useful decision making tool
assesses current situations
considers internal and external factors
Strengths – advantages that are basis for developing competitive advantage e.g. highly skilled employees, brand awareness
Weakness- negative factors e.g. low quality products, bad reputation
Opportunities- potential areas for expansion of the business and future profits e.g. political/economical policies, social statistics & trends
Threats- hindrances to the business e.g. economic environment, market condition competitors.
Ansoff matrix
Analytic tool to determine growth strategy by focusing on product/market combination
Growth strategies
Existing product + existing market = Market Penetration (low risk)
price adjustment
increase of market promotion
New product + existing market = Product Development (medium risk)
Innovation to replace existing products
Focusing on consumer needs
Brand extension
Capitalize on technology
Consumers in existing market may not like the new product
Existing product + new market = Market Development (medium risk)
New distribution channel
Expanding geographically
Attract new market segments
New consumers may not like the product
New product + new market = Diversification (high risk)
If successful, higher gains can be reaped from various industries
Spreads out risks and safeguards against economic shocks over diverse product portfolio

stakeholders
People who can be affected by and therefore have interest or stake in actions of the business
there are internal and external stakeholders
internal stakeholders
employees
shareholders
managers/directors
external stakeholders
customers
suppliers
pressure groups
competitors
Government
stakeholder conflict
inability of organisation to meet all stakeholders competing interests
STEEPLE
Business tool for understanding a business’ external environment (opportunities and threats)
Stands for Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, and Ethical analysis (of the industry)
External environmental factors are analysed in decision making and strategy development because they can heavily influence the business
Social
Attitude of society towards wide range of issues
Population demographics (more young/old, more women/men, etc.)
Roles and attitudes of people
Cultural and religious beliefs
Security and education
Technological
Use of tools and machines
Information technology
Innovations in technology
Economic
State of the economy
Interest and tax rates
Exchange rates and foreign relations
Inflation rates, unemployment rates
Environmental
Abundance of natural resources or raw materials
Threats from nature (or natural disasters)
Waste disposal/recycling
political
Laws (employment, consumer, business) & policies (fiscal and monetary)
Changes brought about by new government
Possible effects of political unrest
Legal
Employment or contract laws
Trade unions
Environmental protection regulations
Ethics
Client confidentiality
Bribery and other forms unethical (and possibly illegal) business transactions
Fair competition
How changes in STEEPLE factors affect a business’s objective and strategy
Changes in trends, social norms, public opinion, views on ethics can affect the company’s products, business activities, and the way they market their products
Changes to legal or political factors may force businesses to change the way they operate to comply with new laws or regulations
Changes to technological factors could result to the company adopting newer technology or machinery to increase efficiency or keep up with industry standards
Changes to environmental factors could force companies to adapt to scarce raw materials, frequent natural disasters, etc.
Changes to economic factors (economic growth, interest rates, etc.) could affect the costs of operations of the business, spending attitude of consumers, etc.
economies of scale
Increase in efficiency of production as the number of output increases
Average cost per unit decreases through increased production
Fixed costs decline and there is an increased number of output
internal economies of scale
achieved by the organisation itself
Purchasing economies
Wholesale discounts
Technical economies
Investing in technology to reduce costs
Financial economies
Easier for large companies to receive loans from banks
Marketing economies
More efficient to advertise a large number of products
Managerial economies
Larger firms are able to hire specialists who help improve efficiency
external economies of scale
External
Improved infrastructure (e.g. transportation)
Advances in the industrial efficiency due to better training, innovations in processes/machinery, etc.
