[MICRO20] LEC 14: Emerging and Re-emerging Infections (Flashcards)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
LEC 14 - Emerging and Re-Emerging Infections
LEC 14 - Emerging and Re-Emerging Infections
2
New cards
Re-emerging Infectious Disease
Disease that was previously controlled but has risen again to be a significant health problem.
3
New cards
mortality, morbidity
TB is the 8th leading Cause of ___ and 10th Leading Cause of ___ in the Philippines.
4
New cards
Primary Complex
If the child’s immune system is not so strong, ___ can lead to massive hematogenous dissemination, leading to Miliary TB.
5
New cards
culture
The gold standard for laboratory confirmation of TB disease
6
New cards
testing
Part of the National Tuberculosis Program of DOH that is done to identify bacteriologically confirmed or clinically diagnosed TB cases; use of rapid TB molecular test as the primary diagnostic tool – GeneXpert/TB LAMP/TrueNAT
7
New cards
Emerging Infectious Diseases (Ereid)
Has emerged and incidence in humans increased in the last 2 decades and is continuously threatening to increase in the near future.
8
New cards
FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO THE EMERGENCE OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Human demographics and behavior - transfer of people from one place to another
Technology and industry
Economic development and land use
International travel and commerce
Microbial adaptation and change
Breakdown of public health measures
Human susceptibility to infection
Climate and weather
Changing ecosystems
Poverty and social inequality
War and famine
Lack of political will
Intent to harm - bioterrorism
Technology and industry
Economic development and land use
International travel and commerce
Microbial adaptation and change
Breakdown of public health measures
Human susceptibility to infection
Climate and weather
Changing ecosystems
Poverty and social inequality
War and famine
Lack of political will
Intent to harm - bioterrorism
9
New cards
Wrong prescribing practices leads to ___
development of resistance to drugs
10
New cards
Deforestation
forces animals into close human contact - increased possibility for agents breach species barrier between animals and humans
11
New cards
Zoonoses
1,415 microbes are infectious for human
Of these, 868 (61%) considered zoonotic
70% of newly recognized pathogens are zoonoses
Emerging influenza infections in human associated with chickens, pigs
Of these, 868 (61%) considered zoonotic
70% of newly recognized pathogens are zoonoses
Emerging influenza infections in human associated with chickens, pigs
12
New cards
Hepatitis B
Identified several decades earlier
Upward trend in all countries
Prevalence >90% in high-risk population
Upward trend in all countries
Prevalence >90% in high-risk population
13
New cards
Hepatitis C
First identified in 1989
In mid 1990s estimated global prevalence 3%
In mid 1990s estimated global prevalence 3%
14
New cards
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Obligate aerobe (needs oxygen to thrive)
Slow-growing (takes up to 8 weeks to grow in culture)
Nonmotile acid-fast bacilli
Slow-growing (takes up to 8 weeks to grow in culture)
Nonmotile acid-fast bacilli
15
New cards
RISK OF TB TRANSMISSION
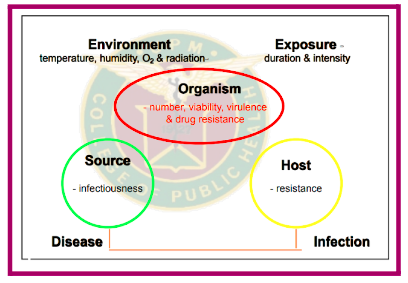
16
New cards
TB TRANSMISSION
Via airborne
Active TB patients can infect 10-15 people annually if they do not practice proper precautions (e.g. cough etiquette)
Active TB patients can infect 10-15 people annually if they do not practice proper precautions (e.g. cough etiquette)
17
New cards
Systemic TB
Fever
Night sweats
Easy fatigability
Anorexia and weight loss
Night sweats
Easy fatigability
Anorexia and weight loss
18
New cards
Pulmonary TB
Cough (>2 weeks) (most common symptom)
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Dyspnea
19
New cards
LIMITATIONS OF CULTURE:
Long turnaround time - 8 weeks/2 mos. to say if there is growth or none
Access - not all labs have access to culture
Cost - quite expensive
Access - not all labs have access to culture
Cost - quite expensive
20
New cards
Drug susceptibility test
This is important because RIF resistance will give an initial clue that this might be a drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
21
New cards
Specimens that can be submitted for GeneXpert:
Fresh sputum
Sputum sediment
bronchial washings (more invasive)
Any Extra-pulmonary tuberculosis specimens (EPTB) e.g. lymph node aspirate, urine, CSF
Sputum sediment
bronchial washings (more invasive)
Any Extra-pulmonary tuberculosis specimens (EPTB) e.g. lymph node aspirate, urine, CSF
22
New cards
Multidrug-Resistant TB (MDR TB)
Resistance to at least INH (Isoniazid) and rifampicin, the most potent anti-TB drugs
23
New cards
Different acid fast bacilli staining:
Ziehl-Neelsen - traditional; requires a heating step
Kinyoun stain - “cold” acid-fast stain (missed out the heating step)
Kinyoun stain - “cold” acid-fast stain (missed out the heating step)
24
New cards
SIGNIFICANT RISK FACTORS OF TB
Age
Urban dwelling
Previous TB treatment
Self-reported Diabetes Mellitus
Lower socioeconomic status
No health insurance
Sex and smoking
Urban dwelling
Previous TB treatment
Self-reported Diabetes Mellitus
Lower socioeconomic status
No health insurance
Sex and smoking
25
New cards
FALSE
Correct statement: Reverse TRANSCRIPTION Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) is the golden standard diagnostic test for SARS-CoV2.
Correct statement: Reverse TRANSCRIPTION Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) is the golden standard diagnostic test for SARS-CoV2.
