Unit 2: Executive Branch and Bureaucracy - AP Government - GENERAL VOCAB, Unit 2: Executive Branch and Bureaucracy - AP Government - WEEK 3, Unit 2: Executive Branch and Bureaucracy - AP Government - WEEK 2, Unit 2: Executive Branch and Bureaucracy -…
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
presidential selection
electoral college
presidential term
4 years, max of 2 terms

22nd amendment
Limits the president to two terms.

presidential qualifications
- natural born US citizen
- at least 35 years old
- live in the US for 14 years prior to running

How many cabinet departments currently are there?
15

Chief Executive
The role of the president as head of the executive branch of the government.

Chief Diplomat
The role of the president in recognizing foreign governments, making treaties, and effecting executive agreements.

Chief Legislator
term for the president as architect of public policy and the one who sets the agenda for congress

Commander in Chief
term for the president as commander of the nation's armed forces

Impeachment in Congress
HoR: articles of impeachment
Senate: holds trial and convicts to remove

US v. Nixon (1974)
Allowed for executive privilege, but not in criminal cases; "Even the President is not above the law;" Watergate.

12th Amendment
Brought about by the Jefferson/Burr tie, stated that presidential and vice-presidential nominees would run on the same party ticket. Before that time, all of the candidates ran against each other, with the winner becoming president and second-place becoming vice-president.

VP in the Constitution
- President of Senate
- Breaks tie in the Senate

25th Amendment
Presidential succession

Chief of party
term for the president as the leader of his or her political party

approval rating
a measure of public support for a political figure or institution
What is the trajectory of bureaucracy and why?
GROWING due to increases in population, boundaries, and demands
responses to crises has also increased in size and scope
Constitutional Basis of the Bureaucracy
Article 2 (president must "execute" the laws -- leads to the creation of the bureaucracy)
First Administration Cabinet Departments
State (Jefferson)
War (Knox)
Treasury (Hamilton)
Attorney General

Federal Bureaucrats Levels
1. Executive Political Appointees
- cabinet secretaries, deputy secretaries
2. Senior Executive Service (SES)
- expected to use their authority to achieve concrete results
3. Career Civil Servants
- job rank clearly defined according to GS levels
- hired based on merit
- job protection from political processes
4 general types of bureaucracies (and examples)
Cabinet --> defense, homeland security
Commissions --> federal communications commission
Executive Agencies --> EPA
Corporations --> Amtrak and Post Office
Hatch Act
A federal law prohibiting government employees from active participation in partisan politics.

Take Care Clause
The constitutional requirement (in Article II, Section 3) that presidents take care that the laws are faithfully executed, even if they disagree with the purpose of those laws.
Vesting Clause
Article II, Section 1, of the Constitution, which states that "executive Power shall be vested in a President of the United States of America," making the president both the head of government and the head of state.
Presidential Checks on the Bureaucracy
- appoint and remove individuals at the top layers
- write an annual budget
- harder to control lower level
Congressional Checks on Bureaucracy
- Senate confirmation of presidential appointees
- Legislation terminates or creates agencies and programs
- oversight (congressional hearings, GAO)
Government Accountability Office (GAO)
monitors if funds are being spent appropriately
Powers of the President
- commander in chief
- granting pardons
- making treaties
- appointing ambassadors, Justices, etc
- fill up vacancies in Senate
Presidential Powers CHECKED by Senate
- securing treaties
- appointing federal positions and Justices
Both require approval
political patronage
filling administrative positions as a reward for support, rather than solely on merit

Pendleton Act
an act of Congress that created the first United States Civil Service Commission to draw up and enforce rules on hiring, promotion, and tenure of office within the civil service. Also known as Civil Service Reform Act of 1883.

federal civil service
the merit-based bureaucracy, excluding the armed forces and political appointments

merit system
a system of hiring and promotion based on competitive testing results, education, and other qualifications rather than politics and personal connections