Growth of other industries that support the organisation
internal (organic) growth
internal (organic) growth - the business grows through its own capabilities and resources
Methods used to achieve internal growth:
Change of pricing strategies
Increase advertising and promotions
Offer flexible financing schemes
Improve and innovate the product or service
Sell in different locations
Increase capital expenditure on production and technologies
Train and develop staff
advantages
control and coordination
inexpensive
corporate culture
less risky
disadvantages
diseconomies of scale
need to restructure
dilution of control and ownership
slower growth
external (inorganic) growth
The business grows through dealings with outside organisations
ways to grow:
horizontal integration - companies in the same industry
vertical integration- businesses in a different stage of production
lateral integration- firms with similar operations but not in direct competition
conglomerate- businesses are in different industries
advantages
faster
reduces competition
greater market share
sharing ideas
firm evolves- risk is spread across more markets
disadvantages
costly
M&A
merger- two or more firms agree to join together
acquisition(or takeover) - a company buys controlling interest in another company
could be hostile takeover when unwanted
Joint-venture
Two or more businesses split the costs, risks, rewards of a business project
two or more business becoming a new legal entity
advantages
spreading costs and risks
entry into foreign markets
relatively cheap
competitive advantage
exploitation of local knowledge
high success rates
disadvantages
rely on goodwill and resources of other organisations
culture clashes
strategic alliances
Like a joint venture, but NO new legal entity is created (only for a specific project or product)
Profit is split between the two companies
franchise
An original business, known as the franchisor, that developed the business concept and product, then sells to other businesses (franchisees) the right to offer the concept and sell the product
HR planning
Process of anticipating current and future demand for workers in both the short and long term
A workforce plan includes
Careful consideration of current abilities and what will be needed in the future (short-term or long-term)
Identifying gaps and considering ways of addressing them
Noting any training needs
Developing training, recruitment and other personnel policies
CLAMPS
why people tend to leave their jobs
Challenges
Location
Advancement
Money
Pride
Security (job security)
Internal/external factors that influence HR planning
Internal: organisation size, strategies, structure, finances, motivation, corporate culture
External: demographic change, change in labour mobility, immigration, flexi-time, gig economy
Gig economy*
Labour market in which workers are given short-term contracts, paid for each individual job (freelancers)
a market system in which temporary positions are common and organisations hire independent workers for short-term commitments
+ work and life balance, reduced costs for businesses
- lack of job security, limitations in career development, lack of social benefits
Centralisation and decentralisation
Centralisation: decision making is predominately made by a very small group of senior managers at the top of the organisational hierarchy
Decentralisation: decision making authority is delegated throughout
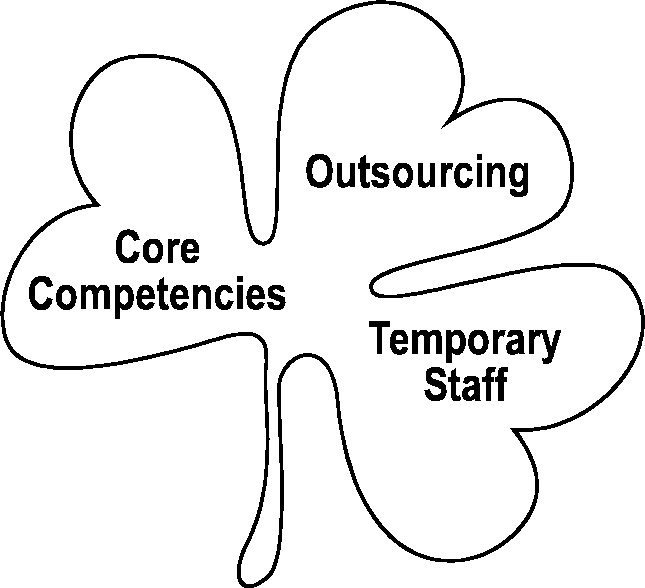
handy shamrock organisational structure
People – important resource
Have to be satisfied through job enrichment and flexible practices
3 main groups of staff
Core staff (full time)
Managers, technicians
E-commerce and teleworking have reduced core staff – implies downsizing
Peripheral workers (part time, contractual)
Employed only when required
Less job security and morale but offer more flexibility
Outsourced workers (subcontracting)
Paid to do specialised tasks e.g IT, accounting
Leadership style
The ways in which a manager and leaders provide direction for others
job security
The assurance given to employees that they will keep their current jobs for the foreseeable future
Sources of conflict in the workplace (& impacts)
Conflict occurs as a result of opposing goals between two or more parties
- can cause miscommunications, misunderstandings, stress, grievances, and power struggles
collective bargaining
The process of negotiation of working conditions and pay between employees and employers
internal sources of finance
personal funds- personal savings of owners and risk for owners
Retained profits- Value of profit kept by the business after paying off the tax, interest, and dividends (to the shareholders) to use within the business
Often used for purchasing and/or upgrading fixed assets which will increase returns
advantages- cheap, permanent source, flexible, controlled by owners
Disadvantages- start ups are rarely profitable at first, might be insufficient for expansion, might be used up
Sale of assests- Businesses can sell their unused assets, such as selling old machinery and computer equipments that have been replaced
advantages- no interest or borrowing costs
disadvantage- available to established businesses only
External sources of finance
share capital- money raised from selling shares in a company
Loan
Overdrafts
Grants
Debt factoring
Trade credit- payment made a later stage agreed upon between seller and buyer
Leasing- the lessee pays rental income to hire assets from the lessor, who is the legal owner of the assets.
