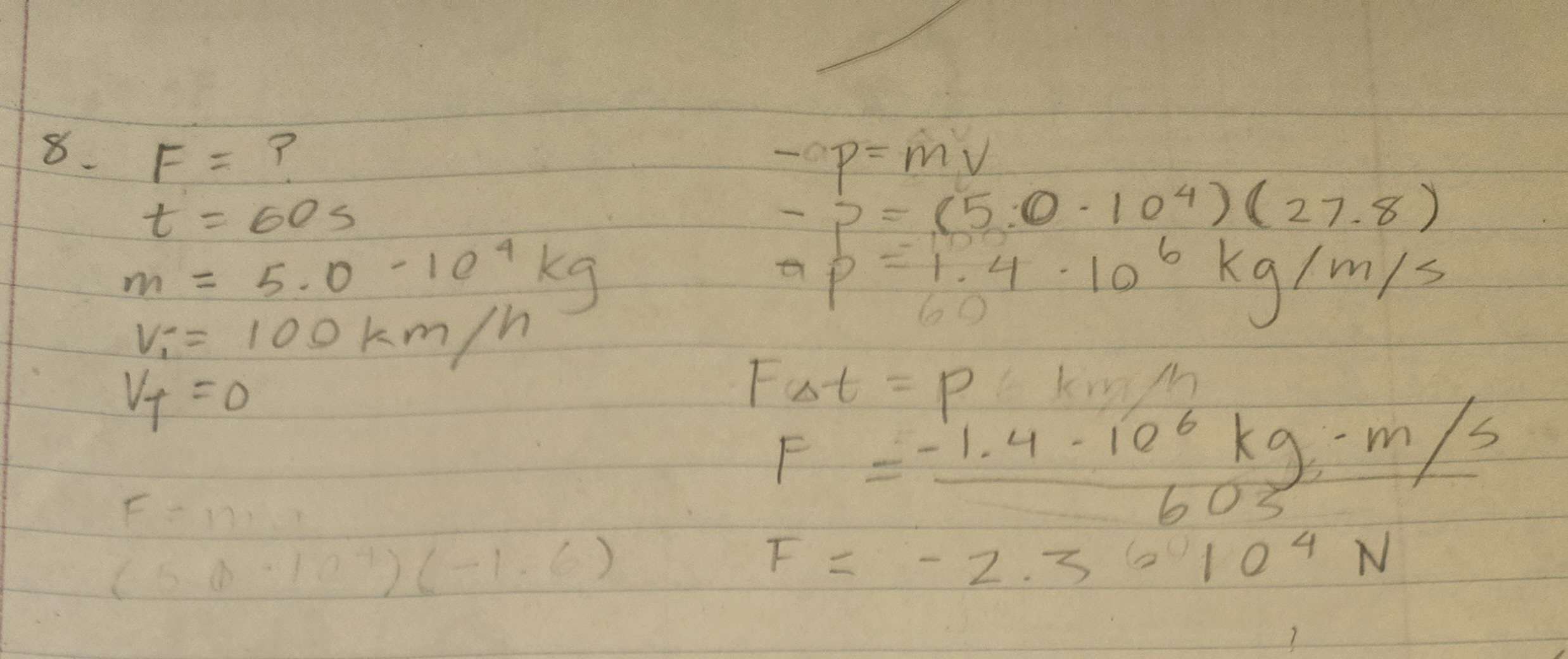Physics 11
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
A puck mass of 450 grams travelling at a speed of 32 cm/s collides head-on with a stationary puck 150 gram puck.
a) If the two stick together on impact (a completely inelastic collision), what is their common speed?
