Urology Physiology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Pudendal nerve
#1
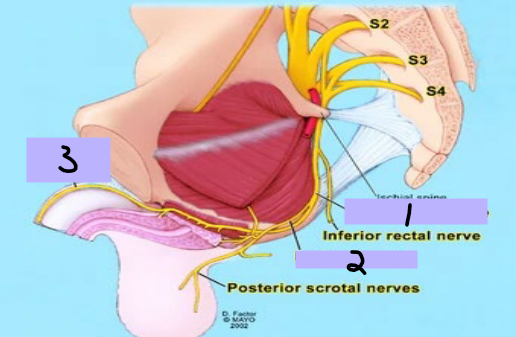
Perineal nerve
#2
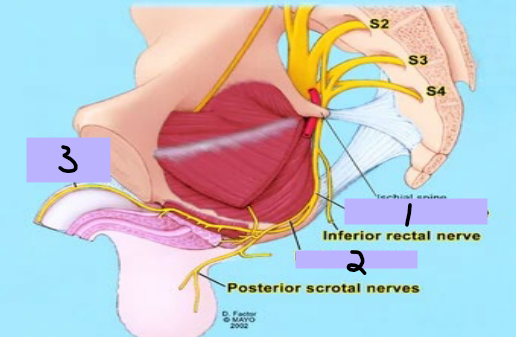
Dorsal nerve
#3
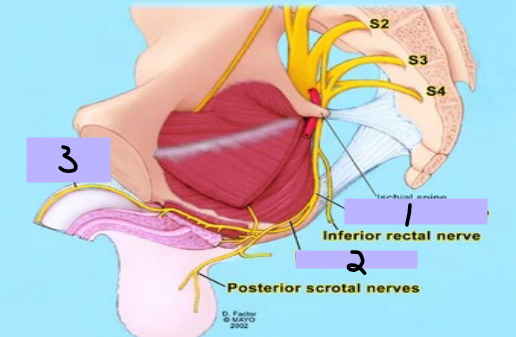
skeletal, sphincters, penis
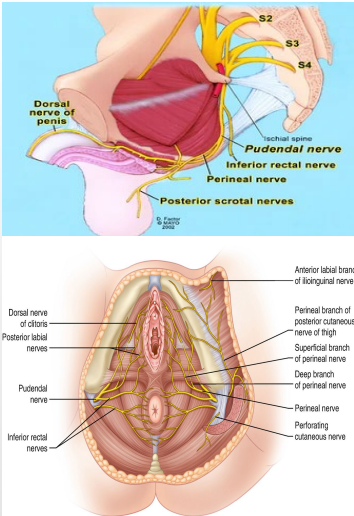
Nerves of the Pelvis/Perineum: Sacral Plexus
-Pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, dorsal nerve
-Motor Function → __________ muscles in the perineum including the external urethral and anal _____________, levator ani and coccygeus muscles
-Sensory Function → most skin of the perineum, _____, and clitoris
splanchnic, erection, contraction, bladder
Nerves of the Pelvis/Perineum: Sacral Plexus
-Pelvic ___________ nerves
-Motor (visceral) Function → stimulate __________, bladder _________; inhibitory to internal urethral sphincter
-Sensory (visceral) Function → pain from cervix and possibly _________ and proximal urethra
sensory, skin
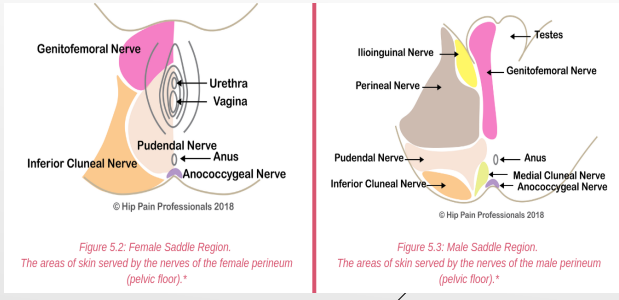
Nerves to Pelvis/Perineum: Coccygeal Plexus
S4-Co
-Anococcygeal nerves
-__________ (cutaneous) Function → perianal ____
relaxed, contracted
Phases of Bladder Function: Filling
-During filling, the detrusor muscle is __________. This allows the bladder to be filled with urine. The detrusor muscle is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system.