venture capital- a form of high-risk capital, usually in the form of loans or shares, invested by venture capital firms, usually at the start of a business idea
overdrafts
When a lending institution allows a firm to withdraw more money than it currently has in its account
grants
Funds usually provided by a government, foundation, trust, or other agency to businesses which does not need to be repaid.
subsidies
Financial Assistance granted by a government, NGO, or an individual to support businesses that are in the public interest
loan
Money sourced from financial institutions such as banks, with interest charged on the loan to be repaid
short-term finance
Day to day running of business
one year or less
examples- overdrafts, trade crediting, debt factoring
medium- term finance
1-5 years
equipment, machinery, vehicles
examples - leasing, grants, loans
long-term finance
expansion of business
5-30 years
examples - loans, share capital
fixed cost
costs of production which have to be paid regardless of output level
Examples- rent, interests, lease payments
independent of output level
variable cost
cost of production which change in proportion to output level
Examples- raw materials, packaging
revenue stream
Revenue streams are the sources of revenues or incomes for a company or a business
Firms utilising different sources/methods to generate income
revenue streams examples
Advertising revenue: this is when an organisation is offering advertising space and charges other organisations for posting ads in this space
Royalties/franchisor: royalty payments are made to artists for the use of their artworks or to franchisors for the use of franchise
Sponsorship deals: the way it usually works is sponsor gives you financial support in exchange for an extra advertising space and publicity.
Subscriptions: use or access goods or services
Merchandise: in addition to the main trading activity, some organisations sell their souvenirs or clothes to get extra revenues
Dividends: companies that own stock/shares within another business can also get dividends
Donations: charities and non-profit
Interest earnings: on cash deposits in banks
Subversions: Government subsidies- aimed at benefiting society
wholesale market
a market where a trader buys goods from a manufacturer in bulk and re-sells the goods to business houses or retailers to further sell the goods to end consumers
Dividends
A sum of the money paid to shareholders which is decided by the board of directors
Balance Sheet
a statement of the financial position of a business in terms of assets, liabilities and owner's equity at a particular point in time
Assets
all items of value that are owned by the firm, such as cash or buildings
Profitability Ratios
show a company's overall efficiency, performance and financial position
liquidity ratio
ability of firm to pay its short-term liabilities
For BON issues may occur because of the absence of sales revenue between the months April - September
current ratio
looks at whether a company can pay/cover its short-term debts
current assets/current liabilities
short-term liquidity problems
occur due to-
poor credit control
expanding too quickly
hence cashflow management is key
cash flow
Financial document that shows expected movement of cash inside and outside of a business per time period
Cash inflows – usually from sales revenues when cash payment is received