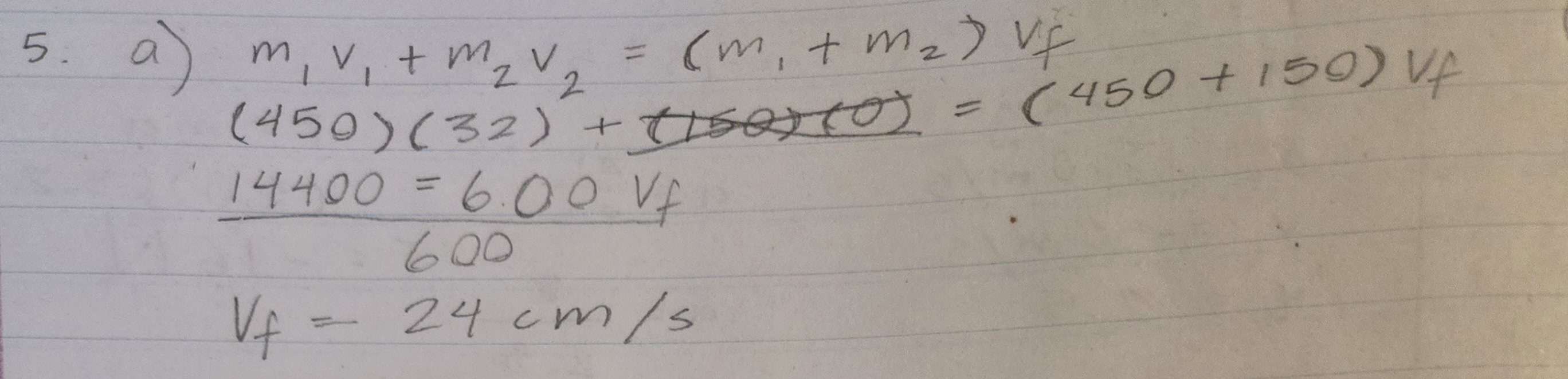
A puck mass of 450 grams travelling at a speed of 32 cm/s collides head-on with a stationary puck 150 gram puck.
b) If the pucks undergo a partially elastic collision and the lighter puck travels on with a speed of 32 cm/s, what is the resulting velocity of the first puck?
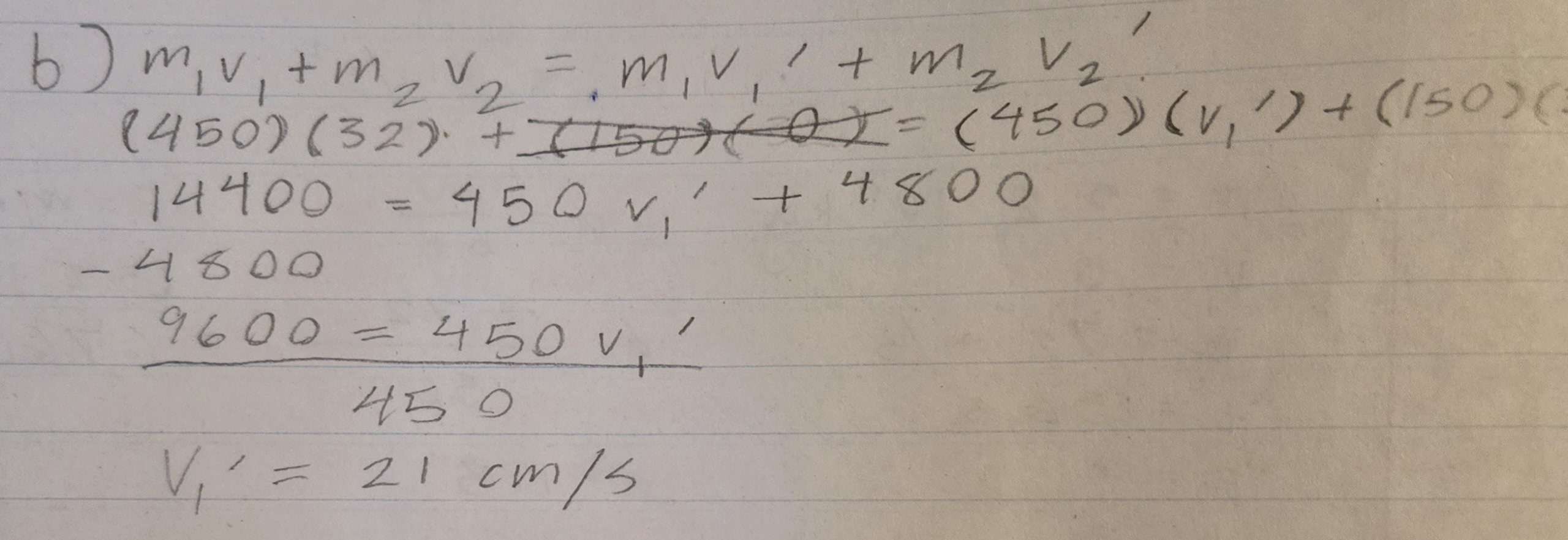
A puck mass of 450 grams travelling at a speed of 32 cm/s collides head-on with a stationary puck 150 gram puck.