TRUE or FALSE
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) is the golden standard diagnostic test for SARS-CoV2.
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) is the golden standard diagnostic test for SARS-CoV2.
26
New cards
FALSE
Correct statement: RT-PCR does not distinguish between infectious virus and viral genetic material remnants that is why it is NOT a good test for recovery.
Correct statement: RT-PCR does not distinguish between infectious virus and viral genetic material remnants that is why it is NOT a good test for recovery.
TRUE or FALSE
RT-PCR does not distinguish between infectious virus and viral genetic material remnants that is why it is a good test for recovery.
RT-PCR does not distinguish between infectious virus and viral genetic material remnants that is why it is a good test for recovery.
27
New cards
2
Whenever RT-PCR is performed for SARS-COV2, a Biosafety Level ___ facility is required, and biosafety precautions must be observed.
28
New cards
Antibody Test
An indirect type of test because it tests the presence of Tests IgM, IgG or both.
29
New cards
FALSE
Correct statement: Best to test after at least 7 days of symptoms or exposure because during the first 7 days the disease, the body will not yet produced antibodies
Correct statement: Best to test after at least 7 days of symptoms or exposure because during the first 7 days the disease, the body will not yet produced antibodies
TRUE or FALSE
Best to test after at least 5 days of symptoms or exposure because during the first 5 days the disease, the body will not yet produced antibodies
Best to test after at least 5 days of symptoms or exposure because during the first 5 days the disease, the body will not yet produced antibodies
30
New cards
Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test (PRNT)
Gold standard for the antibody test
31
New cards
Rapid Test
More commonly utilized antibody test and provides point-of-care testing (gives immediate results). It is also cheap.
32
New cards
FALSE
Correct statement: Once an antibody test is validated, it can be used to assess recovery. For example, if it will show "IgG positive", then it will tell you that you had past COVID infection.
Correct statement: Once an antibody test is validated, it can be used to assess recovery. For example, if it will show "IgG positive", then it will tell you that you had past COVID infection.
TRUE or FALSE
Once an antibody test is validated, it can be used to assess recovery. For example, if it will show "IgA positive", then it will tell you that you had past COVID infection.
Once an antibody test is validated, it can be used to assess recovery. For example, if it will show "IgA positive", then it will tell you that you had past COVID infection.
33
New cards
RT-PCR
Which diagnostic test is used for suspected COVID-19 with symptoms and for highly exposed (HCWs) asymptomatic patients?
34
New cards
January 13, 2021
Date when Philippines was able to identify the first variant – SARS-COV2 UK Variant.
35
New cards
Spikes
SARS-CoV-2 has ______ that the virus uses to attach to human cells.
36
New cards
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE
Changes in the spike protein can result in changes in virus transmissibility or disease severity
Changes in the spike protein can result in changes in virus transmissibility or disease severity
37
New cards
FALSE
RNA viruses have a higher mutation rate than DNA viruses
RNA viruses have a higher mutation rate than DNA viruses
TRUE or FALSE
DNA viruses have a higher mutation rate than RNA viruses
DNA viruses have a higher mutation rate than RNA viruses
38
New cards
Strain
It is a variant with demonstrably different phenotype, such as difference in antigenicity, transmissibility, or virulence.
39
New cards
The WHO Virus Evolution Working Group (VEWG)
They monitor changes to SARS-CoV-2 to detect potential VOC and VOI that pose an increased risk to global public health
40
New cards
Greek
WHO recommends labels using letters of the ______ alphabet, such as Alpha, Beta, Gamma to label the variants of COVID-19.
41
New cards
Delta
Transmission of the _____ variant is higher than other variants of SARS-CoV-2
42
New cards
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE
Existing vaccines will still work against new variants of the virus since mutations alter only a minor piece of a large protein of the virus.
Existing vaccines will still work against new variants of the virus since mutations alter only a minor piece of a large protein of the virus.
43
New cards
July 16, 2021
Date when the first local case of the Delta Variant was reported in the Philippines.
44
New cards
Ebola
Ebola was first discovered in 1976 near the ______ River.
45
New cards
Monkey
In what animal was Zika first discovered in the Zika Forest of Uganda in 1947?
46
New cards
Brazil
Which country is by far the most affected country of the Zika virus, reporting the most cases of people infected with the virus.
47
New cards
Candida auris
It is a novel ascomycetous yeast isolated from the external ear canal of an inpatient in a Japanese hospital. It causes invasive infections, predominantly fungemia, or fungi in the blood.
48
New cards
93% resistant to fluconazole (antifungal for Candida)
54% resistant to voriconazole (antifungal)
35% resistant to amphotericin B (antifungal)
7% resistant to echinocandins (antifungal)
4% resistant to azoles, amphotericin B, AND echinocandins
54% resistant to voriconazole (antifungal)
35% resistant to amphotericin B (antifungal)
7% resistant to echinocandins (antifungal)
4% resistant to azoles, amphotericin B, AND echinocandins
What are the drug resistance rates of Candida auris
49
New cards
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE
Candida auris have higher prevalence than other Candida species
Candida auris have higher prevalence than other Candida species
50
New cards
FALSE
Correct statement: It forms white to cream colonies with a smooth edge on the Sabouraud-dextrose agar and pink colonies on CHROMagar Candida medium
Correct statement: It forms white to cream colonies with a smooth edge on the Sabouraud-dextrose agar and pink colonies on CHROMagar Candida medium
TRUE or FALSE
It forms white to beige colonies with a smooth edge on the Sabouraud-dextrose agar and pink colonies on CHROMagar Candida medium
It forms white to beige colonies with a smooth edge on the Sabouraud-dextrose agar and pink colonies on CHROMagar Candida medium