Cash outflows – payment of bills, usually itemised expenses
Net cash flow – the differences between cash inflow and outflow
reasons for cashflow
business planning
is the business financially healthy
plan for and alleviate liquidity crisis
causes of cashflow problems
overtrading
over borrowing
overstocking
poor credit control
unforeseen changes
strategies to deal with cash flow problems
reducing cash outflows
improving cash inflows
seeking alternative sources of finance
marketing goods and service
Promotion- to build brand recognition, awareness and trust
use physical environment
make it easy to visualise service quality
branding, logos, celebrity endorsement, slogans
Product strategy - a tangible good or intangible services that satisfies the needs and wants of a customer (attracts more customers)
Price strategy- The amount paid for a particular good or service that should entice customer yet allow the firm to be profitable
source of value to customer- used to price product
Place strategy- Distribution channels that enable customers to conveniently buy the product
online
customers would not go to inconvenient and remote location

marketing goods vs service
Goods: Use of the 4Ps (place, price, product, promotion)
- Services: Use of the 7Ps (place, price, product, promotion, process, people, physical evidence)
Market research
Market research is essential in helping businesses to identify products/services they can develop in response to the needs and wants that their customers have
Market research is the process of systematically gathering data from consumers which can be used to influence the business decisions
marketing plan
The process of formulating the marketing strategies and tactics that will help a business to achieve its marketing objectives
Three tools of marketing planning include
Market segmentation
Market mapping
Market positioning
marketing audit- review of current position of an organisation’s marketing- once completed marketing plan is prepared
Marketing objectives
These are specific SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time bound)
Research
Marketing research identifies the factors expected to impact upon the marketing plan such as
Market size and growth
Market segments
Competitor positioning- SWOT
Customer tastes, preferences and views
The nature of distribution channels
The marketing mix
This involves planning the medium- and short-term marketing activities the business intends to undertake
Pricing strategies and tactics
Promotional activity
Distribution and logistical plans
Product specifications, features and packaging
Physical evidence such as branding
How people and process are developed to support delivery of the rest of the marketing mix

advantage and disadvantages of market planning
advantages-
improves chances of success
clearer idea of objectives
disadvantages-
no time
inflexible
Quickly outdated
Marketing objectives
Targets the marketing departments aims to achieve
These are specific SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time bound)
Ansoff matrix
Market development-
selling existing products in new markets
e-commerce- selling over the internet
internationally
Product development-
new products in existing markets
Diversification-
new products in new markets
high risk
stable businesses looking for growth
Product innovation-