b) If the pucks undergo a perfectly elastic collision, the lighter puck travels off at 48 cm/s. Predict the final velocity of the first puck.
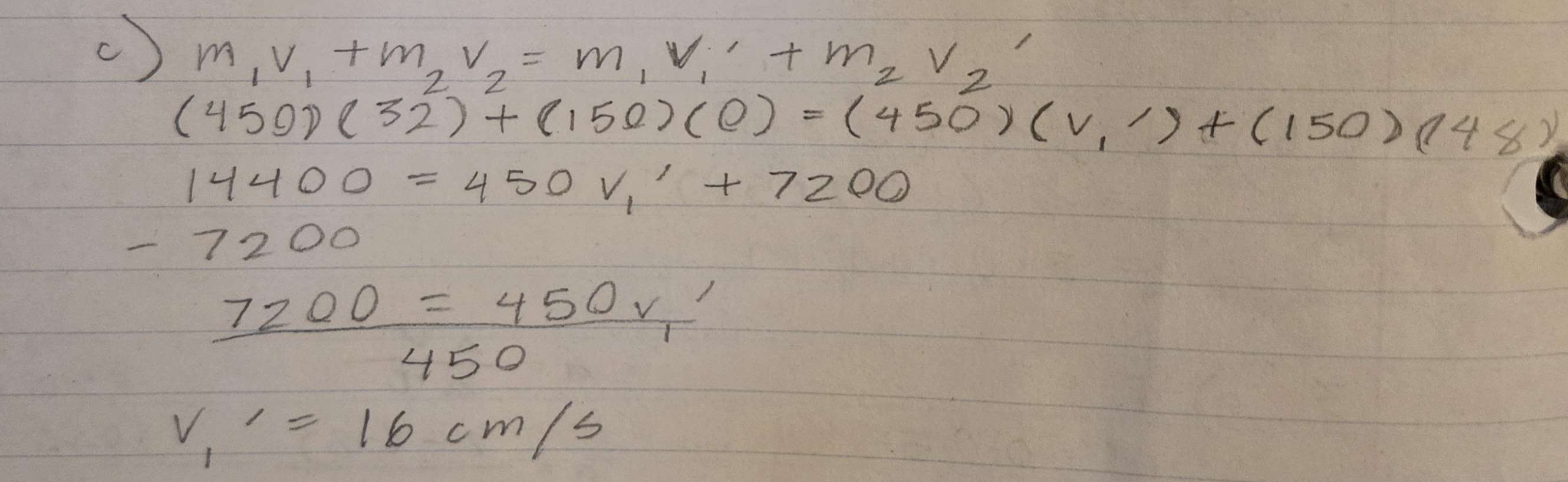
A 64 tonne boxcar travelling at 8.0 km/hr rams a train consisting of 12 similar boxcars travellings at 5.0 km/hr in the same direction. Predict the resulting speed of the train, given that the 13 cars lock together.