iron triangle
coordinated and mutually beneficial activities of the bureaucracy, Congress, and interest groups to achieve shared policy goals
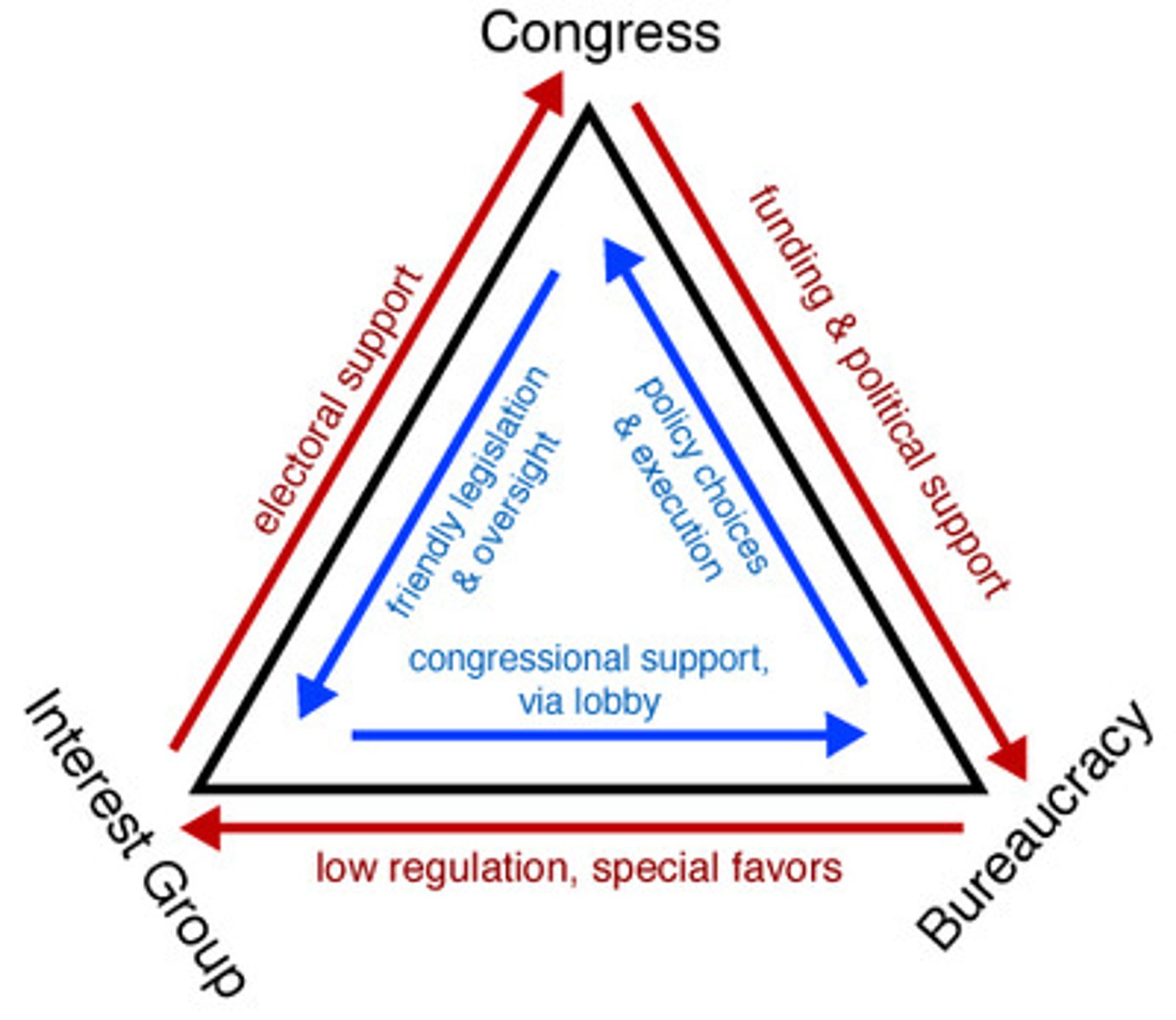
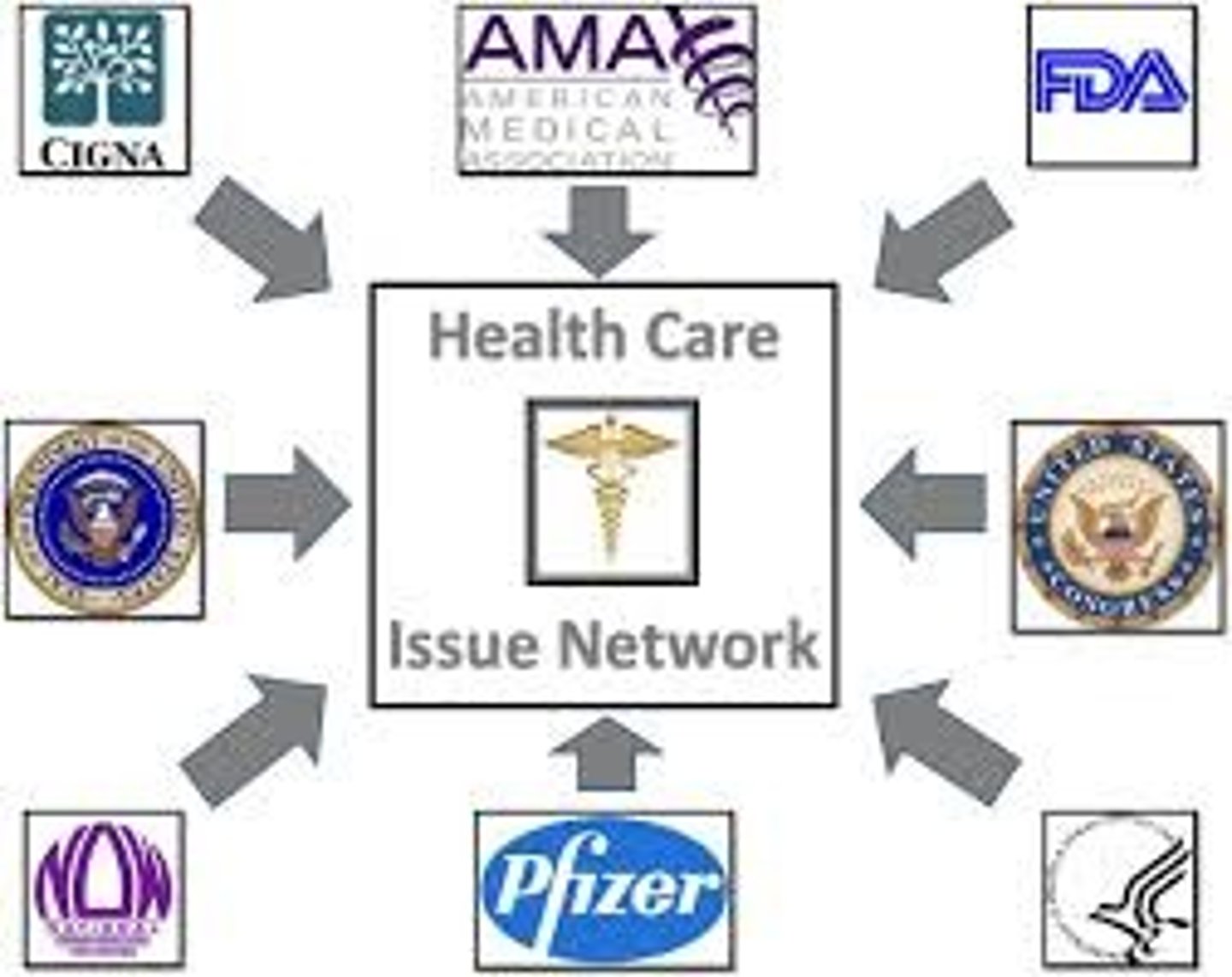
issue network
webs of influence between interest groups, policymakers, and policy advocates
implementation
the bureaucracy's role in putting into action the laws that Congress has passed

