CDC Enterobiasis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
self-inoculation
Gravid adult female Enterobius vermicularis deposit eggs on perianal folds (1) Infection occurs via _______(transferring eggs to the mouth with hands that have scratched the perianal area) or through exposure to eggs in the environment (e.g. contaminated surfaces, clothes, bed linens, etc.)
infective eggs
(2) Following ingestion of _______, the larvae hatch in the small intestine establish themselves in the colon, usually in the cecum
cecum
Following ingestion of infective eggs the larvae hatch in the small intestine establish themselves in the colon, usually in the ________.
1 month
(4) The time interval from ingestion of infective eggs to oviposition by the adult females is about ______ . At full maturity adult females measure 8 to 13 mm, and adult males 2 to 5 mm
2 months
the adult life span is about _______. Gravid females migrate nocturnally outside the anus and oviposit while crawling on the skin of the perianal area.
4 to 6 hours
(5) The larvae contained inside the eggs develop (the eggs become infective) in _____ under optimal conditions
asymptomatic
Enterobiasis is frequently _______.
perianal pruritus (Anal itching)
The most typical symptom is ______, especially at night, which may lead to excoriations and bacterial superinfection.
vulvovaginitis
Occasionally, invasion of the female genital tract with ____________ and pelvic or peritoneal granulomas can occur.
airborne and be inhaled
Rarely nterobius vermicularis, eggs may become ________ and swallowed. Retroinfection, or the migration of newly hatched larvae from the anal skin back into the rectum, may occur but the frequency with which this happens is unknown.
teeth grinding, enuresia, insomnia, anorexia, irritability
Other symptoms include,_________, and abdominal pain, which can mimic appendicitis.
appendix on appendectomy
E. vermicularis larvae are often found within the __________, but the role of this nematode in appendicitis remains controversial.
Very rare instances of eosinophilic colitis associated with E. vermicularis larvae have been reported.
perianal area
Microscopic identification of eggs collected in the ______ is the method of choice for diagnosing enterobiasis.
done in the morning, Scotch test
To improve sensitivity, collection should be_________, before defecation and washing, by pressing transparent cellulose tape (“_______”, cellulose tape slide test) on the perianal skin and then examining the tape placed on a microscope slide.