-At the same time, the internal (sympathetic) and external (somatic) sphincters are _____________. They stay this way to keep the urine in the bladder.
contracted, relaxed, inhibited
Phases of Bladder Function: Voiding
-During the voiding phase, the detrusor muscle is ____________ (parasympathetic).
-At the same time, the internal (parasympathetic) sphincter is ________, as is the external sphincter (_________ somatic)
autonomic, central, storage, voiding, reflex, supraspinal
Overview of Bladder Neural Control
-Bladder function is regulated by ___________ nervous system, somatic nervous system, and ________ nervous system
-Coordinates ________ and __________ phases
-Involves spinal cord ______ arcs and __________ centers
sensory, pelvic, stretch, spinal cord
Afferent Pathways
-________ pathways
-______ nerve afferents (S2-S4) detect bladder ________ and fullness
-Signals project to _______ ______ (S2-S4), periaqueductal gray (PAG), and pontine micturition center (PMC)
hypogastric, detrusor, internal, pelvic, contracts, relaxes
Autonomic Efferent Pathways
-Sympathetic nervous system
___________ nerve (T11-L2)
Effects during voiding → relaxes _________, contracts _______ sphincter (storage)
-Parasympathetic nervous system
______ nerve (S2-S4)
Effects during voiding → _________ detrusor, ________ internal sphincter (voiding)
pudendal, external, storage, voiding
Efferent Pathways
-Somatic pathways → voluntary, determine when you want to pee