bureaucratic discretion
the power to decide how a law is implemented and, at times, what Congress actually meant when It passed a given law

regulation
the process through which the federal bureaucracy makes rules that have the force of law, to carry out the laws passed by Congress

bureaucratic adjudication
when the federal bureaucracy settles disputes between parties that arise over the implementation of federal laws or determines which individuals or groups are covered under a regulation or program

signing statement
text issued by presidents when signing a bill into law that usually consists of political statements or reasons for signing the bill but that may also include a president's interpretation of the law itself

executive order
policy directives issued by presidents that do not require congressional approval

War Powers Resolution
a law passed over President Nixon's veto that restricts the power of the president to maintain troops in combat for more than sixty days without congressional authorization

impeachment
the process of removing a president or government official from office

Executive Office of the President
a collection of offices within the White House organization designed mainly to provide information to the president

bargaining and persuasion
an informal tool used by the president to persuade members of Congress to support his or her policy initatives

bully pulpit
presidential appeals to the public to pressure other branches of government to support his or her policies

going public
a tactic through which presidents reach out directly to the American people with the hope that the people will, in turn, put pressure upon their representatives and senators to press for a president's policy goals

federal bureaucracy
the departments and agencies within the executive branch that carry out the laws of the nation

bureaucrat
an official employed within a government bureaucracy

executive branch
the institution responsible for carrying out laws passed by the legislative branch

formal powers
powers of the president expressly granted in the Constitution

informal powers
powers not laid out in the Constitution but used to carry out presidential duties

treaty
an agreement with a foreign government negotiated by the president and requiring a two-thirds vote in the Senate to ratify

State of the Union
the annual speech from the president to Congress updating that branch on the state of national affairs

veto
formal rejection by the president of a bill that has passed both houses of Congress

pocket veto
an informal veto caused when the president chooses not to sign a bill within ten days, during a time when Congress has adjourned at the end of a session

presidential pardon
presidential authority to forgive an individual and set aside punishment for a crime

executive privilege
a right claimed by presidents to keep certain conversations, records, and transcripts confidential from outside scrutiny, especially that of Congress

executive agreement
an agreement between a president and another nation that does not have the same durability in the American system as a treaty but does not require Senate ratification