urine or vaginal smears
Alternatively, anal swabs or “Swube tubes” (a paddle coated with adhesive material) can also be used for collection. Eggs can also be found, but less frequently, in the stool, and occasionally are encountered in the _________.
anorectal or vaginal examinations
Adult worms are also diagnostic, when found in the perianal area, or during ______.
cervicovaginal Papanicolaou (Pap Test)
In cases of ectopic infection, eggs may be seen in the urine or in ______ smears.
collects cells from the cervix and vagina
Cervicovaginal Papanicolaou (Pap) test is a routine screening that ____________________to check for abnormal changes, often caused by Human Papillomavirus (HPV), that could lead to cervical cancer
Eggs on perianal folds
(1) Diagnostic Stage
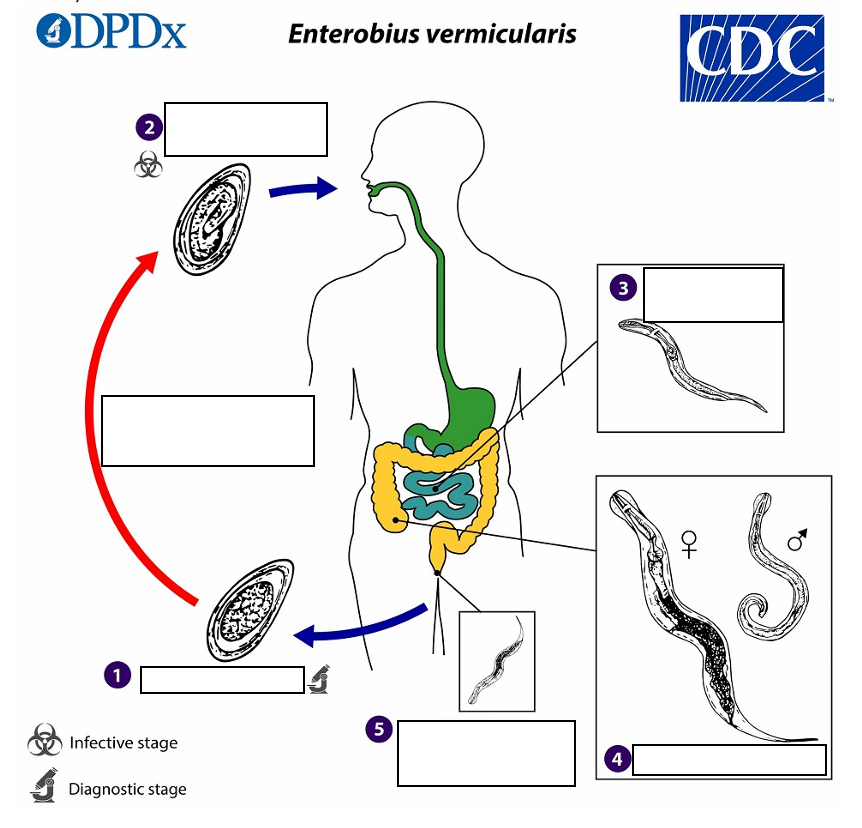
Embryonated eggs ingested by human
(2) Infective Stage
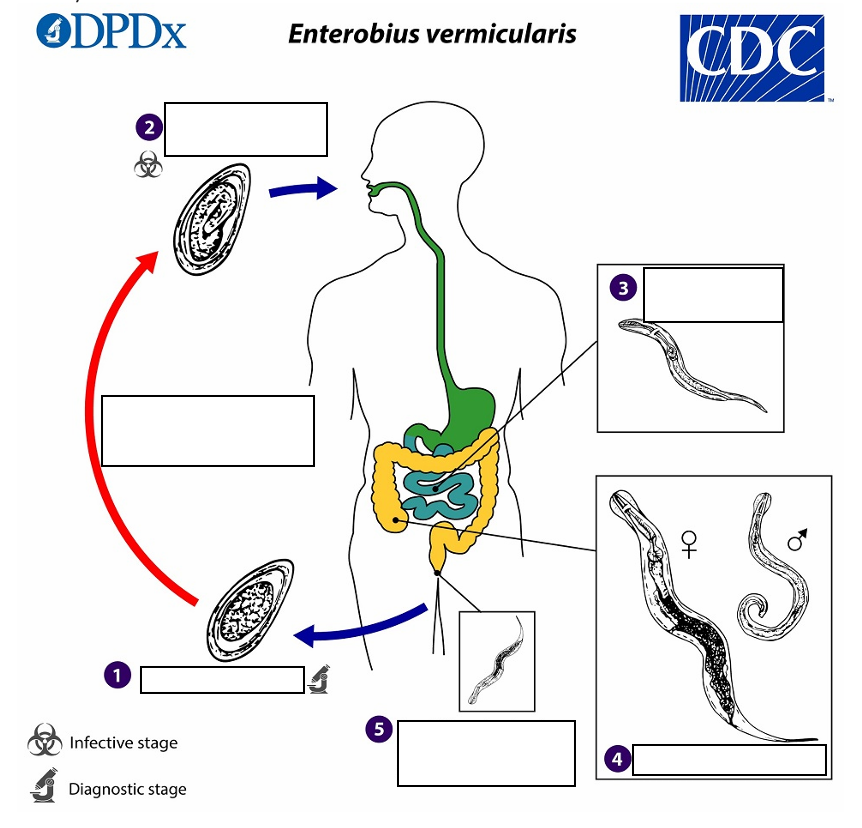
Larvae hatch in small intestine
(3)
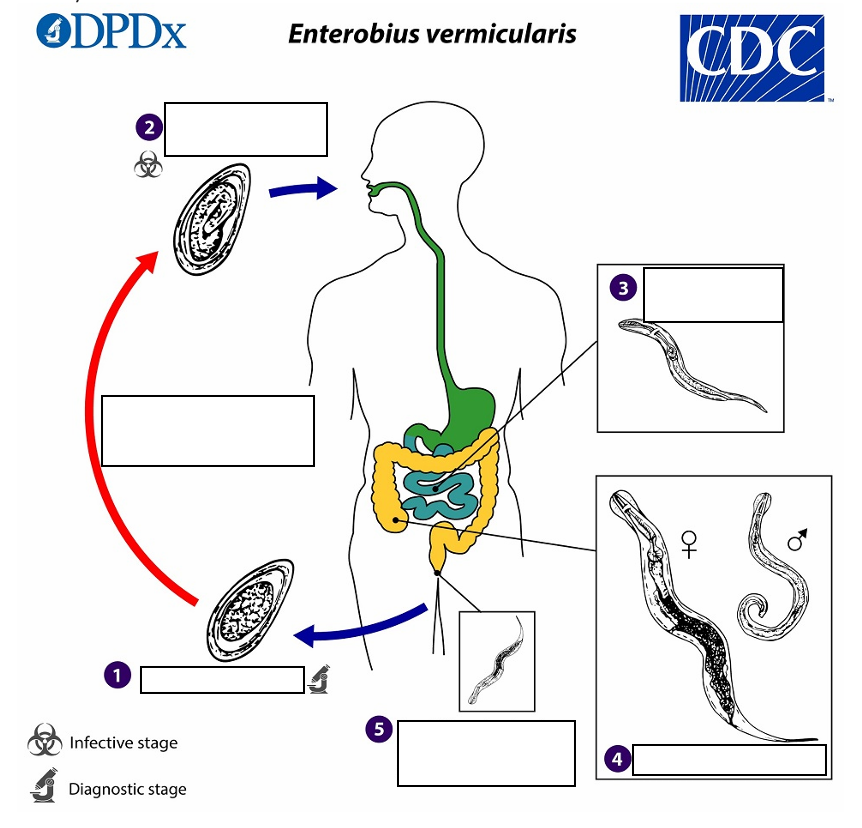
Adults in lumen of cecum
(4)
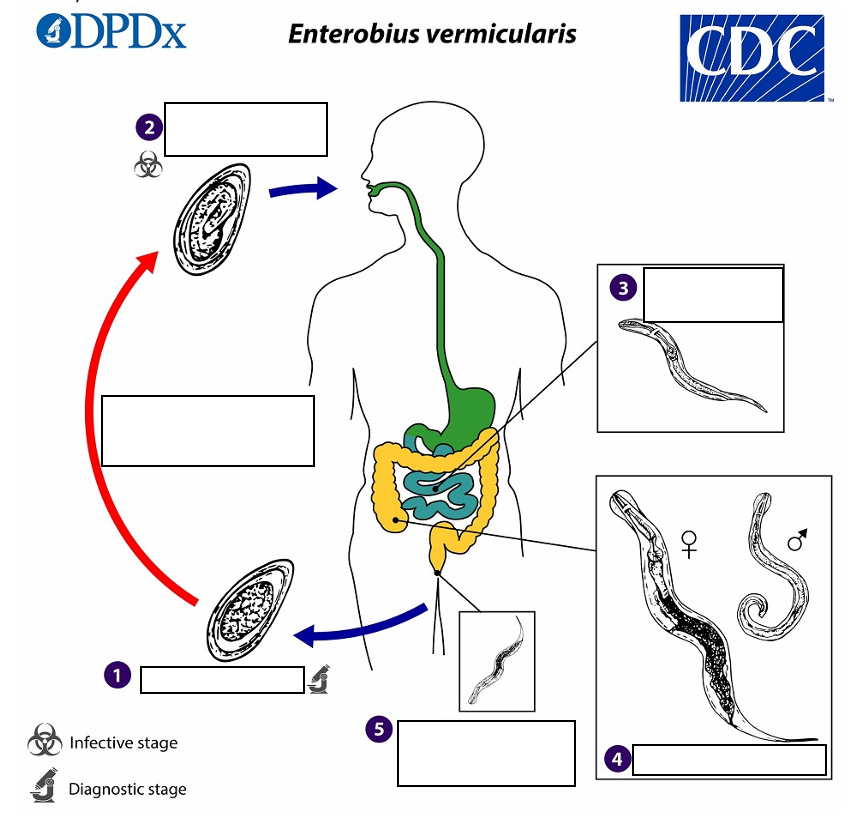
Gravid female migrates to perianal region at night to lay eggs.