-_________ nerve (S2-S4), controls ________ urethral sphincter (voluntary)
-Activated during _________, inhibited during _________
voiding, detrusor, relaxation, afferent, PMC, voluntary, micturition, urge
Central Nervous System Control
Pontine Micturition Center (PMC)
-Initiates __________ reflex
-Coordinates __________ contraction with sphincter __________
Periaqueductal Gray (PAG)
-Integrates bladder __________ signals
-Communicates with ___ and cortex
Cerebral Cortex
-_________ inhibition or initiation of ___________
-Damage → _____ incontinence
sympathetic, continence, parasympathetic, detrusor, involuntary, bladder
Reflexes of Bladder System
-Storage reflex → __________ and somatic activation to maintain ___________
-Voiding reflex → ______________ activation for _______ contraction, sphincter relaxation
-Guarding reflex → ___________ sphincter contraction during _________ filling to prevent leakage
300-400, stretch, cord, parasympathetic, contraction, relaxation, voluntarily
Micturition Reflex (Peeing Reflex)
-Initiated when bladder volume reaches ____-____ mL
-Involves: bladder _______ → spinal _____ → _____________ efferents → detrusor ___________
-Inhibition of sympathetic and somatic output → sphincter ___________
-Can be _________ overridden by higher centers (pons, cortex)
urge, coordination, spastic, flaccid
Clinical Correlations by Lesion Site
-Cortical → _____ incontinence
