Science Exam Revision
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Space science - Physics - (No chemistry ye) (add if needed please)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Star
a fixed luminous point in the night sky which is a large, remote incandescent body like the sun.
Planet
a celestial body moving in an elliptical orbit around a star.
Solar system
the gravitationally bound system of the sun and the objects that orbit it.
Galaxy
a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction.
Universe
space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy.
Apparent magnitude
the brightness of the light as observed from the earth
Absolute magnitude
the brightness of the light from a set distance (10 parsecs)
Light years
it tells us the distance that light would travel in a year. 1 light year is 9.5 trillion km.
Parsecs (pc)
it is equivalent to 3.26 light years.
Supernova
it is an explosion of a Super Giant
How can Nuclear fusion emit light
at the core, 2 hydrogen atoms fuse together to create helium. This produces energy which comes off in the form of heat and light.
Red shift
when an object more red as the object is moving further away. This is because of the doppler effect.
Blue shift
when an object is more blue it is moving closer to us. This is because of the doppler effect.
Scalors
only has a magnitude
Vectors
has a magnitude and a direction
Examples of scalors
mass
speed
distance
Examples of vectors
time
displacement
force
velocity
weight
acceleration (gravity)
Converting Astronomical units to Kilometres
1 AU ——> 150 million km
Describe how Aboriginal Australians used stars
they use the stars to know the different seasons so they know when to go hunting and for dreamtime stories.
Describe the Big Bang Theory and any evidence supporting this theory
is a theory that states the universe is created at a certain point. At that point it expanded and stretched to how big it is now.
EVIDENCE:
Edwin Hubble noticed that some galaxies where moving away and moving towards us. Over time some stars started to admit red or blue light.
The doppler effect is the apparent change in frequency when a moving object gets closer to an observer. This can be explained by the Doppler Effect, if the star moves away, the light will decrease therefore red light appears. This shows that the universe is slowly expanding and that nothing is taking the place between Earth and Sirius.
Cosmic Background Radiation: the dish in Parkes NSW was experiencing small disturbances. They thought it was pigeon poop, but they found an afterglow of the Big Bang Theory.
factor that affects a star’s colour
temperature
factors that affect a star’s brightness
temperature and distance
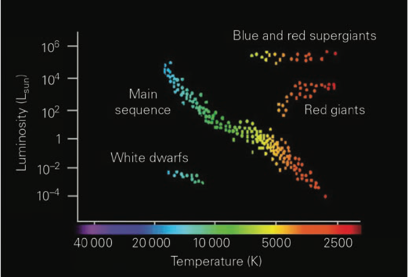
Interpret a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
the Hertzsprung-Russell is a plot of star brightness (measured as luminosity) against star temperature/colour.
remember the luminosity scale gives us an idea of how bright a star is compared to our sun
Newtons 3 laws
Inertia
F=ma
Action reaction
Inertia
an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
F=ma
for a constant force, mass and acceleration inversely proportional (one up, one down)
for a constant mass, force is proportional to the acceleration (both up)
Action reaction
whenever a body exerts a force on another body, the second body exerts a force equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.