(5)
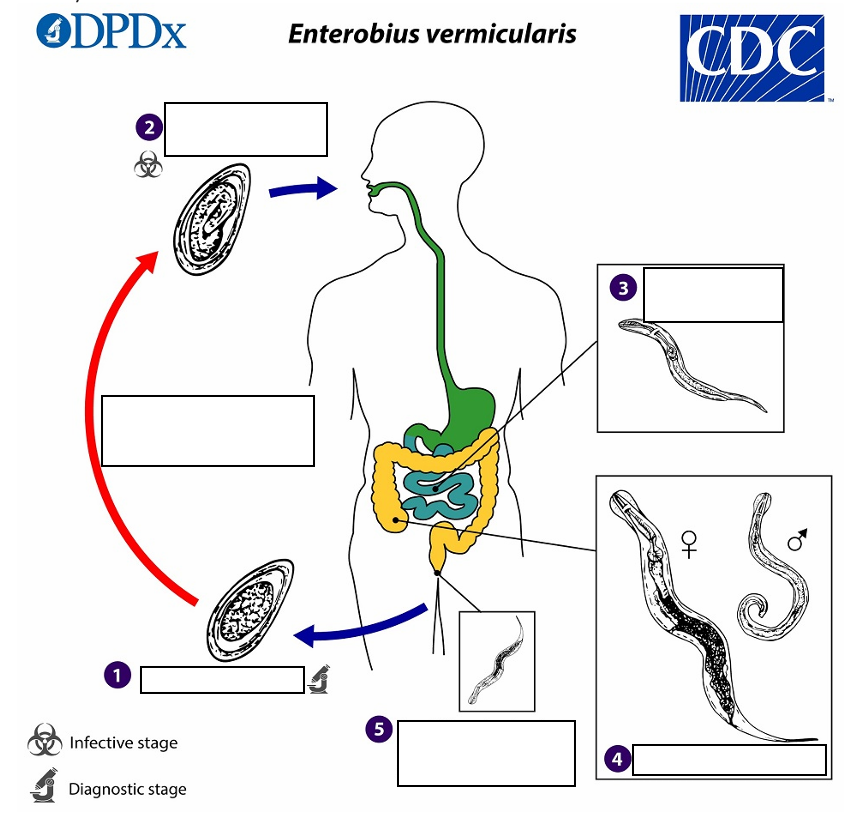
pinworm
Enterobiasis also called
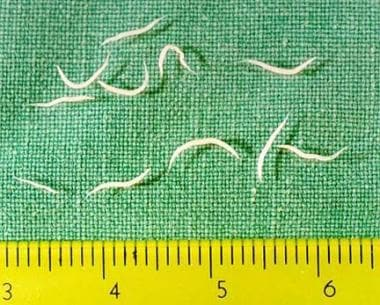
nematode (roundworm)
The _________ Enterobius vermicularis is widely known as the human pinworm due to the female’s long, pointed tail.