-Pontine → loss of ___________ (detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia)
-Spinal cord (above S2) → reflex (______) bladder
-Peripheral (S2-S4) → _______ bladder (overflow incontinence)
gonads, scrotum, vaginalis, weak
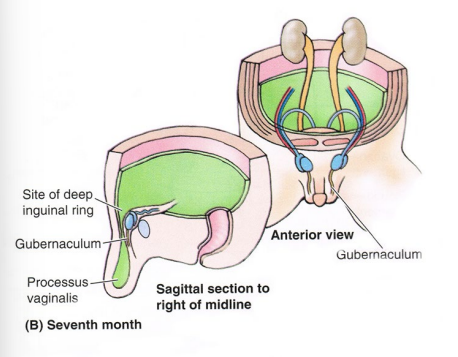
Inguinal Canal Development
-_______ descend from posterior abdominal wall → _______ in males
-Inguinal canal created by processus ________ → normally closes a few weeks before or few weeks after birth. ______ area in males, which is why inguinal hernias happen
deep inguinal ring, superficial inguinal ring
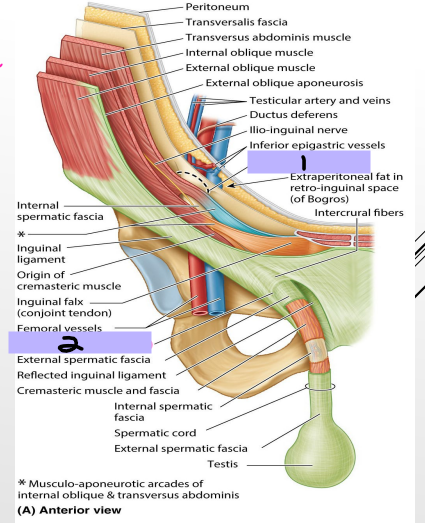
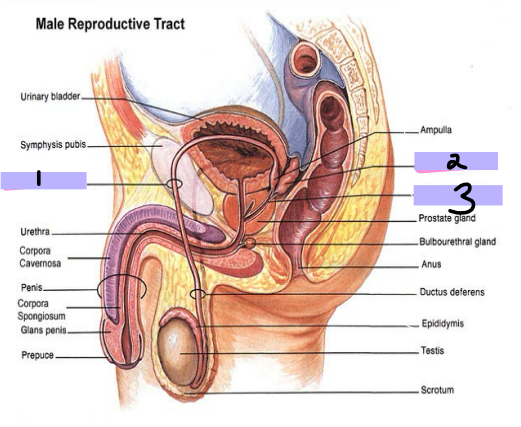
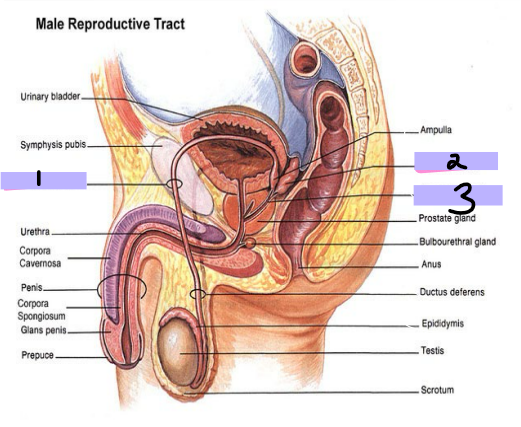
Inguinal Canal
-_______ _______ _______ (#1)
The spermatic cord starts here and goes for 4cm before reaching #2
-__________ _________ ______ (#2)
-Anterior wall → aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle
-Posterior wall → transversalis fascia
-Floor → inguinal ligament
-Roof → fibers of the transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles
epigastric, rectus abdominis, inguinal
Hesselbach’s Triangle (Inguinal Triangle)
-Location of direct inguinal hernias
-Lateral border → inferior __________ vessels
-Medial border → lateral edge of _______ ________
-Inferior border → ________ ligament (lacunar portion)
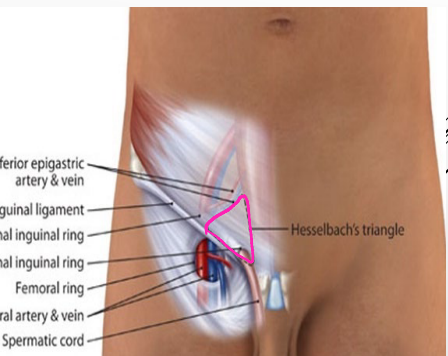
hernia, inguinal, lacunar, femoral, pectineal
Femoral Ring (Medial Compartment)
