Carbohydrates
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Information through Carbohydrates note. I am not responsible for any misinformation. Best used if you click: Learn -> options -> turn on: "written only", "answer with term", and "shuffle terms"
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
ose
what is the suffix usually at the end of a sugar
Monosaccharides
Single units of sugars are known as?
OH
what are the hydrocarbon chains of sugars usually studded with?
carbonyl
what functional group is always found in a sugar? (hint: not hydroxyl)
121
(just type number no space)
What is the ratio of C:H:O in sugars?
S
Quick note (press s to skip):
Functions:
Fuel for cell respiration
Energy storage
Structural Components
Cell surface markers
Glucose
Molecular formula: C6 H12 O6
What is this also known as?
Isomers
______________ are molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structures
Glucose
What is the main carbohydrate used in cell respiration
rings
what shape are sugars almost always found in?
Alpha
Is this the alpha or beta glucose molecule?
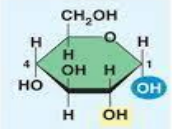
Beta
Is this the alpha or beta glucose molecule?
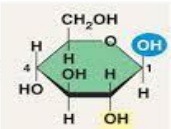
Disaccharides
the name when 2 monosaccharides combine
Glycosidic Linkage
The oxygen bridge between two monosaccharides is called?
Dehydration Synthesis
2 monosaccharides joining to create a disaccharide requires the process known as?
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose = ?
Lactose
Galactose + Glucose = ?
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose = ?
Alpha
what type of glucose polymer (alpha or beta) focuses on energy storage
Beta
what type of glucose polymer (alpha or beta) focuses on structure
Beta
What glucose polymer makes lots of H-bonds?
Glycogen
Type of alpha polymer that is stored in the body and used when the body needs a quick boost of energy, or if the body is in need of food.
Starch
Type of alpha polymer that is usually found in plants and is used for energy storage.
away
On an alpha-glucose molecule, does the -OH group point at you or away from you? (at or away)
at
On a beta-glucose molecule, does the -OH group point at you or away from you? (at or away)
Polysaccharides
starch is an example of? (what kind of saccharide)
release
Polysaccharides cost little energy to build and they are easily reversible, which means they can ________ energy.
faster
the more branches a molecule is, the (faster/slower) it will release glucose units for use in cell respiration
Cellulose
Indigestible substance that plants have
Beta
is cellulose a(n) alpha or beta polymer?
H-bonds
what is the key feature that Cellulose and Chitin have?
Chitin
A sugar found in the cells walls of fungi and shells of arthropods
NH2
for Chitin, what functional group replaces an -OH
Hydrolysis
The reaction that breaks disaccharides into two monosaccharides is called?
Right
Which glucose is the most common? (left or right)