Chapter 18- rates of reaction
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
how do you calculate the rate of reaction
rate= quantity reacted or porduced/time
what is the unit for rate
moldm-3S-1
what is a zeroth order reaction
when the concentration of a reactant has no effect on the rate
what is a first order reaction
when the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant.
what is a second order reaction
when the rate is proportional to the square of the concentration of the reactant.
why is the rate equation important
gives a mathematical relationship between the concentrations of reactants and the reaction rate
what is the rate equation
rate =k[A]m[B]n
what is k in the rate equation
the proportionality constant
how do you calculate the overall order of a reaction
sum of orders with respect to each reactant
for unit calculations, if more units on bottom
the signs flip to dm3mol-1s-1
what is an order in rates of reaction
the exponent to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate equation, indicating its influence on the reaction rate.
what is an example of a continuous monitoring graph
concentration-time graphs
how do colorimeters work
the wavelength of light passing through a coloured solution is controlled using a filter
the amount of light absorbed by a solution is measured
what does a zeroth order concentration-time graph look like
a straight line with a negative gradient
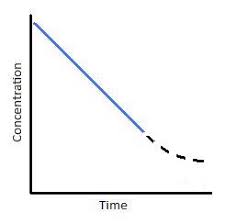
what does a first order concentration-time graph look like
a downward curve with a decreasing gradient over time
how can rate constant be found from a FIRST ORDER graph
using the constant half lives
what does a second order concentration-time graph look like
a steeper version of a first order graph
what is the equation linking rate constant and half life
k=ln(2)/ half life
what is half life
the time taken for half of a reactant to be used up
what is the half life of a first order reaction
constant due to exponential decay
what does a rate-concentration graph show
the measurements of rate of reaction at different concentrations
what does a zeroth order rate-concentration graph look like
a horizontal straight line with no gradient

what does a first order rate-concentration graph look like
a straight line with a positive gradient through the origin
what does a second order rate-concentration graph look like
an upward curve with an increasing gradient
how to calculate rate of reaction from a first order rate-concentration grpah
tangent + gradient
what is the initial rate
the instantaneous rate at the start of a reaction when t=0
what is the best way of finding an initial reaction
a clock reaction
how does the iodine clock work
aqueous iodide ions are orange-brown , the time for the start of the reaction and appearance of iodine colour is measured
how can you increase colour change in the iodine clock
add starch as this forms a complex with iodine which is blue-black
is the iodine clock accurate
no its an approximationdue to potential variability in reaction conditions and measurement errors.
why may a reaction need a 2 step mechanism
the simultaneous collision of two specific particles is extremely unlikely
the rate equation may not match the stoichiometry of the balance equation
what is the rate determining step
the slowest step in a reaction mechanism that determines the overall rate
how can i rate equation be produced from the RDS
the rate equation only contains species in the RDS
the orders in the rate equation match the number of species in the RDS
how to calculate the two step mechanism
add both reactants —> make one product in the balanced eq + anthing left
anything left + reactants not used yet ——> products in the balanced
what factors affect the rate constant
increasing temperature increases proportion of particles that exceed the Ea
increasing temperature means particles move faster and collide more frequently
what does e-Ea/RT represent in Arhenius
the proportion of molecules that exceed Ea and have sufficient energy for reaction
what does the pre-exponential term take into account in Arhenius
the frequency of collisions with the correct orientation
how to find Ea in Arhenius
gas constant x gradient
in Arhenius unit for Ea
KJmol-1
how to find the Ea with LnK and 1/T
choose two points
(change in LnK)/ (change in 1/.T)
then x gas constant
divide by 10000