-Femoral ______, weak area where the abdomen contents meet the thigh
-Anterior border → _______ ligament
-Medial border → ________ ligament
-Lateral border → _________ vein
-Posterior border → _________ ligament and pectineus muscle
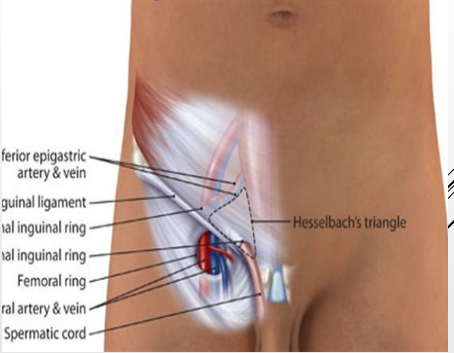
descend, scrotum, gametes, hormones, connects, abdominal, sac, peritoneum, tests
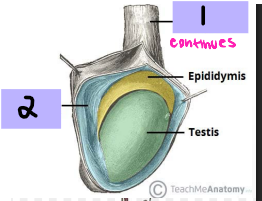
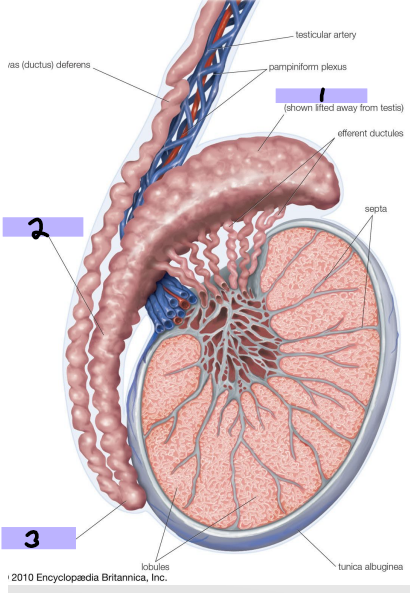
Testes
-Originally develop high on the posterior abdominal wall then _______, usually before birth into the ______
-Function → production of ________ (sperm), production of sex __________ (androgens and testosterone)
-Spermatic cord → tube-like structure that _________ testes to ________ wall
-Tunica vaginalis → closed ___ of __________ surrounding most of _____
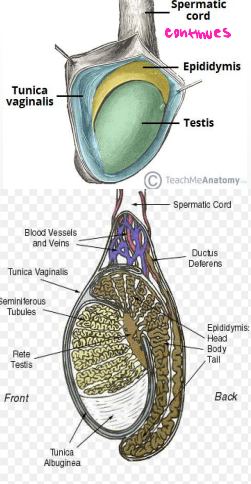
Spermatic cord
#1
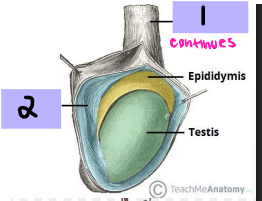
Tunica vaginalis
#2
Seminiferous tubules, spermatozoa
#1
-Within testes and produce ___________
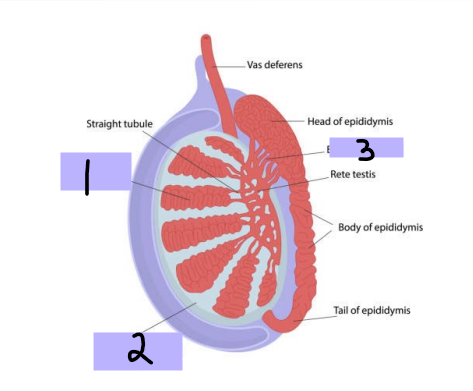
Tunica albuginea
#2
-Thick connective tissue capsule surrounding testes
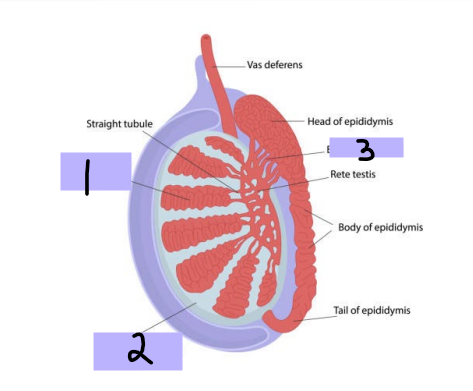
Efferent ductules
#3
-Originate from rete testis and connect and form head of epididymis
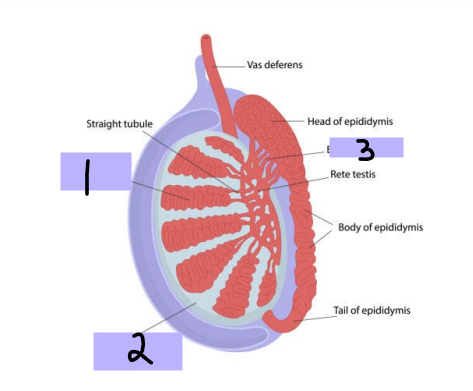
seminiferous, androgens, testosterone
Leydig Cells
-Found between ____________ tubules
-Produce _________ (mostly ___________)