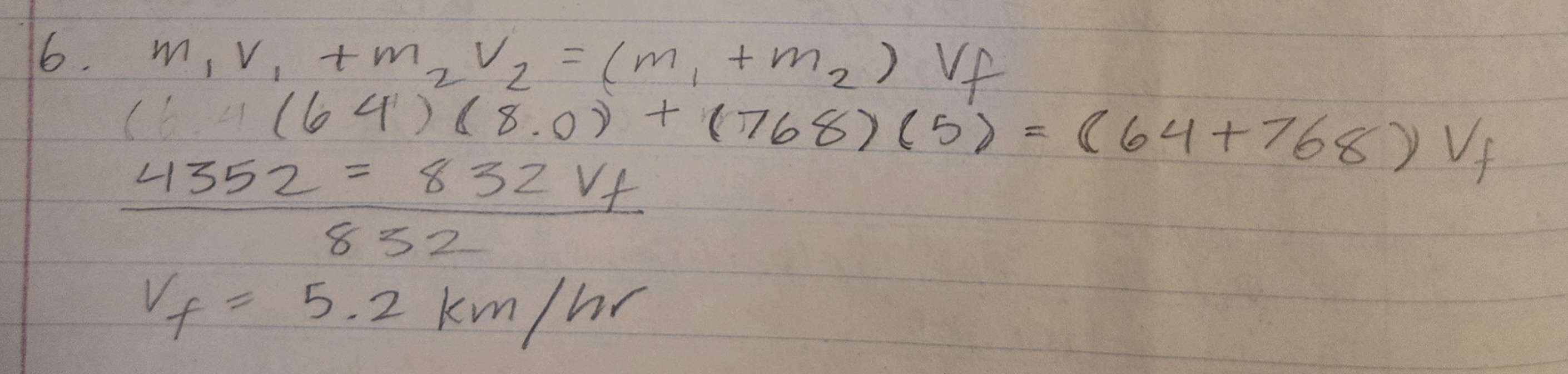
A 2200 kg car travelling South on an icy road at 15 m/s, collides head on with a 5500 kg truck travelling at 8.0 m/s North. If the two lock together, what is their common velocity just after impact.
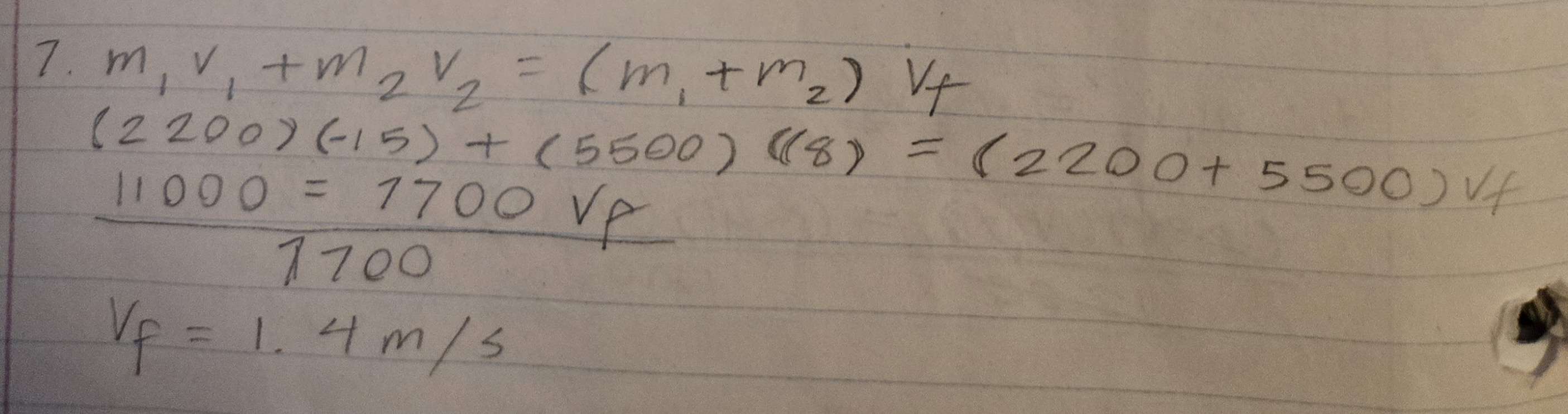
Estimate the force exerted on a vertical wall by 100 km/h wind. Assume that the air stops on impact and that over a 1.0 minute perioud 5.0 × 104 kg of air contacts the wall.