original or new product launch
first mover advantage
Unique selling point
A unique selling point (USP) is a distinguishing factor or characteristic of a product, service or brand that sets it apart from its competitors
The USP helps a business to differentiate itself and give customers a reason to choose one product or service over others because it offers something distinct and valuable
There are a range of reasons why businesses develop a USP which can include
Developing a brand identity
Achieving a competitive advantage over rivals
Effective communication with customers
The attraction and retention of customers
Achieving power over pricing
Encouraging innovation and adaption
Differentiation
Product differentiation is an attempt by a business to distinguish its products from those of competitors
reasons for differentiation
Strong product differentiation helps the firm to develop its competitive advantage
The development of product differentiation often helps a firm to create a unique selling point for its product which can be used in marketing
Common methods used by businesses to differentiate products include
Marketing and branding activities
Eye-catching packaging
Attractive functions and features
Product customisation
Excellent customer service
Commercial marketing
marking strategies that focus on meeting the demands of customers in a profitable way
the main purpose is to generate benefits for the owners of the business
Four P's of marketing mix
Marketing mix: Key elements of a marketing strategy that ensure the successful marketing of a product
Product: a tangible good or intangible services that satisfies the needs and wants of a customer
Price: The amount paid for a particular good or service that should entice customer yet allow the firm to be profitable
Promotion: communicating relevant products information to inform and persuade customers to buy the good or service
Place: distribution channels that enable the customers to conveniently buy the product
Market segment
A distinct group of customers with similar characteristics, tastes, preference
Targeting
Targeting is the marketing practice of creating and using an appropriate marketing mix and marketing strategies to cater for different marketing segments
Target market
The group of customers that an organisation focuses on selling its product to
Niche market
marketing approach that focuses on supplying highly specialised products to cater to a small and select target market
Mass market
industries that buy and sell mass market products, catering for a broad range of target markets
people
the employees who deliver the customer service element of the extended marketing mix
physical evidence
the observable and tangible aspects of a service
psychographic segmentation
segmentation that involves characterising consumers according to people’s lifestyle choices and personal values
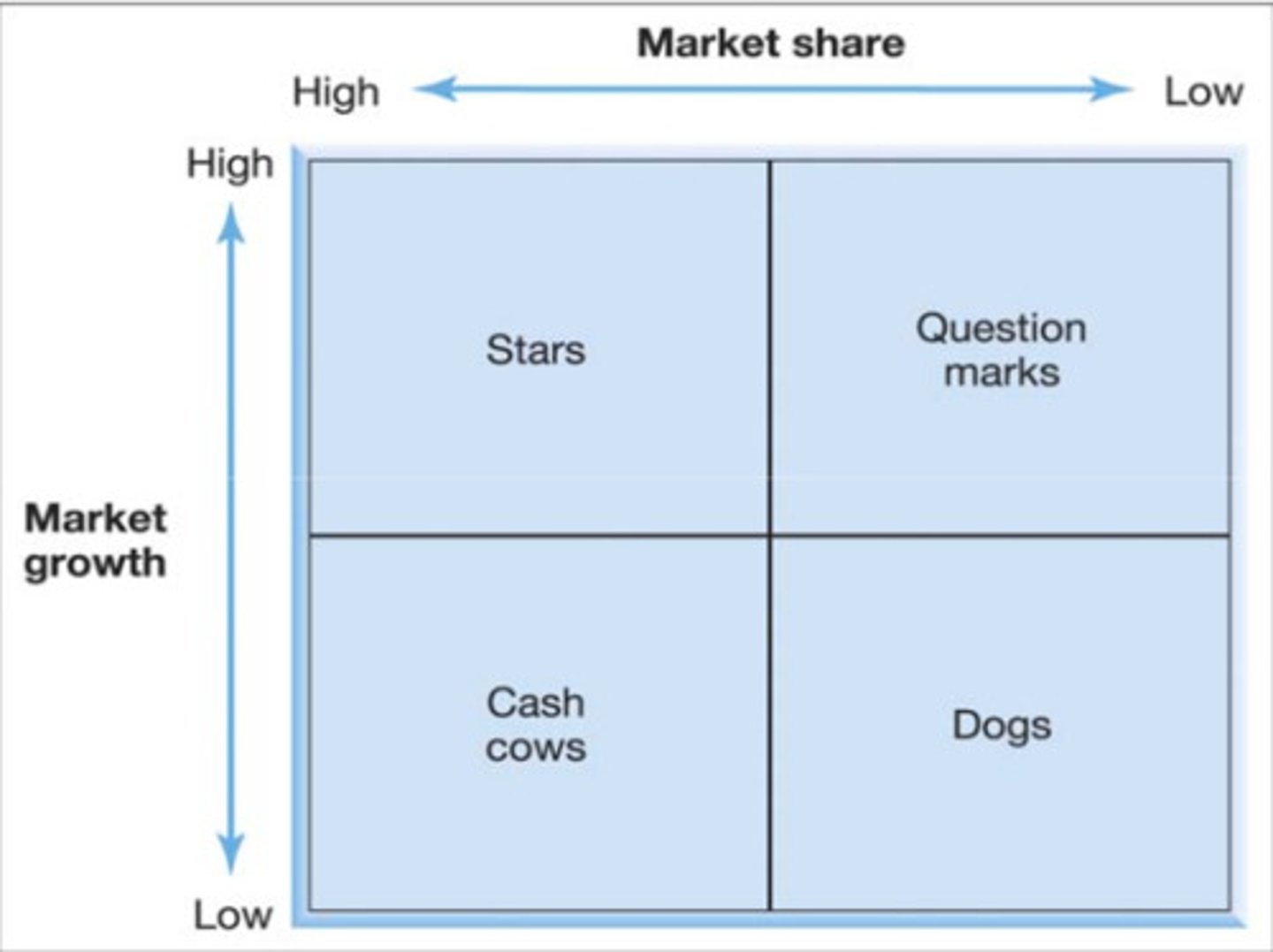
BCG matrix
Visual marketing management tool used to analyse a firm’s product portfolio
Stars: High market growth and high market share
Cash cows: Low market growth and high market share
Question mark: High market growth and low market share
Dogs: Low market share and low market growth
Cost plus pricing
Adding a percentage or predetermined amount (markup) to average cost per unit to set the selling price
Ensures a product will produce contribution