testis, maturation, ejaculation, head, body, tail, ductus
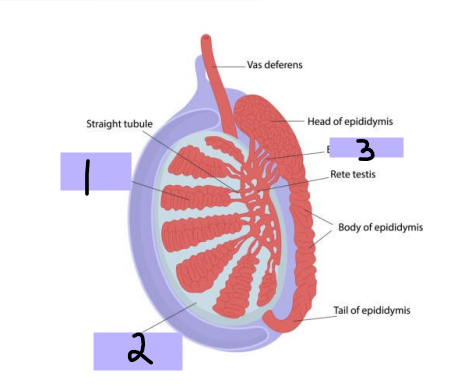
Epididymis
-Comma shaped, courses along the posterolateral side of ______
-Spermatozoa acquire ability to move and fertilize an egg (___________ of sperm)
-Stores spermatozoa until _____________
-____ (#1)→ formed by coiled mass of efferent ductules, sits on posterior superior pole of testis
-____ (#2) → along the posterolateral margin of testis
-____ (#3) → located at the inferior pole of testis, continuous with _____ deferens
spermatozoa, epididymis, ejaculatory, seminal, duct
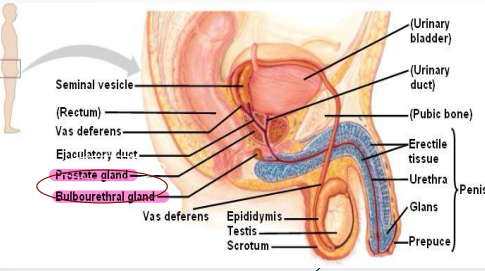
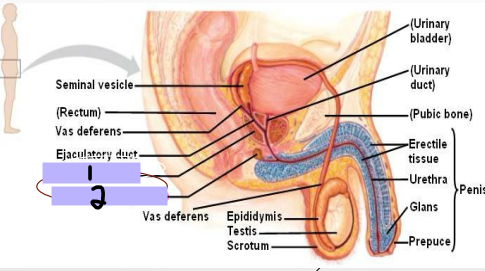
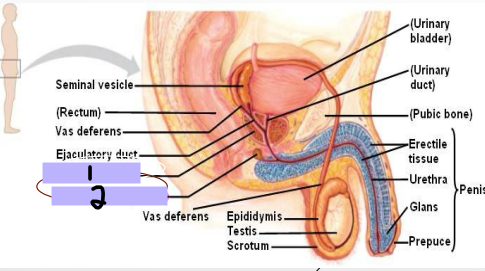
Ductus Deferens
-Long, muscular duct
-Transports _____________ from _________ to __________ duct
-Located within spermatic cord, joins ________ vesicle duct to form ejaculatory ____
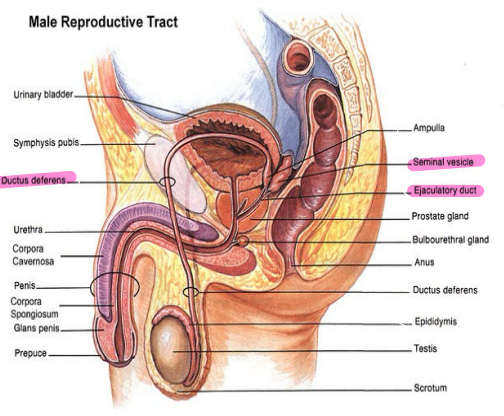
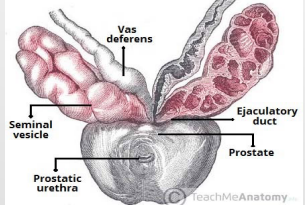
Ductus deferens
#1
Seminal vesicle
#2
Ejaculatory duct
#3
Seminal vesicle
#1
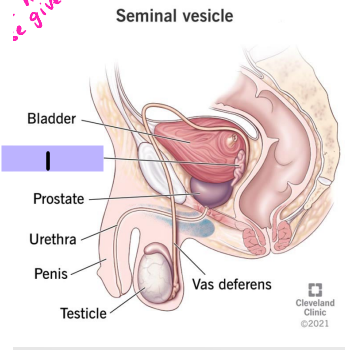
bladder, ejaculatory, volume, glucose, energy, sperm
Seminal Vesicle
-Accessory gland that is an outgrowth from ductus deferens
-Coiled tube with numerous pockets, located between ________ and rectum (towards base of bladder)
-Joins ductus deferens to form ___________ duct
-Secretions contribute to ________ of ejaculate (semen)
Nutritive ______-rich fluid (fructose)
Source of ______ for _____
urethra, secretions, semen, alkaline, sperm, acidic, vagina
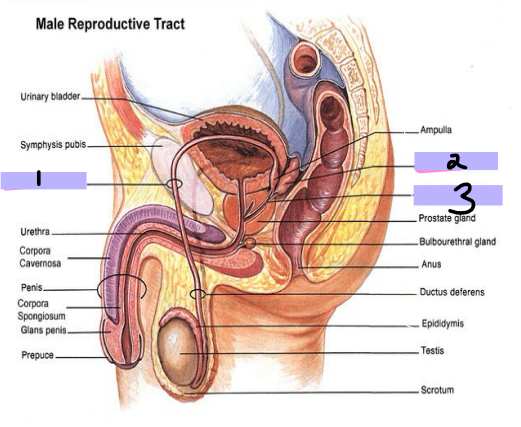
Prostate
-Accessory structure surrounding the _______. Inferior to bladder, posterior to pubic symphysis, anterior to the rectum
-Inverted, rounded, cone like structure that has a large base, narrow apex, and is the size of a walnut. Cradled between levator ani muscles
-____________ contribute to formation of _____ → thin, milky substance with _______ pH
Helps ______ survive the _______ environment of the female ______
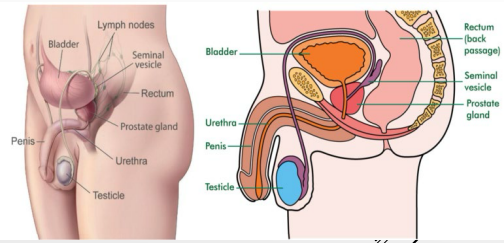
mucous, urethra, lubriction, pre-ejaculate
Cowper’s Glands
-Small, pea-shaped _______ glands. Located in the deep perineal pouch (one on each side)
-Lateral to the membranous _______. Ducts open into the bulb of the penile urethra
-Contribute to _________ of the urethra and ___-________
Prostate gland
#1
Cowper’s gland
#2
corpora cavernosa, corpus spongiosum, prepuce
Penis
-_________ ________ (#1)
A pair, anchored to the pubic arch
Runs along dorsal penis
-________ ___________ (#2)
Single, anchored to perineal membrane
Runs along ventral penis
Surrounds urethra
Forms glans penis
-________ → fold of loose skin covering the glans (Foreskin)
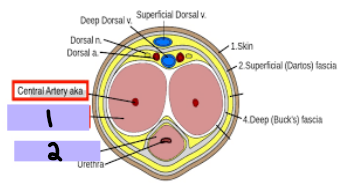
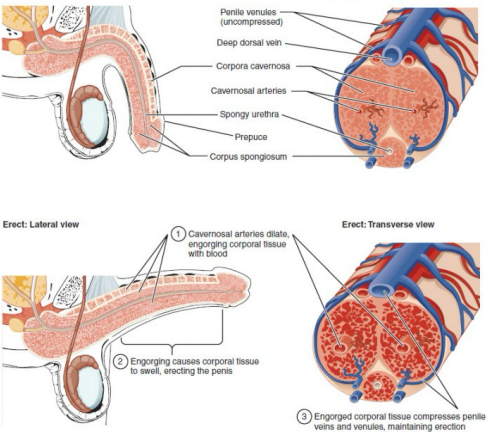
vascular, parasympathetic, arteries, erection, pudendal
Erection
-________ event
-____________ fibers in pelvic splanchnic nerves → relaxation of penile _______ → blood fills penile tissue → __________
-Arteries supplying the penis are branches of internal _________ artery (cavernosal, dorsal, deep, bulbourethral)
posterior, anterior, bladder, ureter, seminal, prostate, perineum, erectile
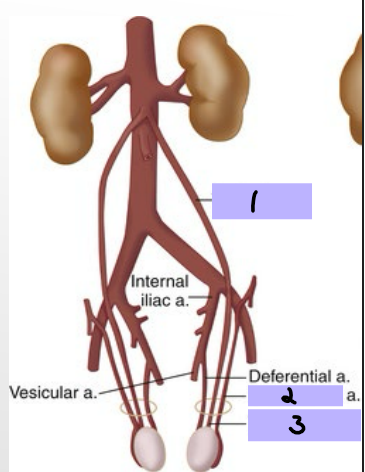
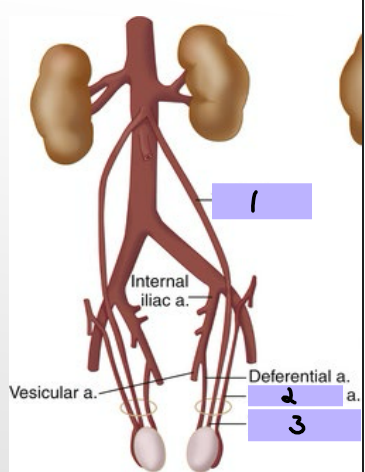
Arteries of the Pelvis/Perineum
-Internal iliac artery is the main supply
-________ trunk → supply of lower posterior abdomen wall, posterior pelvic wall, and gluteal region
-________ trunk → supply pelvic viscera, perineum, gluteal region, adductor region of thigh
Superior vesical artery → supplies superior _______ and distal ______
Inferior vesical artery → supplies bladder, ureter, ______ vesicle, and _______
Internal pudendal artery → main supply to the _________ as well as ______ tissue
Superior vesical artery
#1
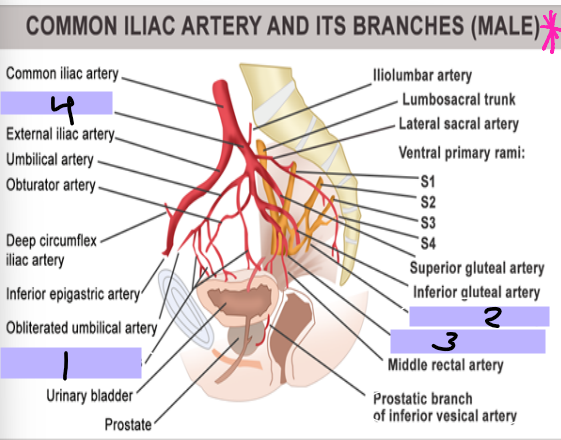
Inferior vesical artery
#2
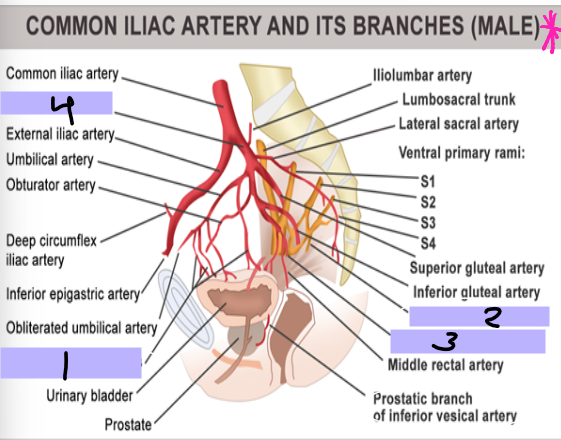
Internal pudendal artery
#3
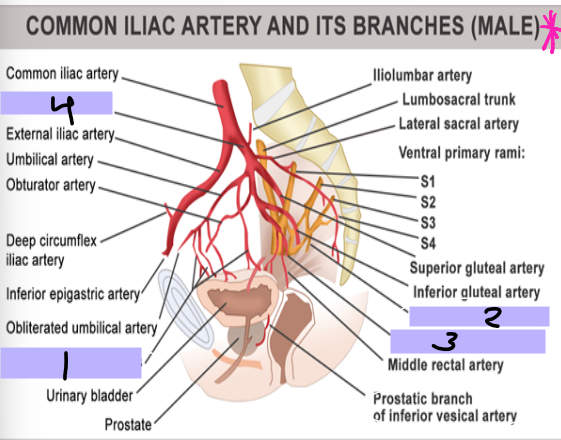
Internal iliac artery
#4
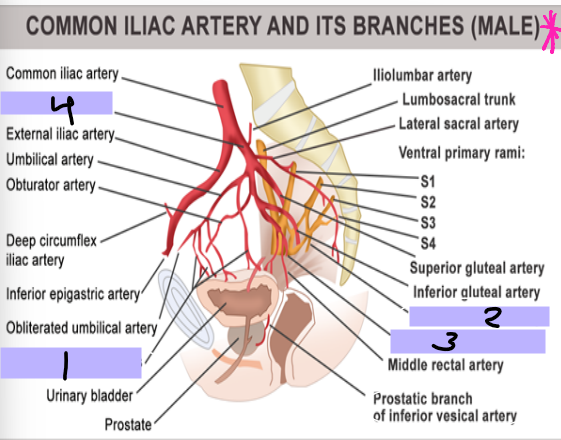
pudendal, scrotum, testicular, testes
Arteries of Scrotum/Testes
-External _________ arteries → skin of penis and _________
-_________ and cremasteric arteries → scrotum/____
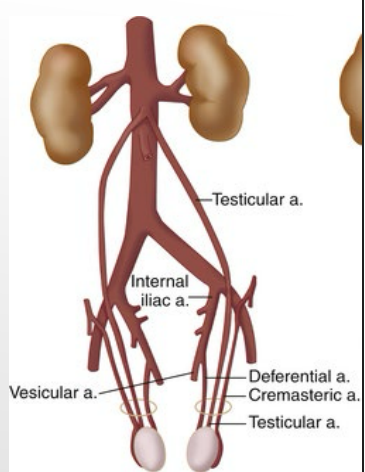
Testicular artery
#1
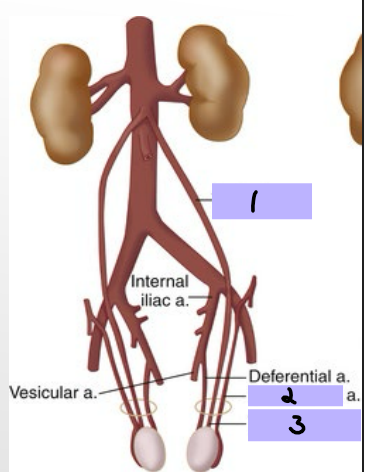
Cremasteric artery
#2
Testicular artery
#3